Like.
The UAE’s orbiter reaches Mars on Tuesday, followed less than 24 hours later by China’s orbiter-rover combo. NASA’s Perseverance rover is due to land on February 18.

Like.
The UAE’s orbiter reaches Mars on Tuesday, followed less than 24 hours later by China’s orbiter-rover combo. NASA’s Perseverance rover is due to land on February 18.

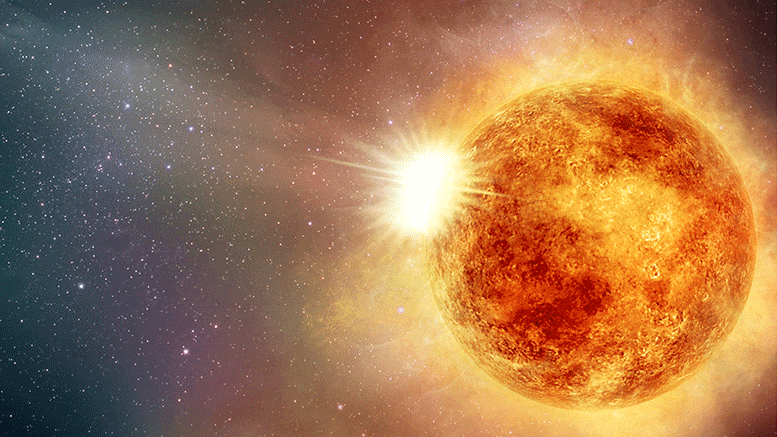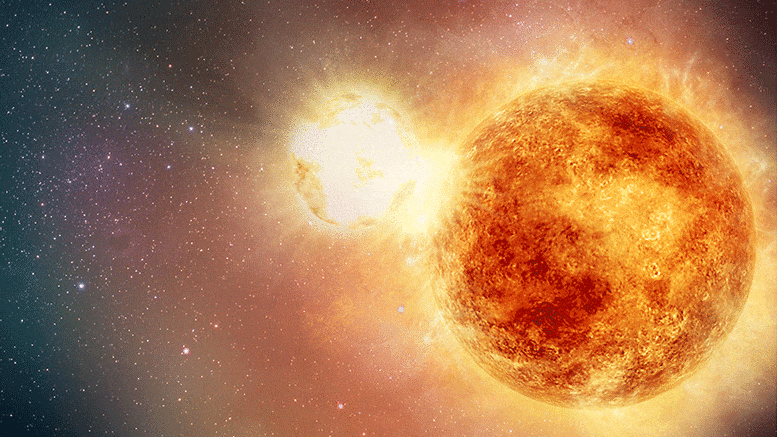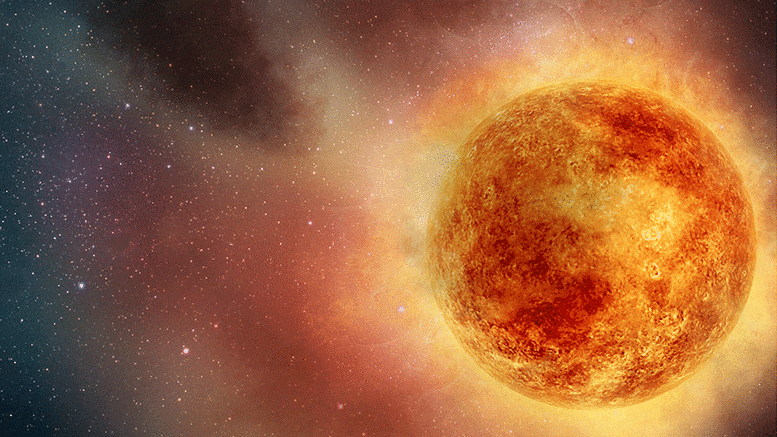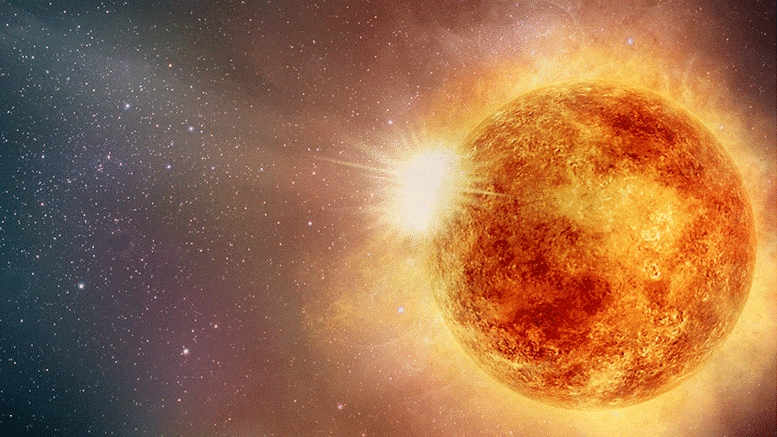
Recalibrated Betelgeuse’s mass, radius, and distance. Betelgeuse is normally one of the brightest, most recognizable stars of the winter sky, marking the left shoulder of the constellation Orion. But lately, it has been behaving strangely: an unprecedentedly large drop in its brightness has been observed in early 2020 (Figure 1), which has prompted speculation that Betelgeuse may be about to explode.

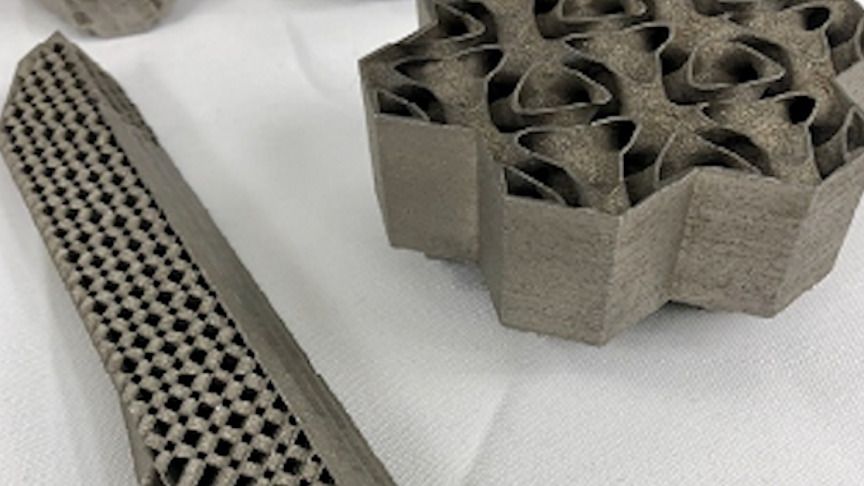
WASHINGTON — The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency wants to hear from the space industry about their capabilities to manufacture large structures on the moon.
This is a new project that DARPA announced Feb. 5 called “Novel Orbital and Moon Manufacturing, Materials and Mass-efficient Design.”

DARPA’s TRAnsformative DESign (TRADES) program, which began in 2017, set out to develop foundational design tools needed to explore the vast space opened by new materials and additive manufacturing processes commonly called 3D printing. The program recently concluded having successfully developed new mathematics and computational techniques, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, that will allow future designers to create previously unimaginable shapes and structures of interest to defense and commercial manufacturing.

50 years ago today, Apollo 14 astronauts Alan Shepard and Edgar Mitchell landed on the Moon for a 33-hour stay full of science, as fellow crew member Stuart Roosa conducted observations from lunar orbit. Revisit this # Apollo50th anniversary: youtu.be/l7MMTm1-DAA

How times have changed since the Apollo era. Within the space of a few days, two space missions from China and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), respectively, are set to reach Mars. The UAE’s Hope mission will go into orbit around Mars on February 9. The next day, the Chinese Tianwen-1 mission – an orbiter and lander — will swing into orbit, with a predicted landing date sometime in May.
It is a very big moment for both countries. Hope is the first interplanetary mission by an Arab nation ever. And if China succeeds, it will be the first country ever to visit and land on Mars on its first try. The odds are stacked against them with nearly 50% of all Mars missions failing. China already lost a Mars orbiter mission (Yinghuo-1) back in 2011.
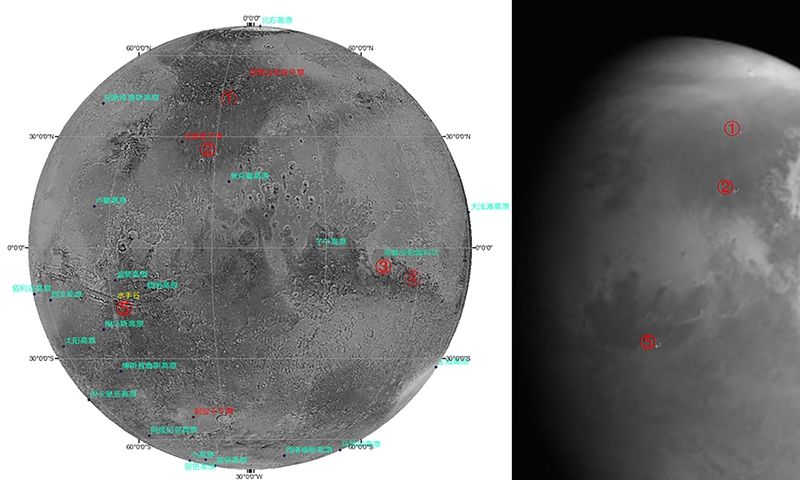



When most of us picture the shape of the Milky Way, the galaxy that contains our own sun and hundreds of billions of other stars, we think of a central mass surrounded by a flat disc of stars that spiral around it. However, astronomers know that rather than being symmetrical, the disc structure is warped, more like the brim of a fedora, and that the warped edges are constantly moving around the outer rim of the galaxy.