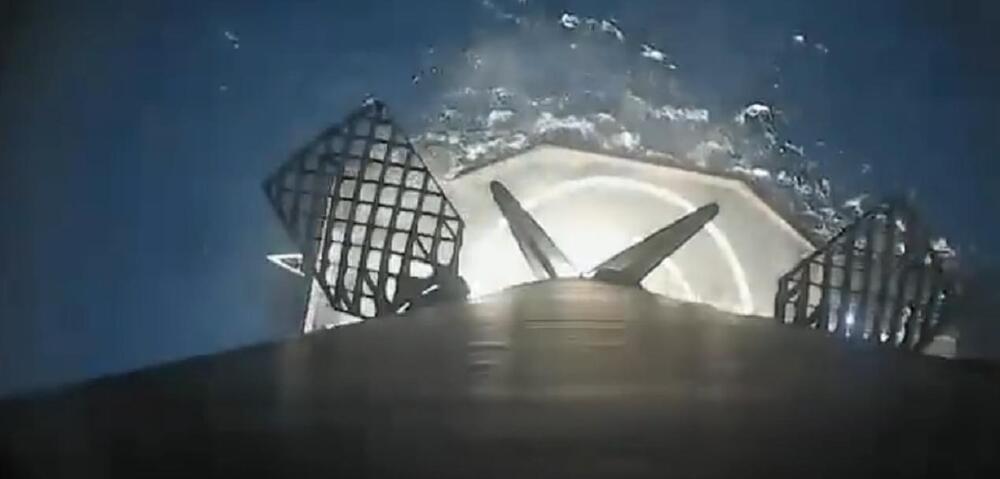
SpaceX has posted a new video that shows off what was once considered as a ‘ridiculous’ rocket landing in clouded darkness.
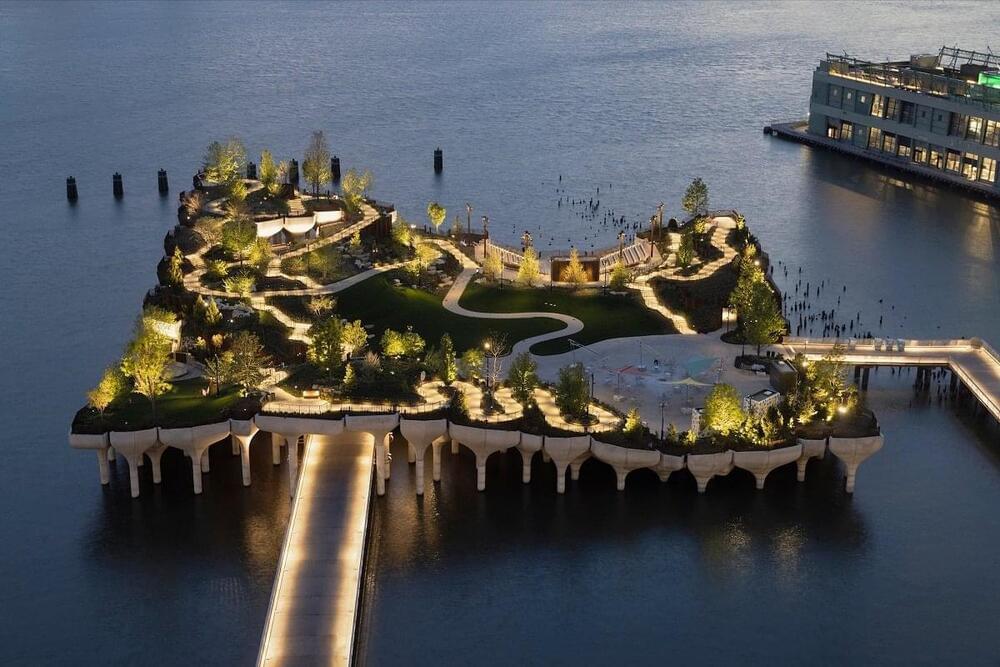



The long-awaited $355 million development of Little Island New York has finally been made reality, offering the Big Apple a unique new space.
Although it’s unlikely travel to the US will be on the cards for Aussies anytime soon, it’s good to keep track of the developments that await us when we eventually graduate from tiny travel bubbles to full-scale international adventure once again. The latest development: the ambitious new US$260 million (AU$335 million) Little Island New York, an offshore public park in the Hudson River that has been one of the city’s most anticipated openings for a couple of years now.
Located at Pier 55 the fascinating public park has been designed to resemble a supersized leaf drifting on the Hudson, buoyed by a base of 280 concrete piles and precast columns driven down as far as 60 metres below water, as well as 132 tulip-shaped concrete pots positioned at various elevations from 4 metres to 18 metres above water, designed specifically by Heatherwick Studio, and developed by engineering firm Arup, to hold the soil, overlooks, and trees. This support base allows for the two-acre park to stay securely afloat so its 687-seat amphitheatre, smaller stage, and plaza don’t suddenly drop to the depths of the Hudson.
The waterborne engineering is almost as fascinating as the park itself, but it’s what’s on top this mini-island that represents what many reports are (hopefully not naively) likening to a bridge between New York City’s pre-and post-COVID era.
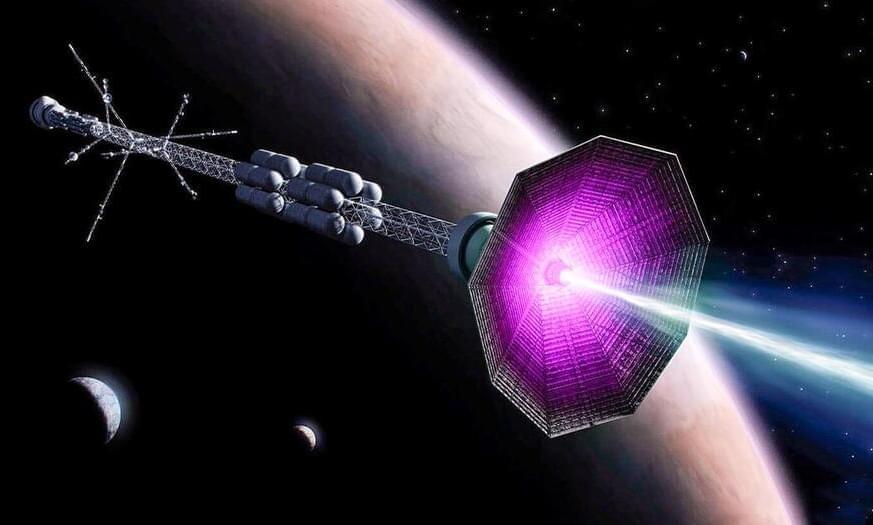


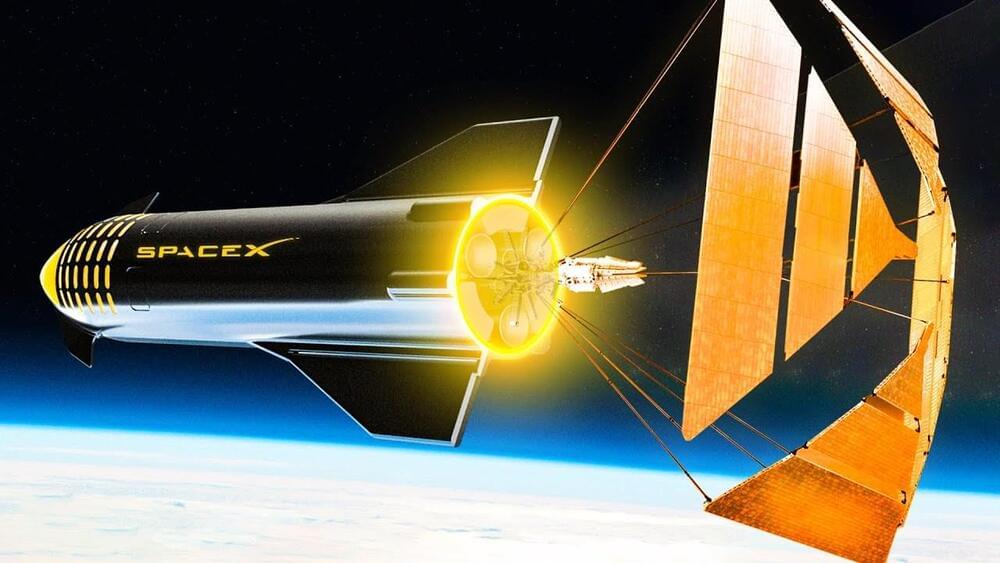
It’ll take about seven months to send humans to Mars using today’s spaceships. That’s not exactly a quick jaunt, but it is doable.
Trips to other planets could take years, though, and if we want to explore the rest of our solar system — or the places beyond it — we’re going to need a faster way to travel.
Now, a physicist has designed a new rocket thruster that could potentially allow humans to travel 10 times faster in space — and it’s inspired by nuclear fusion.

Thumbnail Credit: Charlie Burgess: https://www.behance.net/cburg.
Video Credit:

“If we make life multiplanetary, there may come a day when some plants & animals die out on Earth, but are still alive on Mars,” Musk tweeted in mid-April.
What Musk probably didn’t know was that his destiny was already sealed. Not in the stars, but on paper.
In 1,953 a book was published that predicted plans for an “Elon” to take humans to Mars.



High-energy cosmic rays have proven elusive… but we may have found their source.
Thanks to new research led by the University of Nagoya, scientists have quantified the number of cosmic rays produced in a supernova remnant for the first time. This research has helped resolve a 100-year mystery and is a major step towards determining precisely where cosmic rays come from.
While scientists theorize that cosmic rays originate from many sources — our Sun, supernovae, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), and active galactic nuclei (sometimes called quasars) — their exact origin has been a mystery since they were first discovered in 1912. Similarly, astronomers have theorized that supernova remnants (the after-effects of supernova explosions) are responsible for accelerating them to nearly the speed of light.
As they travel through our galaxy, cosmic rays play a role in the chemical evolution of the interstellar medium (ISM). As such, understanding their origin is critical to understanding how galaxies evolve.