New home proposal for a Martian habitat, designed by marek podlaha and antónia pohanková, uses a prefabricated spaceship as the center of the structure.
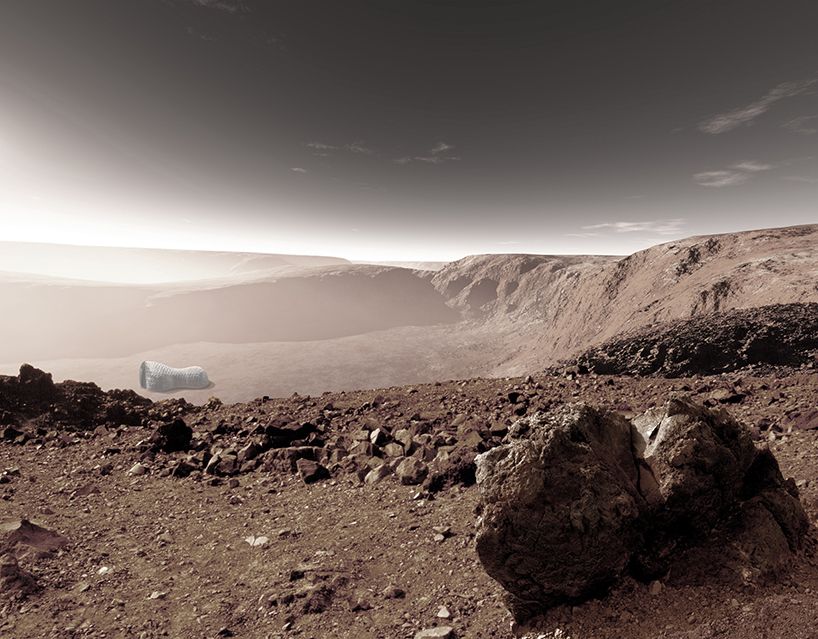


New home proposal for a Martian habitat, designed by marek podlaha and antónia pohanková, uses a prefabricated spaceship as the center of the structure.
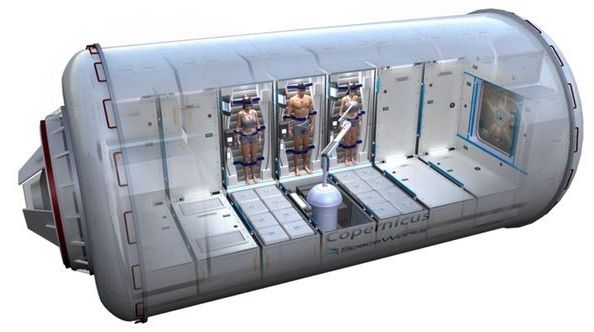
Deep space travel is circumscribed by an interactive conflict. For those that may want to make extended space journeys, the distances are remarkably great, and our spaceships are slow. These combine to make the trip times exceedingly long. When one attempts considering interstellar transit, you quickly realize that a normal human life span prevents an adult from ever even returning to Earth. Yet even for missions to nearby Mars travel times are projected to take about eight months one-way.
We cannot do anything about the physical distances, nor can we expect much more performance out of current chemical rockets for projected near-term transports within the solar system. While there are projected improvements in velocity in the future through introduction of fission propulsion, fusion-drive rockets, or other exotic space transport engines, space travel will continue to require long transit times. Even if one is able to exploit velocity-enhancing tricks like gravity-assist planetary flybys, deep space trips to, say, mineral-rich asteroids in the main belt will still be measured in years.
So, for transporting people around our solar system, the fundamental question has and continues to be whether anything practical can be done about adjusting the impacts for the humans on board. More precisely, are there practical near-term methods to improve space transport human system design factors that could allow us to create more cost-efficient spaceships and improve the safety to passengers and crew during these long voyages?

Four decades ago, Voyager 1 and 2 began their journey to the stars. When will humans follow them?
Editor’s note: This is a companion piece to the science fiction short “Dark was the night, and cold the ground,” published Thursday in Terraform.
As the summer of 1977 drew to a close, twin siblings bid farewell to Earth to explore the ultimate frontier. They wrote back often, and sent lots of beautiful postcards, so that everyone at home could keep up with their adventures. Each of them carried an identical golden time capsule, filled with the sights and sounds of the world they left behind, so they could act as ambassadors to any other lifeforms they might encounter on their endless journey.

https://youtube.com/watch?v=a3QXjbdE9Tw
China and Russia are set to sign a milestone agreement in October on joint space exploration from 2018 to 2022, sending manned missions to the Moon for the first time. The bilateral agreement will cover five areas including lunar and deep space exploration, developing special materials, collaboration in the area of satellite systems, Earth remote sensing, and space debris research. This is the first bilateral agreement to cover a partnership spanning five years. It is to be signed against the background of space exploration race the US is trying to win, so the two partners decided to join the efforts. In February, the Trump administration asked NASA to look into the possibility of manning a heavy-lift rocket mission, expected to be launched in 2018, setting the stage for a human return to the Moon.
Russia’s Glavkosmos space launch operator is also working with Chinese partners on joint experiments aboard the International Space Station (ISS). China was interested in buying the world’s most powerful Russian-made RD rocket engines produced by Energomash while Russian Space Systems showed interest in Chinese electronic technology.
The first module of China’s space station Beijing is expected to be launched in 2018. The project is to be completed in 2022. According to the plans, a Chinese mission will be sent to Mars in 2020 to land a robot vehicle for scientific research. Last year, Beijing put into operation the world’s largest radio telescope half a kilometer (0.3 miles) in diameter. In 2014, China caught up with Russia having launched about the same number of satellites – 117 (72% increase in 2011–14). Russia had 118 launched by the time (the number increased by 20% during the same period).

Our Andromeda interstellar probe article has been featured in MlT Technology Review :
Business Impact.
Femto-spacecraft could travel to alpha centauri.
Earth’s nearest exoplanet twin orbits a star about four light years from here. Now scientists say it’s possible to visit this system in our lifetimes by propelling a tiny spacecraft on the tip of a laser beam.

At a test facility in rural Illinois, engineers fabricate structural segments for buildings. But instead of using typical assembly techniques, here at this dirt-floor arena with tightly controlled conditions, teams employ robotic nozzles to extrude domes, beams and cylinders using material chosen for its similarity to the regolith found on the surface of the planet Mars.
The activity comprises part of the 3D-Printed Mars Habitat Design Challenge, which focuses on how to go about building structures on Mars to eventually house human explorers. It’s a component of the NASA Centennial Challenges, a contest series that solicits the public to solve the practical problems of future space exploration. The third phase of the challenge, underway now, focuses on creating stable structural members using an additive manufacturing process based on basaltic rock geologically similar to what is found on Mars.
“This leg of the competition is focused on the materials, specifically the indigenous Mars regolith,” explains Tony Kim, deputy program manager for NASA’s Centennial Challenge. “All of the teams are approaching it differently.” Previous phases of the challenge focused on conceptual designs for habitats and proof-of-concept 3D-printed shapes. But this showdown emphasizes pure structural strength, as the 3D-printed cylinders, beams and domes will be subjected to loading until they fail.

To get us to Mars and beyond, a team of students from around the world has a plan involving lunar rovers mining ice and a space station between the Earth and the moon.

As part of its support for the application 3D printing technology to deep space exploration, NASA has awarded a $250,000 prize to a joint team consisting of members from Foster+Partners California and Branch Technology (based in Chattanooga, Tennessee).
NASA’s competition, which has now reached level three of its second phase, aims to “advance construction technology needed to create sustainable housing solutions for Earth and beyond”, most notably with the aim of accommodating astronauts on Mars and building human colonies in outer space.

(Natural News) Space has become a veritable goldmine of natural resources for many companies, yet can anyone lay claim to them? That’s the question legal experts claim will become relevant in the future as firm turn to the stars for precious metals and minerals, and it’s one that also needs to be answered as soon as possible to avoid hostility between competing firms and countries.
Barry Kellman, law professor of space governance at DePaul University in Chicago, explained: “There is a huge debate on whether companies can simply travel to space and extract its resources. There is no way to answer the question until someone does it.”
According to one international treaty, this need not even be an issue. The Outer Space Treaty of 1967, formally known as the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, Including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies, has served as the main standard for sharing space. As per the 1967 treaty, no single country can claim “national appropriation” of celestial bodies “by occupation or by other means”. (Related: MINING just one large asteroid could COLLAPSE the world economy due to surge of new supply for valuable metals.)

https://youtube.com/watch?v=wvwXgZhrr-s
One manufacturing company just made history by successfully using a special 3D printer in extreme, space-like conditions.
The team printed polymer alloy parts in a super-high vacuum, and hope their new tech will allow the design and manufacture of much more ambitious spacecraft and space-based telescopes.
“This is an important milestone, because it means that we can now adaptively and on demand manufacture things in space,” Andrew Rush, CEO of Made in Space, told Scientific American.