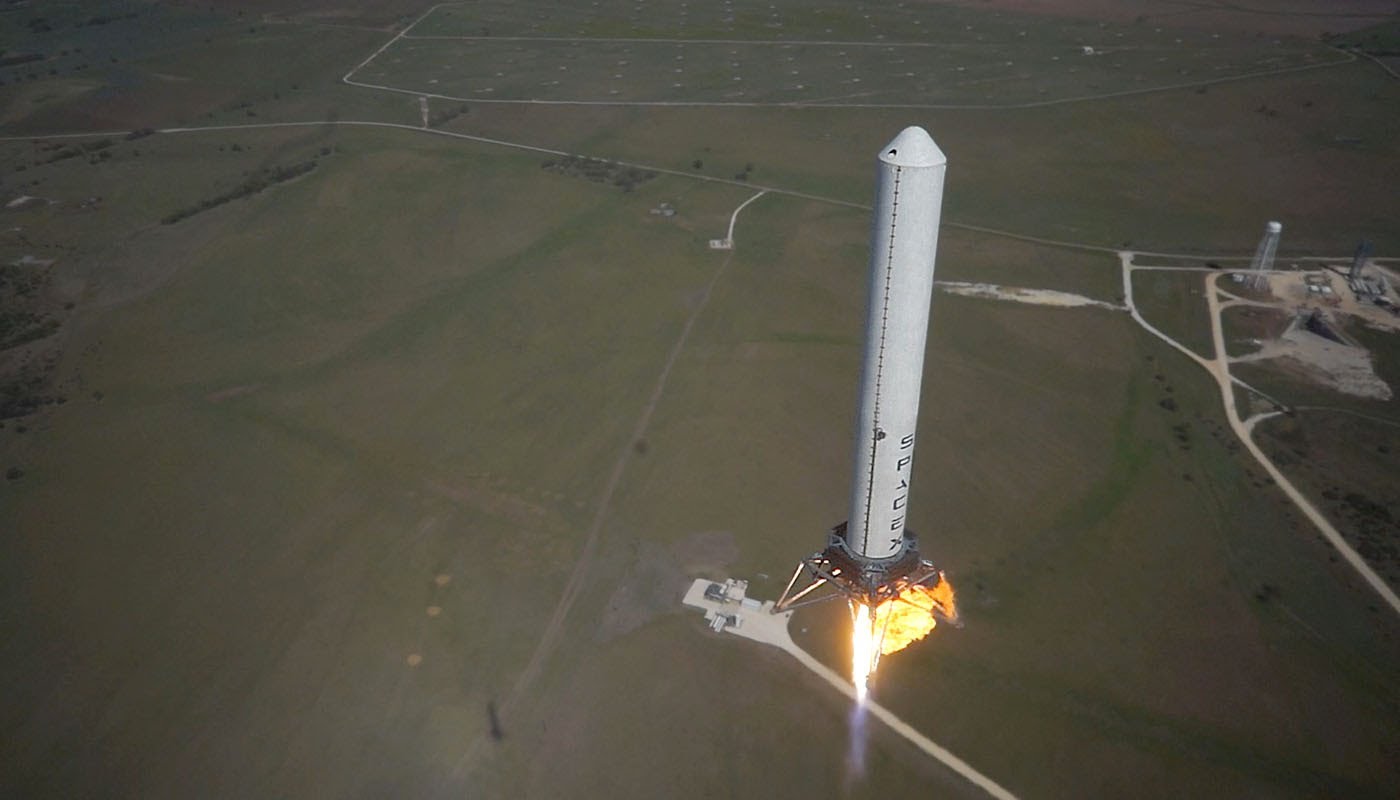
SRI Newsletter #06 2018 Great success both for the public and for the speakers, despite the enrollment fees definitely out of budget for many: more than 6300 registered participants, of which almost 50% very young, more than 2000 papers presented in the various symposia. The title of the Congress was very interesting: “Involving everyone”. This gave the impression that there was plenty of space at the Congress for the themes of civil development in space. The attention to the impetuous development of the NewSpace sector is now felt everywhere, and the most important global space congress could not avoid being impacted. After all, it is thanks to the growth of the NewSpace sector if the IAF Congress has recorded this remarkable success. But which were the predominant themes of the Congress? Has the promise announced in the title been kept? In part, yes, but a lot of work remains to be done. And the main NewSpace entrepreneurs didn’t come to Bremen. Read the whole article.
The 69th Congress of the International Astronautical Federation took place in the halls of the Bremen exhibition center from 1 to 5 October.
Great success both for the public and for the speakers, despite the enrollment fees definitely out of budget for many: more than 6300 registered participants, of which almost 50% very young, more than 2000 papers presented in the various symposia. The title of the Congress was very interesting: “Involving everyone”. This gave the impression that there was plenty of space at the Congress for the themes of civil development in space. The attention to the impetuous development of the NewSpace sector is now felt everywhere, and the most important global space congress could not avoid being impacted. After all, it is thanks to the growth of the NewSpace sector if the IAF Congress has recorded this remarkable success. But which were the predominant themes of the Congress? Has the promise announced in the title been kept? In part, yes, but a lot of work remains to be done.
One aim was to “include everyone”, for example, in the exploration of the Moon. And we have seen some concrete cases of inclusion. The company Part Time Scientists, earlier in the context of the Lunar X-Prize, and then with the development of subsequent innovative projects, has put in place a lunar exploration project, in which some industries not belonging to the aerospace sector are involved as technological partners, as well as sponsors, such as Audi, Nokia, Vodafone. Of course, so far we are talking about exploration, mainly robotics, and not about industrial settlements on the Moon. The Moon Village Association thinks about that and presented their initiatives in a context that is becoming more and more receptive and interesting for many.
Read more