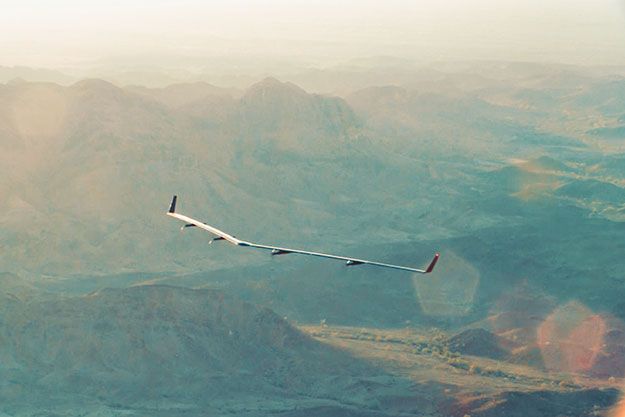
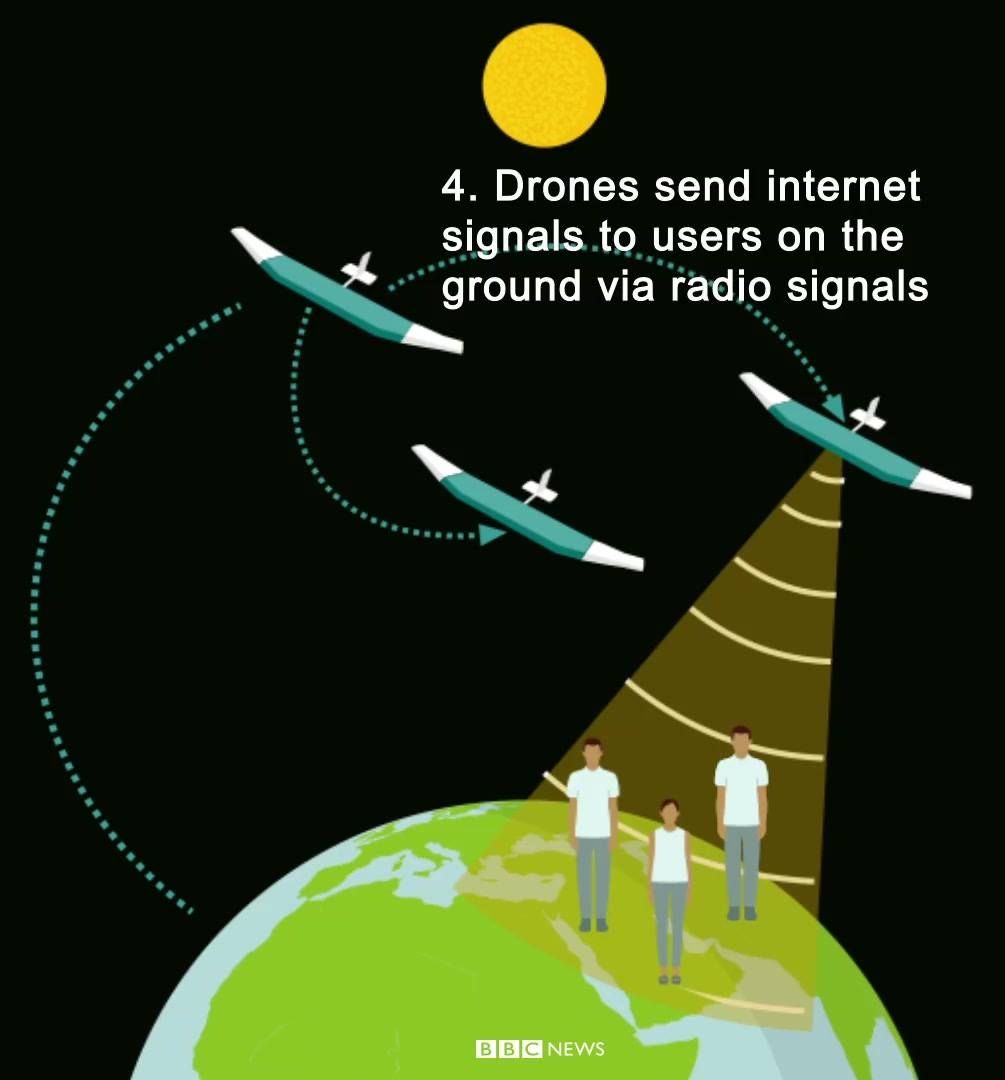
SAN FRANCISCO Facebook Inc (FB.O) said on Thursday it had completed a successful test flight of a solar-powered drone that it hopes will help it extend internet connectivity to every corner of the planet.
Aquila, Facebook’s lightweight, high-altitude aircraft, flew at a few thousand feet for 96 minutes in Yuma, Arizona, Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg wrote in a post on his Facebook page. The company ultimately hopes to have a fleet of Aquilas that can fly for at least three months at a time at 60,000 feet (18,290 meters) and communicate with each other to deliver internet access.
Google parent Alphabet Inc (GOOGL.O) has also poured money into delivering internet access to under served areas through Project Loon, which aims to use a network of high-altitude balloons to made the internet available to remote parts of the world.