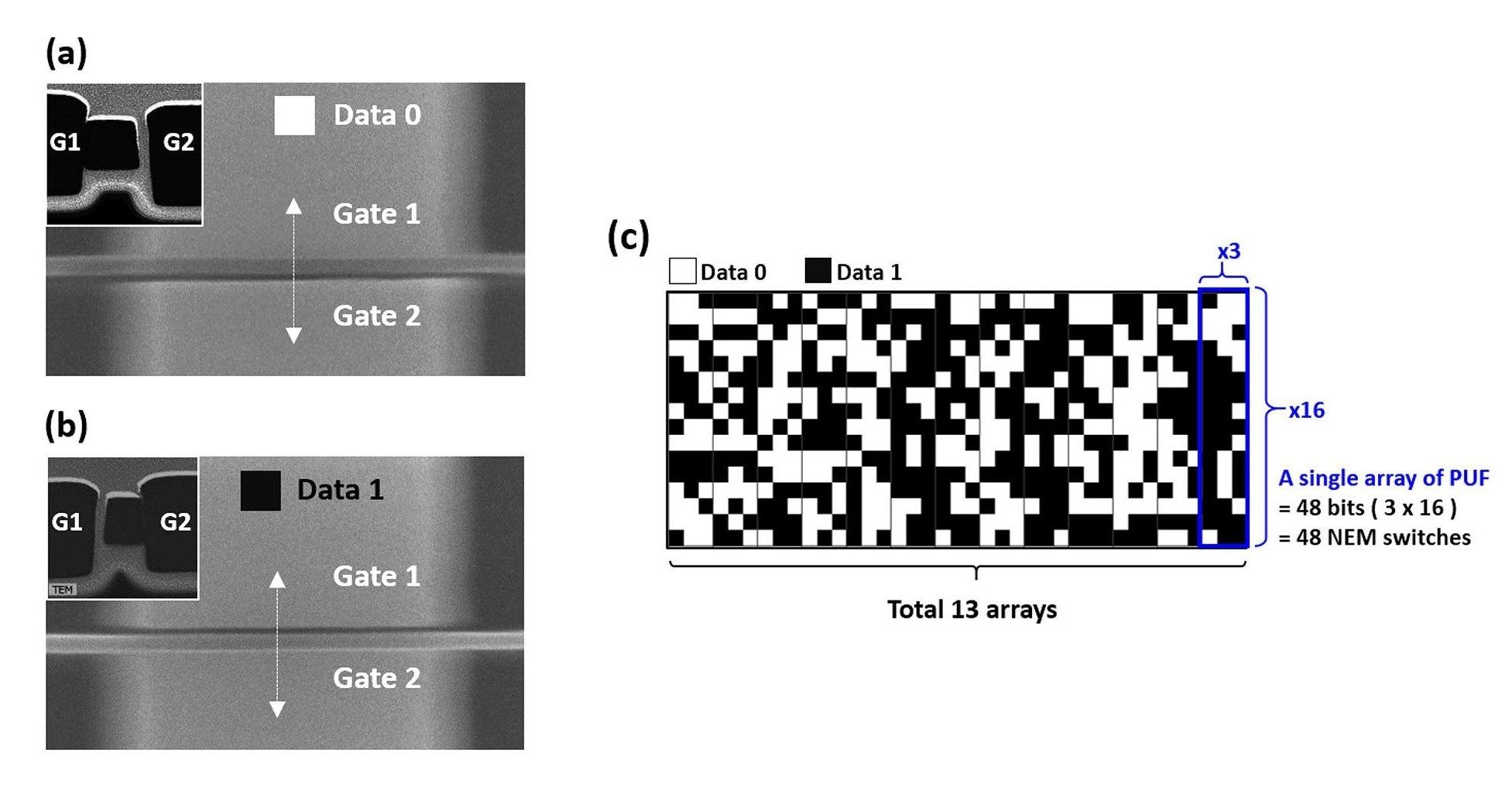
Most of the cryptographic methods that keep important data secure use complex encryption software, and as a result, consume large amounts of power. As more and more electronic devices are being connected to the internet, there is a growing need for alternative low-power security methods, and this is often done by basing the security on hardware rather than software.
One of the most promising approaches to hardware-based, low-power security is to derive cryptographic keys from the randomness that inherently and uncontrollably emerges during the fabrication process of nanoscale devices. These methods, called “physical unclonable functions” (PUFs), convert the random variations in the physical devices into the binary states of “0” and “1” to create unique, random cryptographic keys. These keys can then be used to encrypt data into cipher text, as well as decrypt it back into plain text, in a process that remains secure as long as the key remains private.
However, one of the biggest challenges facing PUF technology is its vulnerability to harsh environments. Since the physical randomness that forms the basis of the key usually arises from variations in electrical characteristics, and electrical characteristics are affected by external factors such as high temperatures and radiation, these devices often do not preserve their states when exposed to such conditions.