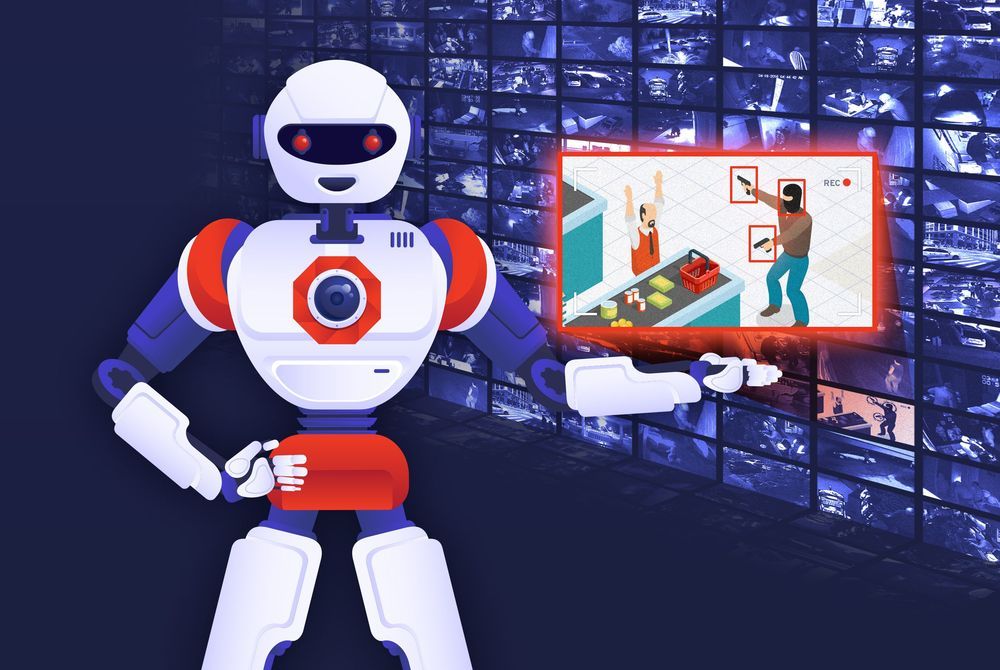
Deep Science AI made its debut on stage at Disrupt NY 2017, showing in a live demo how its computer vision system could spot a gun or mask in CCTV footage, potentially alerting a store or security provider to an imminent crime. The company has now been acquired in a friendly merger with Defendry, which is looking to deploy the tech more widely.
It’s a great example of a tech-focused company looking to get into the market, and a market-focused company looking for the right tech.
The idea was that if you have a chain of 20 stores, and 3 cameras at each store, and people can only reliably keep an eye on 8–10 feeds at a time, you’re looking at a significant personnel investment just to make sure those cameras aren’t pointless. If instead you used Deep Science AI’s middle layer that highlighted shady situations like guns drawn, one person could conceivably keep an eye on hundreds of feeds. It was a good pitch, though they didn’t take the cup that year.