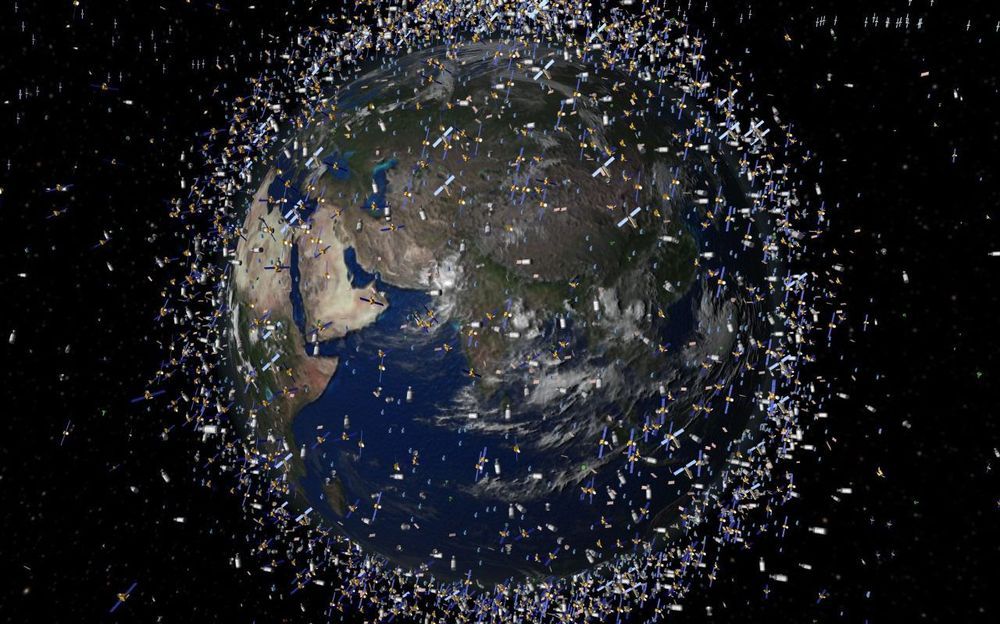
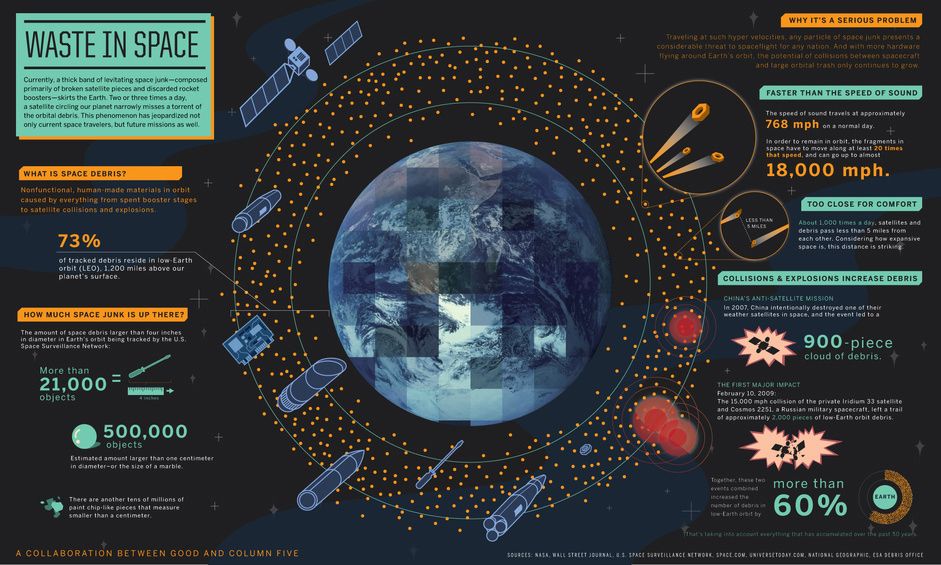
As the number of satellites and space junk in orbit continues to increase, so do the chances of these human-made objects colliding with one another, potentially creating more debris that could threaten other healthy spacecraft. Now, a new tool shows just how crowded Earth orbit is by tracking space objects through their close calls every couple of seconds.
Called the “Conjunction Streaming Service Demo,” the graph tool illustrates in real time the sheer number of space objects — out of an assortment of 1,500 items in low Earth orbit — that get uncomfortably close to one another in a period of 20 minutes. While the X-axis keeps track of the time, the Y-axis shows the short distance between two approaching space objects, ranging from five kilometers to the dreaded zero kilometers. On the graph is a series of arcs demonstrating when two pieces of debris rapidly move toward one another, make their closest approach, and then speed away.