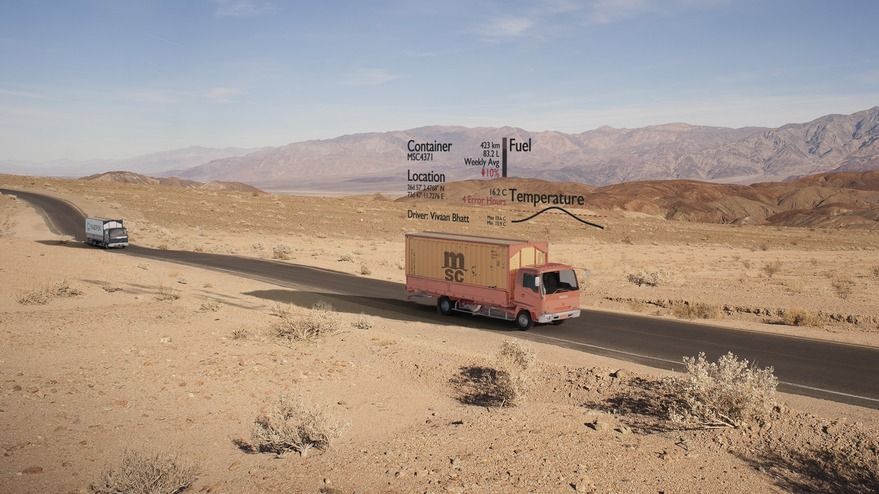
SAN FRANCISCO – Startup Skylo emerged from stealth mode Jan. 21 with $116 million in the bank and plans to connect devices by transferring data over existing geostationary communications satellites.
“The key challenge we wanted to address was how data was going to be moved from machines and sensors outside of the areas where traditionally connectivity has existed,” Parthsarathi “Parth” Trivedi, Skylo co-founder and CEO, told SpaceNews. “If we could lower the cost of providing ubiquitous, affordable and reliable connectivity, there would be a phenomenal number of applications.”
Skylo raised $13 million in a Series A investment round led by DCM Ventures and Innovation Endeavors with participation by Boeing HorizonX and Moore Strategic Ventures. In its latest Series B round led by SoftBank with participation by all the firm’s previous investors, Skylo raised $103 million, according to the firm’s Jan. 21 news release.