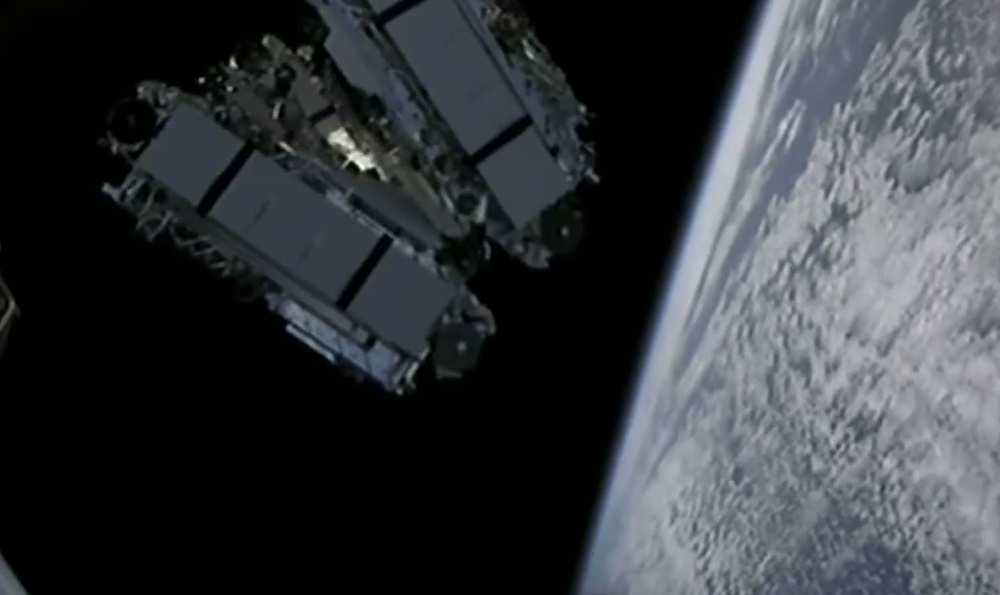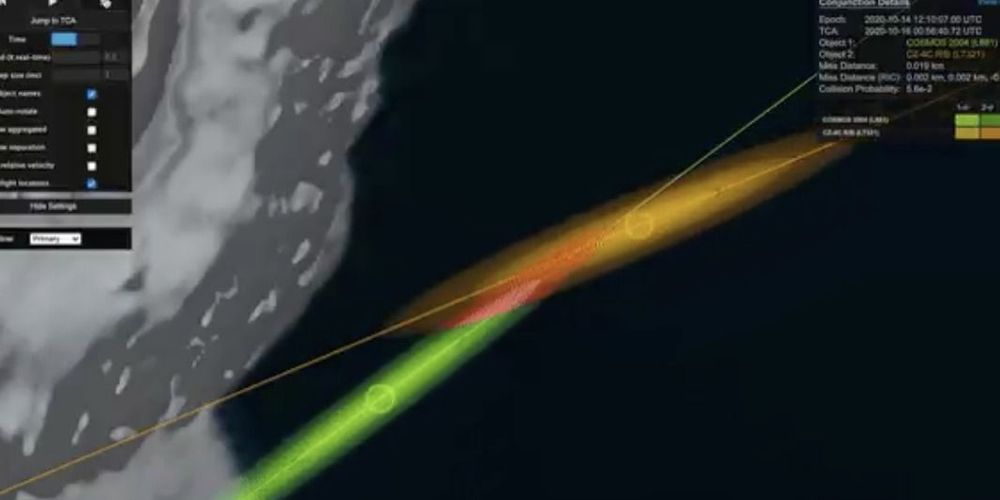
In 2016, I proposed LEO HTS Mega Constellation a viable solution for Australia’s broadband national coverage. I have been doing research on these constellations right from the beginning and they are inevitable!
Introduction
Utilizing the announced Lower Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites constellations of OneWeb, SpaceX, LeoSat & Samsung to provide high speed connectivity to entire Australian continent with performance better than fiber networks. This project can eliminate high cost NBN roll out to scattered populations and will considerably improve disaster management. Providing high speed connectivity for mobile communication, internet, high resolution TV broadcast as well as utilizing technologies like IoT & Cloud for improvement in security, education, health, agriculture, livestock farming, mineral resources, wildlife, and environment without any coverage black-spots. This network will not require any infrastructure installations and will help the Government to generate revenues by issuing spectrum licenses to local as well as foreign investors for providing services directly to the end user.
2011 Census
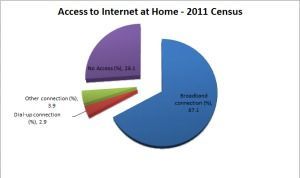
Source: Regional Statistics by ASGS, 2010–2014.