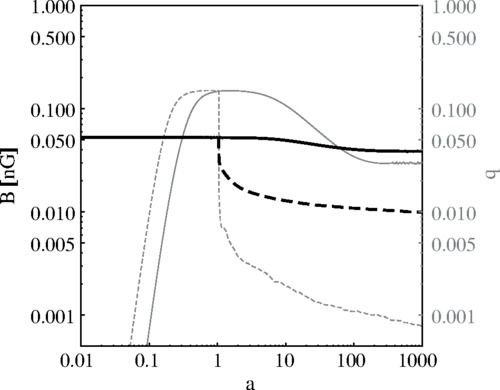
Primordial magnetic fields (PMFs), being present before the epoch of cosmic recombination, induce small-scale baryonic density fluctuations. These inhomogeneities lead to an inhomogeneous recombination process that alters the peaks and heights of the large-scale anisotropies of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation. Utilizing numerical compressible MHD calculations and a Monte Carlo Markov chain analysis, which compares calculated CMB anisotropies with those observed by the WMAP and Planck satellites, we derive limits on the magnitude of putative PMFs. We find that the total remaining present day field, integrated over all scales, cannot exceed 47 pG for scale-invariant PMFs and 8.9 pG for PMFs with a violet Batchelor spectrum at 95% confidence level.