I dont know about his comment. But, this will probably become at least as big as the auto industry. If you had a robot that could cook, clean, take care of the yard, drive, run errands, had various entertainment features, etc… Then, every household in America will want one. It will just come down to getting the robots to the point where they can do all of that, and having the vision to do it, and initially selling it to the public.
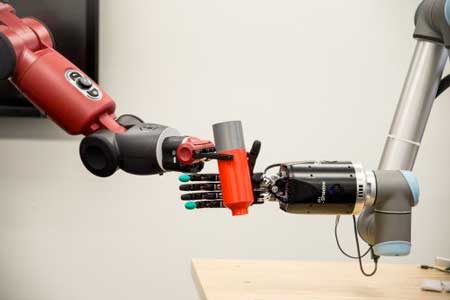
“The Internet lets every person reach out and touch all the information in the world. But robotics lets you reach out and touch and manipulate all the stuff in the world — and so it is not just restricted to information, it is everything,” says Raibert, who spoke from the Future Investment Initiative in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, at the end of October.
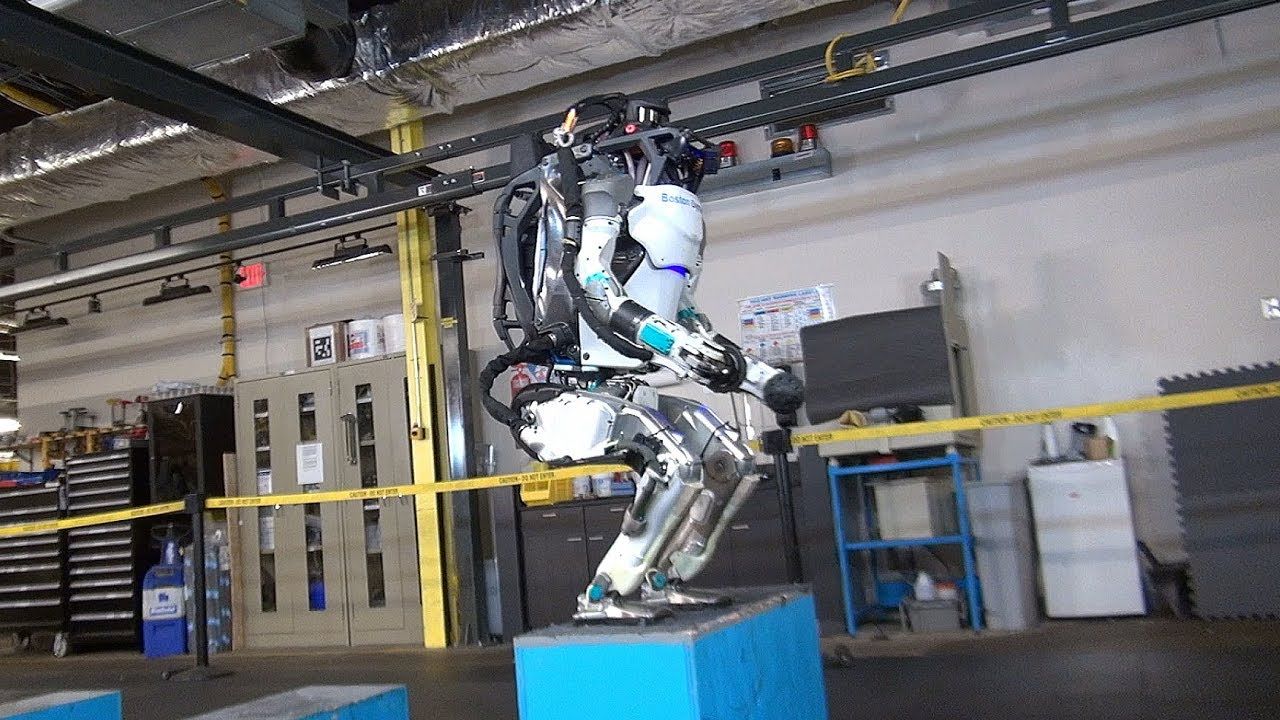
Indeed, Raibert is building that reality. Boston Dynamics, which was bought by SoftBank from Alphabet in June, builds robots that look like humans and animals.
“When we have robots that can do what people and animals do, they will be incredibly useful,” Raibert says.