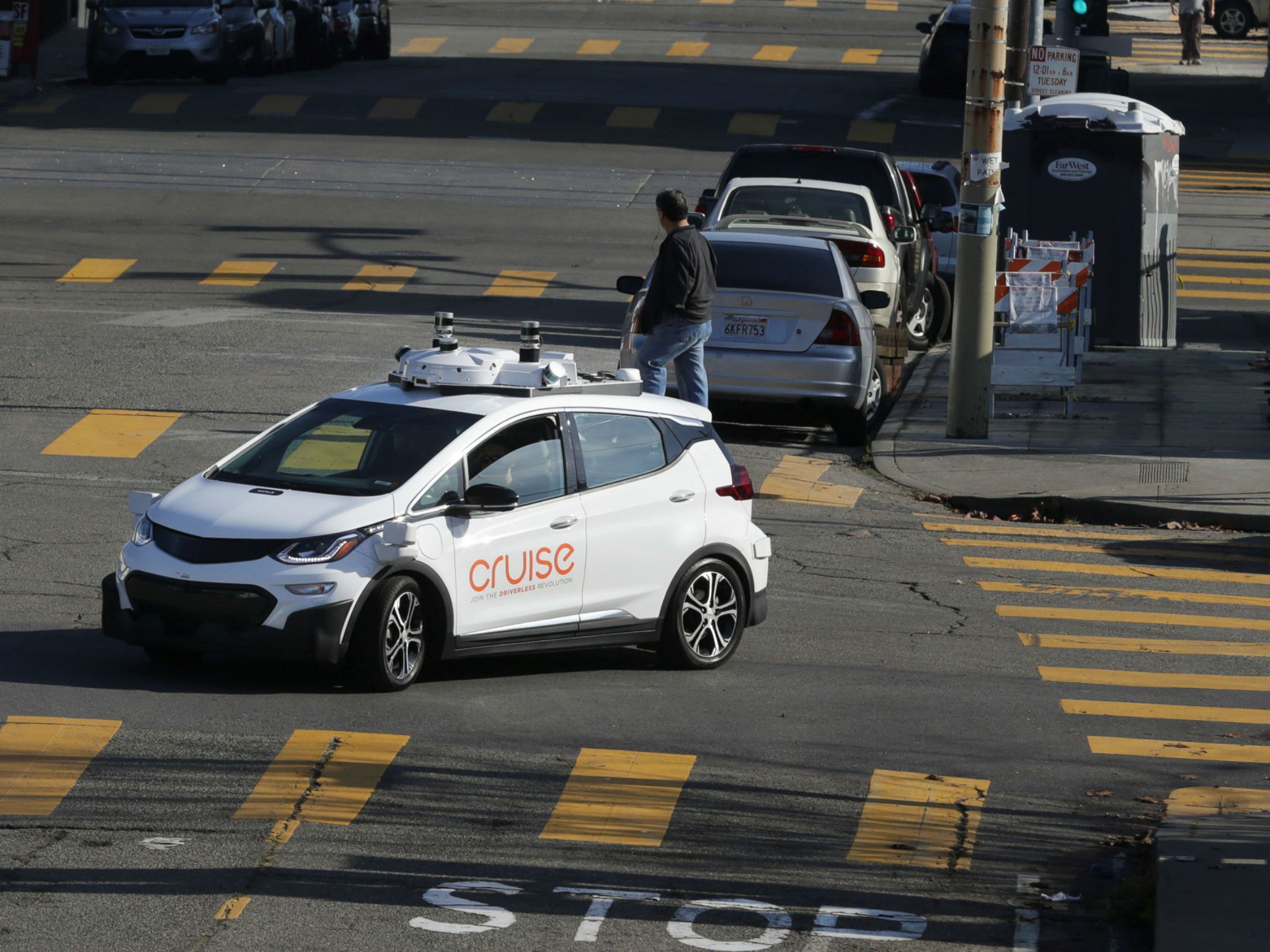
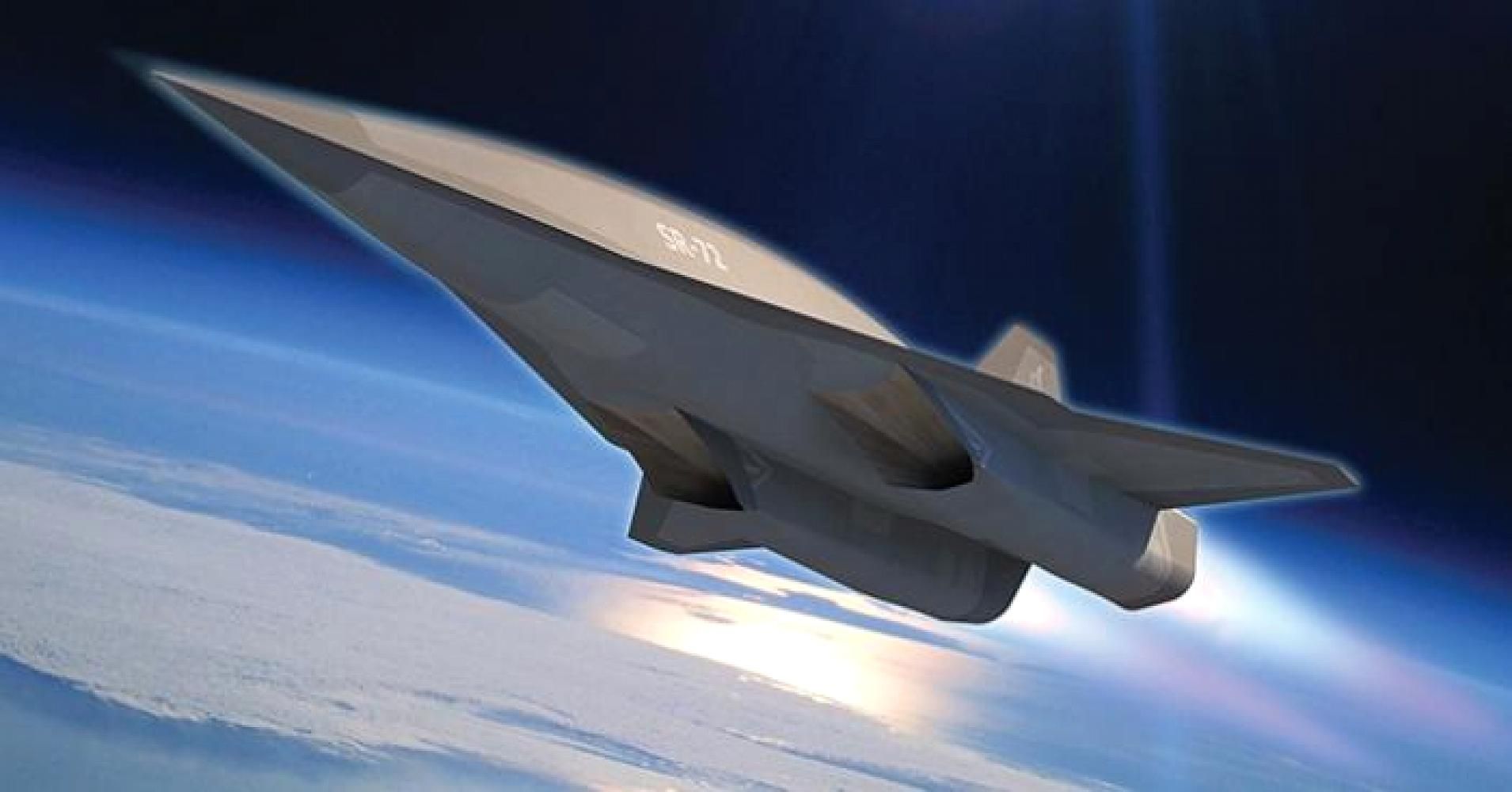
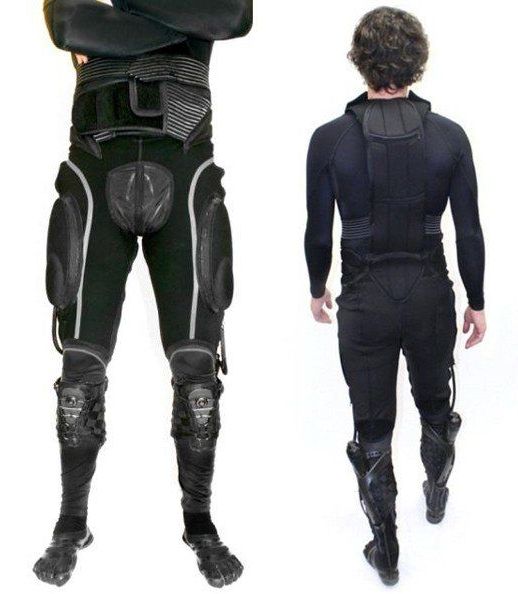
In the course of the last century, science fiction has been a harbinger of things to come. From the automatic sliding doors of Star Trek to visual communication, cyberspace, and even the moon landing, many of our present technological achievements were dreamed up in the futuristic visions of science fiction authors of the 1960s and 70s. Indeed, the fantastical world of science fiction, while not intended to be prophetic, has ended up acting as a blueprint for our modern world.
We have learned from science fiction not only the possibilities of technology, however, but also its irreconcilable dangers. Readers of the genre will recognize the many stories warning us of the hazards of space travel, mind enhancement, and artificial intelligence. These fictional accounts cautioned that if we were not careful, our freedom to transform the world around us would transmogrify into a self-enforced slavery.
Nonetheless, while many of us remembered that these were just stories, intended as speculations about a possible future—in other words, they were fiction before science—through them, we became used to the idea that any advanced technology was inherently dangerous and its use always suspect. Moreover, it became a commonplace idea that technologies whose aim was to change or transform the human being—whether genetic, biological or reconstructive—would lead to a future worthy of Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein.
Read more