Traffic jams could be a thing of the past. Learn more about a driverless future: https://wef.ch/2Op4rCc
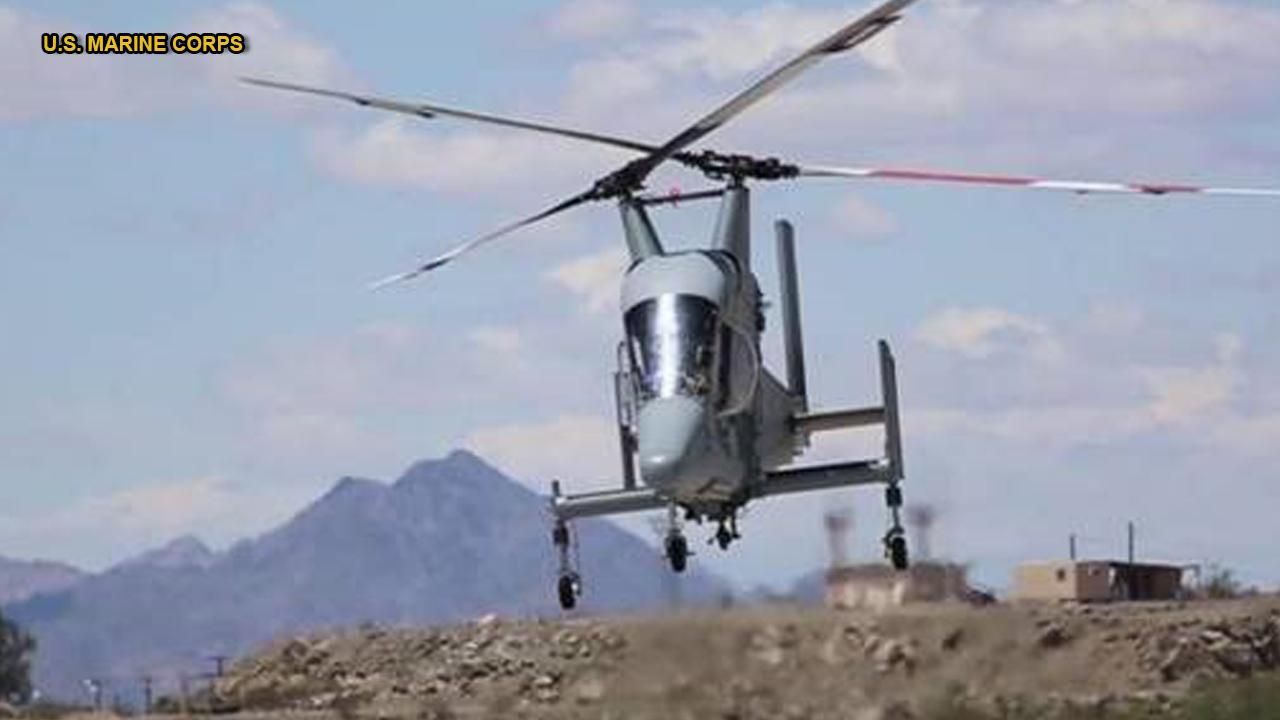



What if an ultra-advanced flying robot designed for extreme military missions could join the fight to combat wildfire alongside human fire crews?
The biggest wildfire in Californian history is raging, with fire officials stating earlier this week that an area almost the size of Los Angeles has been compromised.
It is actually expected to burn through the rest of August, and experts predict the escalation in frequency and scale of wildfires will only continue going forward.

But the grand work-changing projects of A.I., like self-driving cars and humanoid robots, are not yet commercial products. A more humble version of the technology, instead, is making its presence felt in a less glamorous place: the back office.
Artificial intelligence software is making its presence felt in subtle ways, in an unglamorous place: the back office.
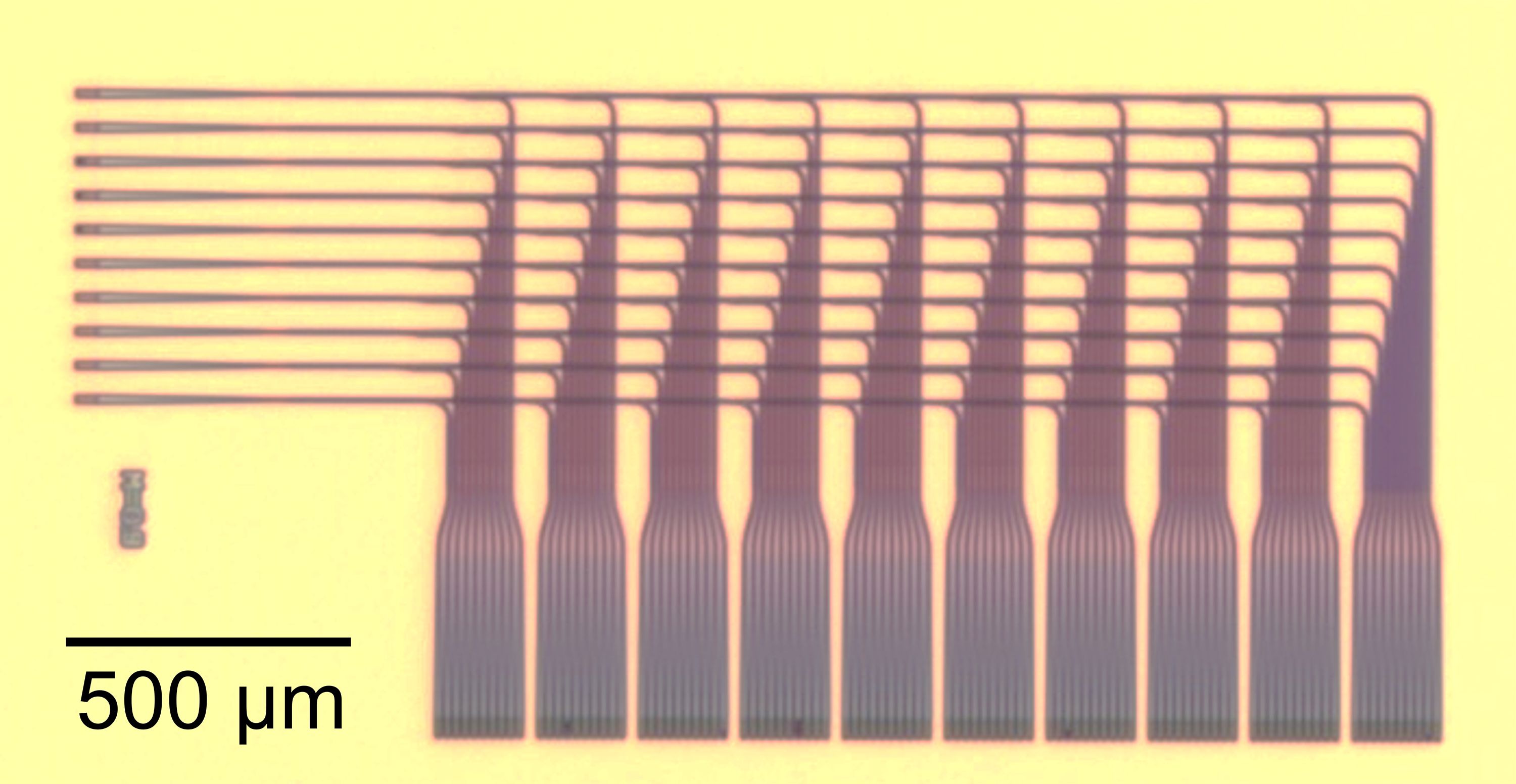
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have made a silicon chip that distributes optical signals precisely across a miniature brain-like grid, showcasing a potential new design for neural networks.
The human brain has billions of neurons (nerve cells), each with thousands of connections to other neurons. Many computing research projects aim to emulate the brain by creating circuits of artificial neural networks. But conventional electronics, including the electrical wiring of semiconductor circuits, often impedes the extremely complex routing required for useful neural networks.
The NIST team proposes to use light instead of electricity as a signaling medium. Neural networks already have demonstrated remarkable power in solving complex problems, including rapid pattern recognition and data analysis. The use of light would eliminate interference due to electrical charge, and the signals would travel faster and farther.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytva8DDV_Ic
This video was made possible by Brilliant. Be one of the first 200 people to sign up with this link and get 20% off your premium subscription with Brilliant.org! https://brilliant.org/singularity
Artificial intelligence has been a topic of growing prominence in the media and mainstream culture since 2015, as well as in the investment world, with start-ups that even mention the word in their business model, gaining massive amounts of funding.
While to many, the hype around AI may appear sudden, the concepts of modern artificial intelligence have been around for over a century and extending further, the concept of artificial intelligence and artificial beings have been in the minds of humans for thousands of years.
To better understand and appreciate this technology and those who brought it to us as well as to gain insight into where it will take us: sit back, relax and join me in an exploration on the history of artificial intelligence.
Thank you to the patron(s) who supported this video ➤
Wyldn pearson collin R terrell kiyoshi matsutsuyu
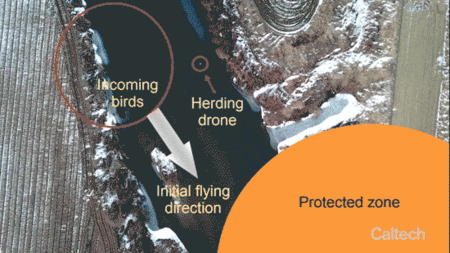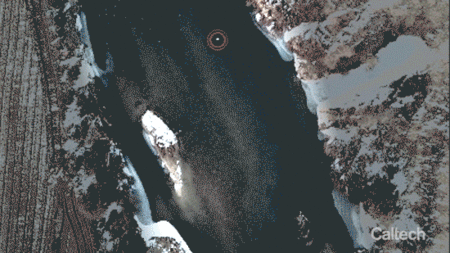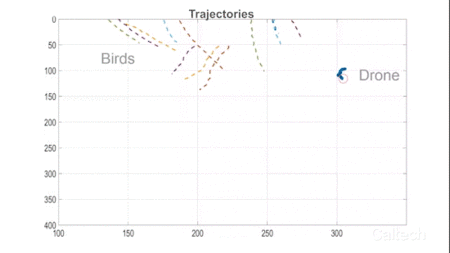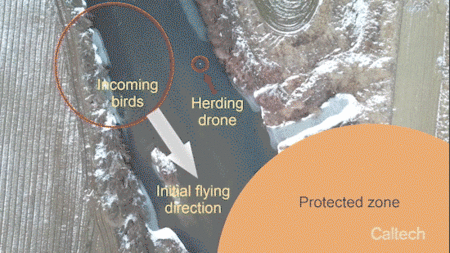
Engineers at Caltech have developed a new control algorithm that enables a single drone to herd an entire flock of birds away from the airspace of an airport. The algorithm is presented in a study in IEEE Transactions on Robotics.
The project was inspired by the 2009 “Miracle on the Hudson,” when US Airways Flight 1549 struck a flock of geese shortly after takeoff and pilots Chesley Sullenberger and Jeffrey Skiles were forced to land in the Hudson River off Manhattan.
“The passengers on Flight 1549 were only saved because the pilots were so skilled,” says Soon-Jo Chung, an associate professor of aerospace and Bren Scholar in the Division of Engineering and Applied Science as well as a JPL research scientist, and the principal investigator on the drone herding project. “It made me think that next time might not have such a happy ending. So I started looking into ways to protect airspace from birds by leveraging my research areas in autonomy and robotics.”
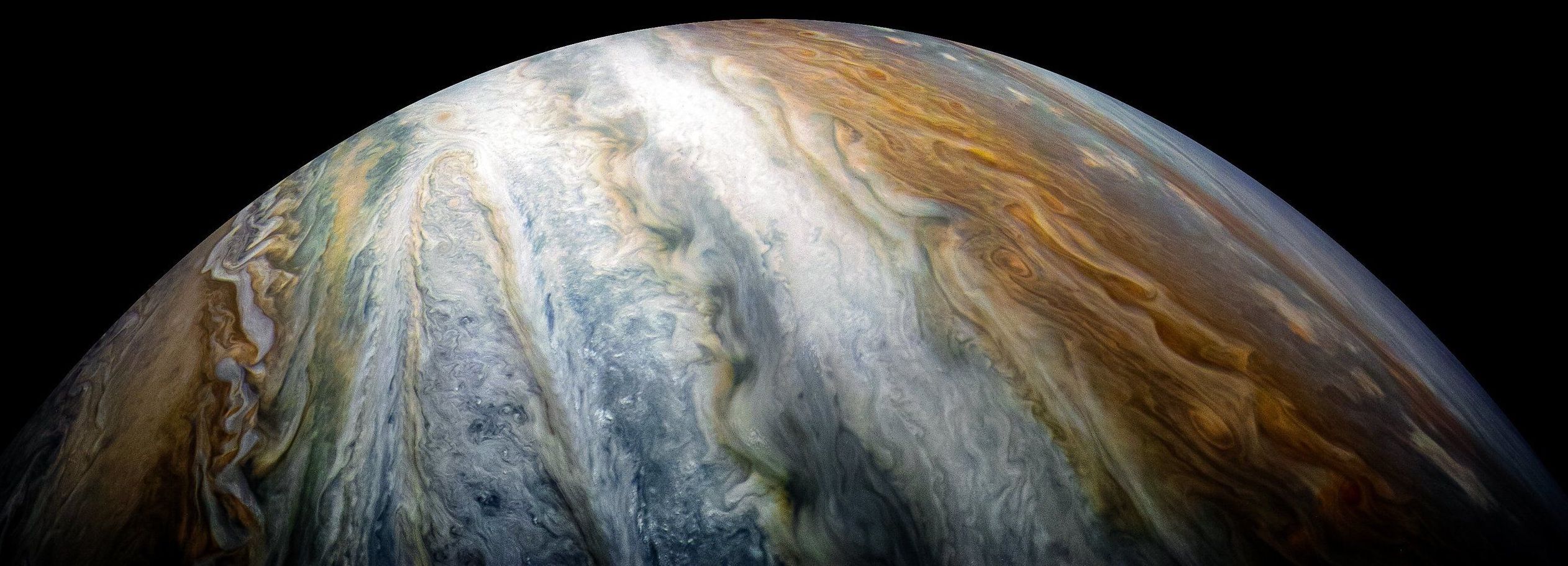

Here on Earth, electromagnetic waves around the planet are typically pretty calm. When the Sun fires a burst of charged particles at the Earth we are treated to an aurora (often called Northern Lights), but rarely are they a cause for concern. If you were to head to Jupiter, however, things would change dramatically.
In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers describe the incredible electromagnetic field structure around two of Jupiter’s moons: Europa and Ganymede. The invisible magnetic fields around these bodies is being powered by Jupiter’s own magnetic field, and the result is an ultra-powerful particle accelerator of sorts, which might be capable of seriously damaging or even destroying a spacecraft.
“Chorus waves” are low-frequency electromagnetic waves that occur naturally around planets, including Earth. Near our planet they’re mostly harmless, but they do have the capability to produce extremely fast-moving “killer” particles that could cause damage to manmade technology if we happened to be in the wrong place at the wrong time.
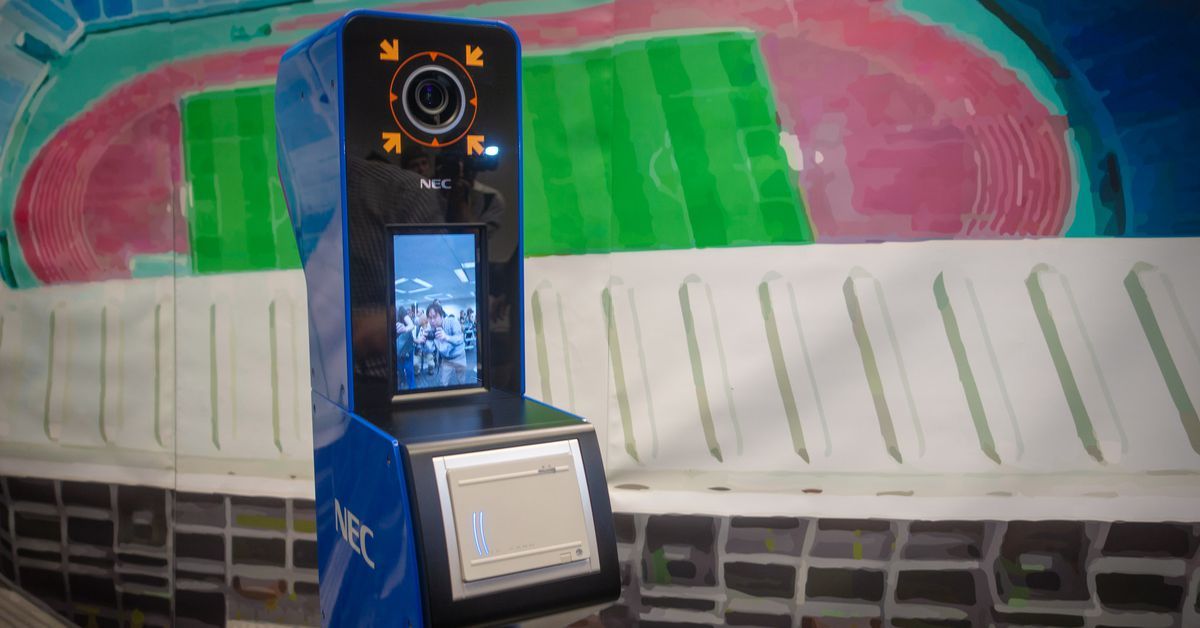

NEC has announced that it will be providing a large-scale facial recognition system for the 2020 Summer Olympic and Paralympic Games in Tokyo. The system will be used to identify over 300,000 people at the Games, including athletes, volunteers, media, and other staff. It’s the first time that facial recognition technology will ever be used for this purpose at an Olympic Games.
NEC’s system is built around an AI engine called NeoFace, which is part of the company’s overarching Bio-IDiom line of biometric authentication technology. The Tokyo 2020 implementation will involve linking photo data with an IC card to be carried by accredited people. NEC says that it has the world’s leading face recognition tech based on benchmark tests from the US’ National Institute of Standards and Technology.
