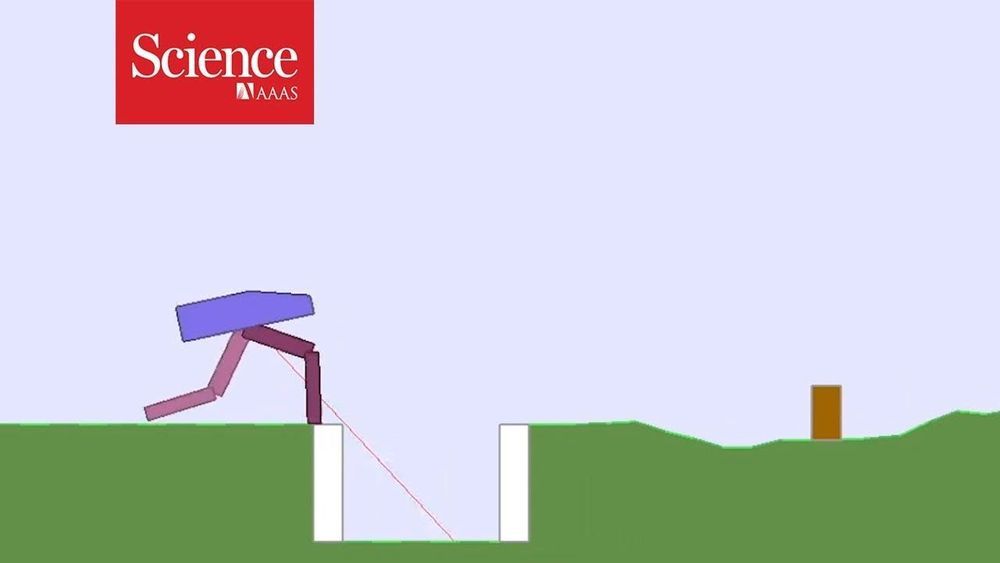
Open-ended style of learning does better than traditional methods.


NAIROBI — Countries must agree strict rules on “killer robots” — autonomous weapons which can assassinate without human involvement, a top Red Cross official has said, amid growing ethical concerns over their use in future wars.
Semi-autonomous weapons systems from drones to tanks have for decades been used to eliminate targets in modern day warfare — but they all have human control behind them.
With rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, there are fears among humanitarians over its use to develop machines which can independently make the decision about who to kill.

Mention artificial intelligence (AI) or artificial neural networks, and images of computers may come to mind. AI-based pattern recognition has a wide variety of real-world uses, such as medical diagnostics, navigation systems, voice-based authentication, image classification, handwriting recognition, speech programs, and text-based processing. However, artificial intelligence is not limited to digital technology and is merging with the realm of biology—synthetic biology and genomics, to be more precise. Pioneering researchers led by Dr. Lulu Qian at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have created synthetic biochemical circuits that are able to perform information processing at the molecular level–an artificial neural network consisting of DNA instead of computer hardware and software.
Artificial intelligence is in the early stages of a renaissance period—a rebirth that is largely due to advances in deep learning techniques with artificial neural networks that have contributed to improvements in pattern recognition. Specifically, the resurgence is largely due to a mathematical tool that calculates derivatives called backpropagation (backward propagation)—it enables artificial neural networks to adjust hidden layers of neurons when there are outlier outcomes for more precise results.
Artificial neural networks (ANN) are a type of machine learning method with concepts borrowed from neuroscience. The structure and function of the nervous system and brain were inspiration for artificial neural networks. Instead of biological neurons, ANNs have artificial nodes. Instead of synapses, ANNs have connections that are able to transmit signals between nodes. Like neurons, the nodes of ANNs are able to receive and process data, as well as activate other nodes connected to it.

As the smartphone market matures, startups are racing to predict what’s next, and venture-capital firms are spraying money into fields like virtual reality, smart watches and even implants in the brain. Here are some of the startups attracting investment.
Venture-capital investors are spraying money into fields like virtual reality, driverless cars and even implants in the brain.

The Singularity is near(er)! At least, that’s what the famous inventor and futurist Ray Kurzweil argues. If you’ve ever had an interest in artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, or the future in general, you’ve more than likely heard of Kurzweil. Whether it’s through documentaries, his various written works, or the vast number of interviews he’s been involved in these last few decades, he’s always provided a cautiously optimistic analysis of the world of tomorrow.
His latest interview, which was conducted during last year’s RAAD Festival, was no different.

Brief mention of AI implications…
As a mathematical concept, the idea of zero is relatively new in human society—and indisputably revolutionary. It’s allowed humans to develop algebra, calculus and Cartesian coordinates ; questions about its properties continue to incite mathematical debate today. So it may sound unlikely that bees — complex and community-based insects to be sure, but insects nonetheless — seem to have mastered their own numerical concept of nothingness.
Despite their sesame-seed-sized brains, honey bees have proven themselves the prodigies of the insect world. Researcher has found that they can count up to about four, distinguish abstract patterns, and communicate locations with other bees. Now, Australian scientists have found what may be their most impressive cognitive ability yet: “zero processing,” or the ability to conceptualize nothingness as a numerical value that can be compared with more tangible quantities like one and two.
While seemingly intuitive, the ability to understand zero is actually quite rare across species—and unheard of in invertebrates. In a press release, the authors of a paper published June 8 in the journal Science called species with this ability an “elite club” that consists of species we generally consider quite intelligent, including primates, dolphins and parrots. Even humans haven’t always been in that club: The concept of zero first appeared in India around 458 A.D, and didn’t enter the West until 1200, when Italian mathematician Fibonacci brought it and a host of other Arabic numerals over with him.

Scientists have developed tiny elastic robots that can change shape depending on their surroundings and can swim through fluids, an advance which may help deliver drugs to diseased tissue one day.
The smart, biocompatible microrobots that are highly flexible are made of hydrogel nanocomposites that contain magnetic nanoparticles allowing them to be controlled via an electromagnetic field.
As a result, these devices are able to swim through fluids and modify their shape when needed. They can also pass through narrow blood vessels and intricate systems without compromising on speed or manoeuvrability, said the group of scientists led by Selman Sakar at Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) and Bradley Nelson at ETH Zurich.

Billionaire Masayoshi Son–not Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, or Mark Zuckerberg–has the most audacious vision for an AI-powered utopia where machines control how we live. And he’s spending hundreds of billions of dollars to realize it. Are you ready to live in Masa World?
[Illustration: Señor Salme]
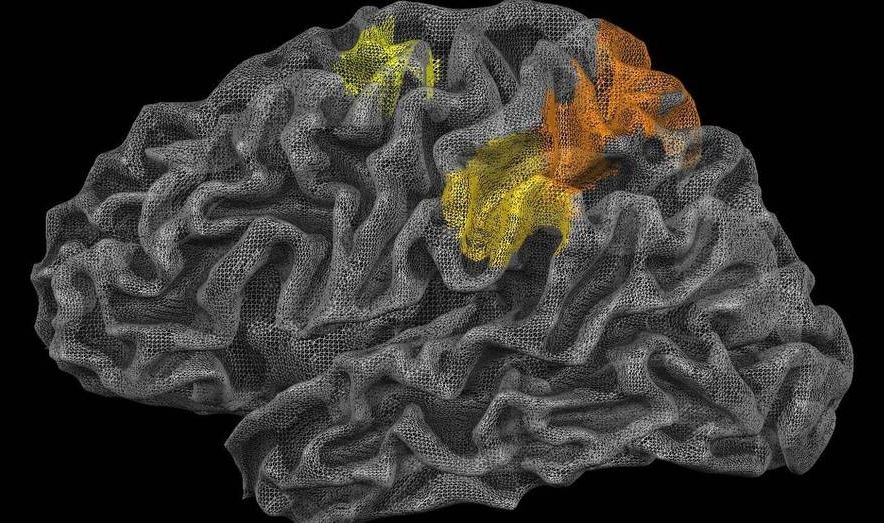
Biofeedback will also be able to help with problems that feel intractable, by conditioning students to make time to think outside the box. Studies show the best way is to deal with a seemingly intractable problem is to consider it intensely for a period of time and then to relax to an almost meditative state to foster the brain’s creative side.
We have trialled technology that can help users manage this approach in Finland, using an app called Study Train that has been designed by Finnish education experts. The app combines the Pomodoro time-management technique with customised learning rhythms based on an individual’s brain waves, telling students to focus when learning efficiency is high and to rest meditatively to promote lateral thinking and creativity when efficiency is low. It is now being used by students in China, Malaysia and Taiwan as well as in Finland and next year will be rolled out further.
We have long known that the brain has good and bad times for retaining information and solving problems. By combining EEG data and machine learning we can now we confident when those different states occur and use that information to improve students’ learning. 2019 will be the year when study becomes turbocharged.