A research group from RIKEN and Kyushu University has developed a new type of material, based on ethylene, which exhibits a number of useful properties such as self-healing and shape memory. Remarkably, some of the materials can spontaneously self-heal even in water or acidic and alkali solutions. The new material is based on ethylene, a compound that is the source of much of the plastic in use today.
Materials that can self-heal have become a popular area of research during the last decade, and a variety of materials have been developed. However, most of the self-healing materials reported to date have relied on sophisticated designs that incorporate chemical mechanisms into polymer networks, such as irreversible or reversible covalent-bond formation, hydrogen bonding, metal-ligand interactions, or ionic interactions. As a result, they require some external stimulus, such as heat or pressure, to prompt them to heal, and in most cases, they do not function in water, acid or alkaline solutions because the chemical networks cannot survive such conditions. The ideal is to create a material that possesses sufficient toughness and can autonomously self-heal under various conditions.
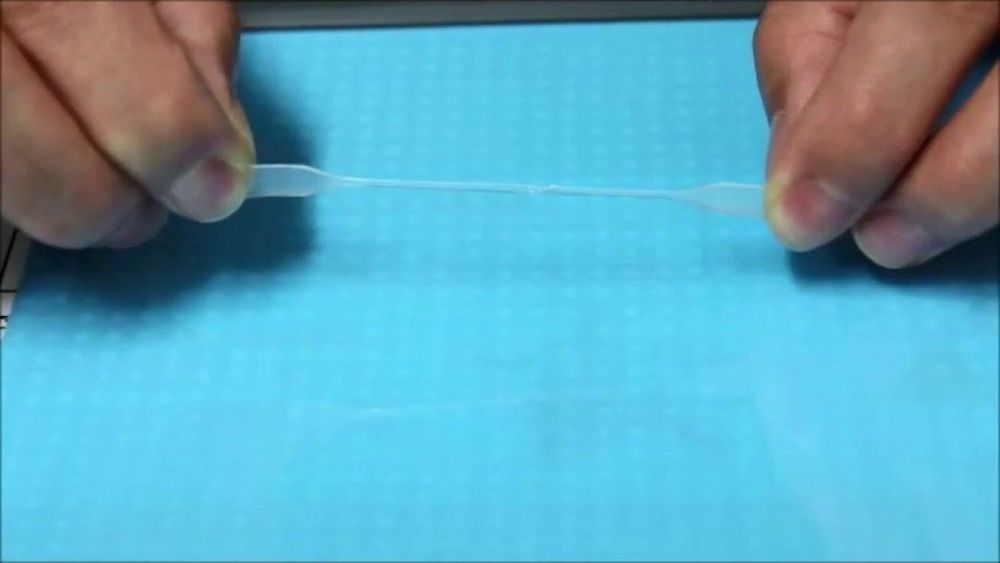
For the present research, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the researchers used a catalyst based on scandium, a rare metal, to create polymers composed of alternating sequences of ethylene and anisylpropylenes and shorter ethylene-ethylene segments by the copolymerization of ethylene and anisylpropylenes. This new class of well-defined, functionalized polyolefins ranged from soft viscoelastic materials—materials that can be both elastic but also exhibit liquid-like properties—to tough elastomers, which can be stretched but return to their original shapes, and rigid plastics. The elastomer copolymers were very elastic, and tough, and also showed remarkable self-healing property, as they autonomously self-healed when subjected to mechanical damage not only in a dry environment but also in water and aqueous acid and alkaline solutions, without the need for any external energy or stimulus.