This thorough review focuses on the impact of AI, 5G, and edge computing on the healthcare sector in the 2020s as well as a look at quantum computing’s potential impact on AI, healthcare, and financial services.
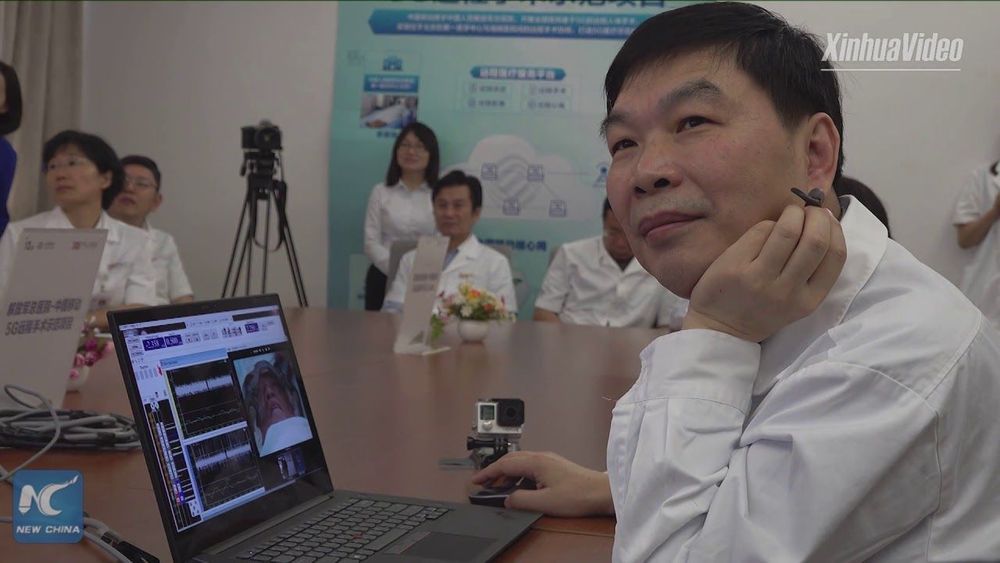


This thorough review focuses on the impact of AI, 5G, and edge computing on the healthcare sector in the 2020s as well as a look at quantum computing’s potential impact on AI, healthcare, and financial services.

Circa 2012
Hundreds of the world’s brightest minds — engineers from Google and IBM, hedge funds quants, and Defense Department contractors building artificial intelligence — were gathered in rapt attention inside the auditorium of the San Francisco Masonic Temple atop Nob Hill. It was the first day of the seventh annual Singularity Summit, and Julia Galef, the President of the Center for Applied Rationality, was speaking onstage. On the screen behind her, Galef projected a giant image from the film Blade Runner: the replicant Roy, naked, his face stained with blood, cradling a white dove in his arms.
At this point in the movie, Roy is reaching the end of his short, pre-programmed life, “The poignancy of his death scene comes from the contrast between that bitter truth and the fact that he still feels his life has meaning, and for lack of a better word, he has a soul,” said Galef. “To me this is the situation we as humans have found ourselves in over the last century. Turns out we are survival machines created by ancient replicators, DNA, to produce as many copies of them as possible. This is the bitter pill that science has offered us in response to our questions about where we came from and what it all means.”
The Singularity Summit bills itself as the world’s premier event on robotics, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technologies. The attendees, who shelled out $795 for a two-day pass, are people whose careers depend on data, on empirical proof. Peter Norvig, Google’s Director of Research, discussed advances in probabilistic first-order logic. The Nobel prize-winning economist Daniel Kahneman lectured on the finer points of heuristics and biases in human psychology. The Power Point presentations were full of math equations and complex charts. Yet time and again the conversation drifted towards the existential: the larger, unanswerable questions of life.
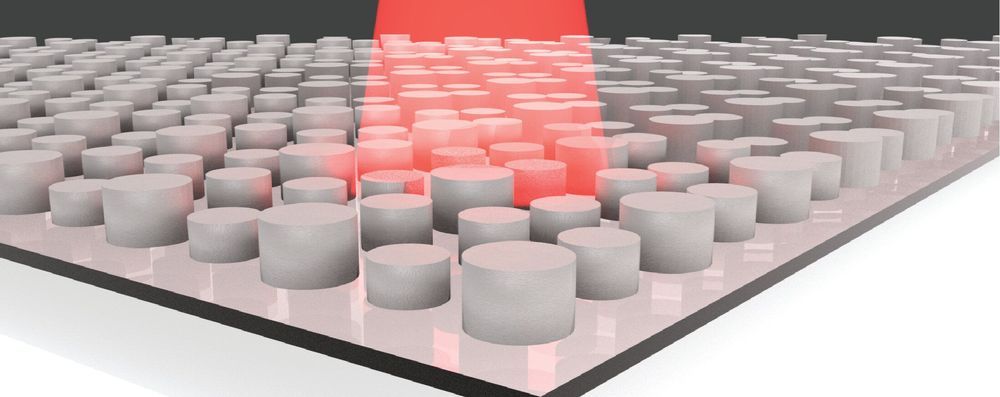
Electrical engineers at Duke University have harnessed the power of machine learning to design dielectric (non-metal) metamaterials that absorb and emit specific frequencies of terahertz radiation. The design technique changed what could have been more than 2000 years of calculation into 23 hours, clearing the way for the design of new, sustainable types of thermal energy harvesters and lighting.
The study was published online on September 16 in the journal Optics Express.
Metamaterials are synthetic materials composed of many individual engineered features, which together produce properties not found in nature through their structure rather than their chemistry. In this case, the terahertz metamaterial is built up from a two-by-two grid of silicon cylinders resembling a short, square Lego.
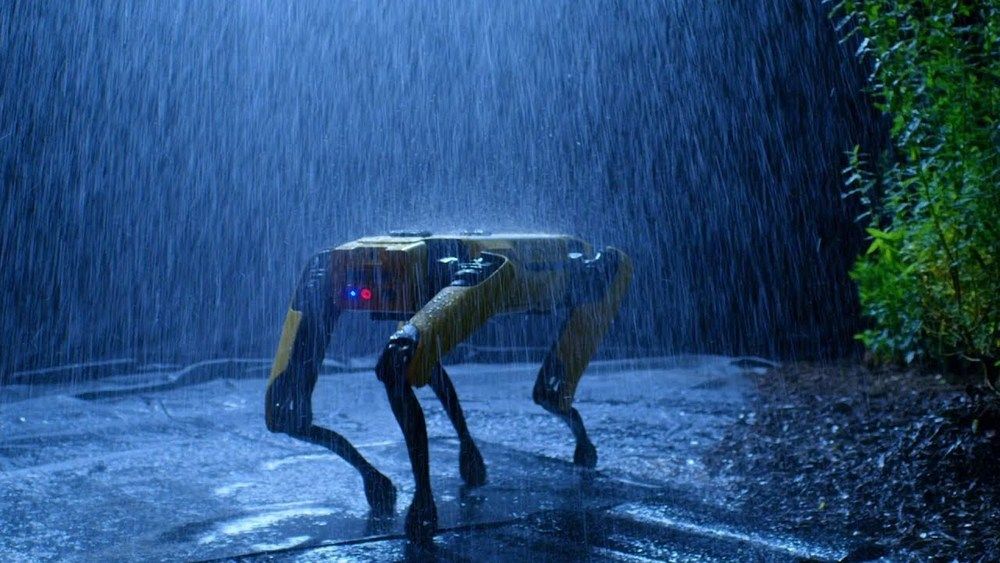

For years, Boston Dynamics’ only commercial product has been vaguely unsettling videos of robots moving in realistic ways. That changes today. No, the robots aren’t getting less creepy. Boston Dynamics has a real commercial product: Spot. This quadrupedal robot is shipping out to select companies, but it could expand to general sales eventually.
We’ve seen Spot (originally known as SpotMini) show up in various video demonstrations. You’ve seen it twerk, and now you might see it work. Boston Dynamics isn’t entirely certain what sort of work Spot will do, but that’s why it’s starting with a limited sales program. It wants to work closely with early adopters to evaluate Spot’s usefulness in the real world.
As part of the launch, Boston Dynamics has posted a video (below) demonstrating the robot’s features. Spot can walk at 3 miles per hour and has an average runtime of 90 minutes. When the battery runs dry, operators can swap in a new battery to get the robot up and running again immediately. It can even operate outside in temperatures ranging from −4 to 113 degrees Fahrenheit (−20 to 45 degrees Celsius). It’s IP54 rated, so it can walk around in the rain, but don’t steer Spot into a lake.

PricewaterhouseCoopers, the large accounting and management consulting firm, released a startling report indicating that workers will be highly impacted by the fast-growing rise of artificial intelligence, robots and related technologies.
Banking and financial services employees, factory workers and office staff will seemingly face the loss of their jobs—or need to find a way to reinvent themselves in this brave new world.
The term “artificial intelligence” is loosely used to describe the ability of a machine to mimic human behavior. AI includes well-known applications, such as Siri, GPS, Spotify, self-driving vehicles and the larger-than-life robots made by Boston Robotics that perform incredible feats.
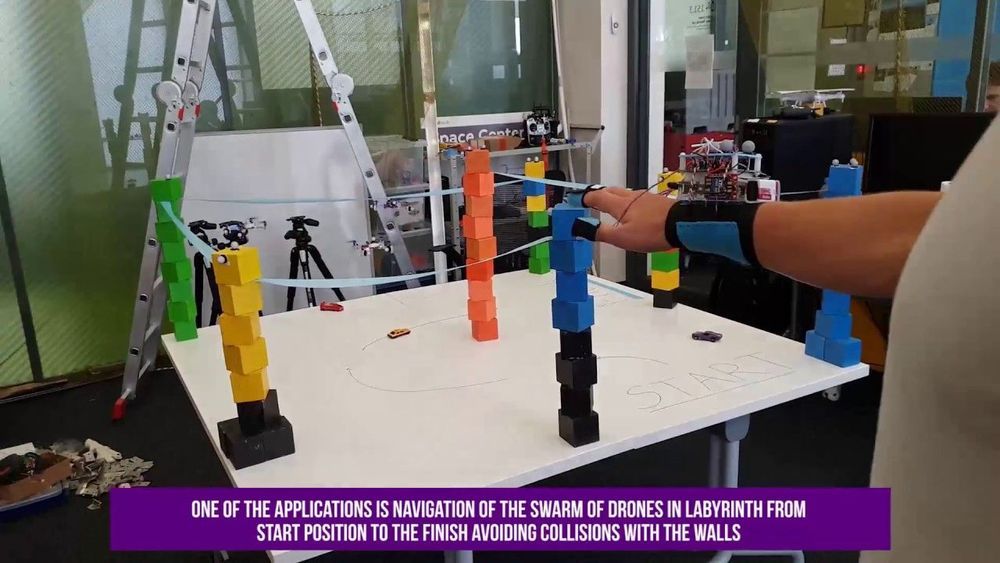


Researchers at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech) in Russia have recently introduced a new strategy to enhance interactions between humans and robotic swarms, called SwarmTouch. This strategy, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv, allows a human operator to communicate with a swarm of nano-quadrotor drones and guide their formation, while receiving tactile feedback in the form of vibrations.
“We are working in the field of swarm of drones and my previous research in the field of haptics was very helpful in introducing a new frontier of tactile human-swarm interactions,” Dzmitry Tsetserukou, Professor at Skoltech and head of Intelligent Space Robotics laboratory, told TechXplore. “During our experiments with the swarm, however, we understood that current interfaces are too unfriendly and difficult to operate.”
While conducting research investigating strategies for human-swarm interaction, Tsetserukou and his colleagues realised that there are currently no available interfaces that allow human operators to easily deploy a swarm of robots and control its movements in real time. At the moment, most swarms simply follow predefined trajectories, which have been set out by researchers before the robots start operating.

Fintech risk management systems are getting a makeover. By adding machine learning technologies to their traditional rules-based fraud management systems, banks hope that they can do better at catching real criminals while declining fewer legitimate credit card transactions. ML technologies, though, have their own gotchas.
Here and there, although not necessarily everywhere, banks are introducing machine language technologies into their fraud detection systems. Essentially, the objective is twofold: to detect real incidents of fraud quickly and accurately, and to do so while preventing false positives, in which legitimate transactions are wrongly tagged as suspicious.
Large banks have led the way in spending on ML-enabled risk management, says Steven D’Alfonso, a research director at IDC responsible for compliance, fraud, and risk analytics strategies for IDC Financial Insights. Lots of bigger banks plan to expand the artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled fraud detection systems into enterprise-wide decision support systems. Many smaller banks that haven’t yet embarked on ML are expected to follow by signing on for ML managed services.
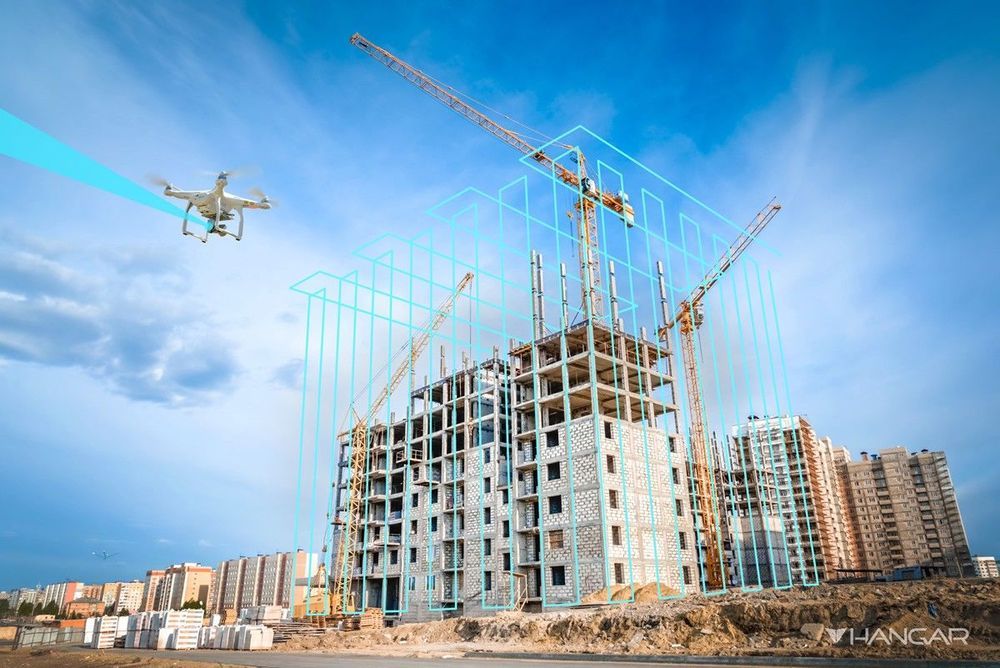

We hear it daily — “Launch your drone program!” Uninspired marketing campaigns littered across social media, websites and emails. A detrimental circle of brands mirroring brands, unwittingly stalling the rise of drones. The problem is, as an industry, they’re missing the damn point. Take for example a use case we see all too often — construction. When handheld drills started showing up on jobsites, we didn’t hear Black + Decker say, “launch your drill program!” Why not? Drills are just enablers. They allow workers to do what they were already doing — except better, faster and more efficiently. The breakthrough had little to do with the actual tool itself, and more the new ability to enable faster holes. Drones are no different.
The goal isn’t to “put a drone on every construction site.” Drones are promising new vehicles that have the potential to transform industry, but they also inherently introduce new costs and complexities. The thought of adding new tools, new responsibilities, new certifications and permits, and new burdens to an already complex operation is the exact opposite of what most project managers consider helpful. This might begin to explain why drone service providers today are collectively struggling to grow at any meaningful velocity. We’re creating “launch your drone programs” solutions that make it easier for businesses to own and operate drones, when we should be making the drone invisible, and become laser-focused on the data drones generate and an infrastructure that supports rapid spatial insights.
We need to stop putting drones on construction sites, and start giving the industry the very thing that drones enable — insight. Drones will be on every job site in the next few years, but not as another tool on the tool belt. The project manager isn’t adopting a drone program. They’re adopting a visual insights program that captures a new, historical perspective across their sites. They’re providing situational awareness holistically throughout their organization. They’re making decisions based on the actual state of projects, and the insights affordable by new perspectives and sensors.