Space exploration company SpaceX’s founder and chief executive officer Elon Musk on Tuesday said he expected humans to land on Mars in six years. He also said that SpaceX plans to launch an unmanned spacecraft and land on Mars in two years, with a chance of the first human landing on Mars in four years instead of six.
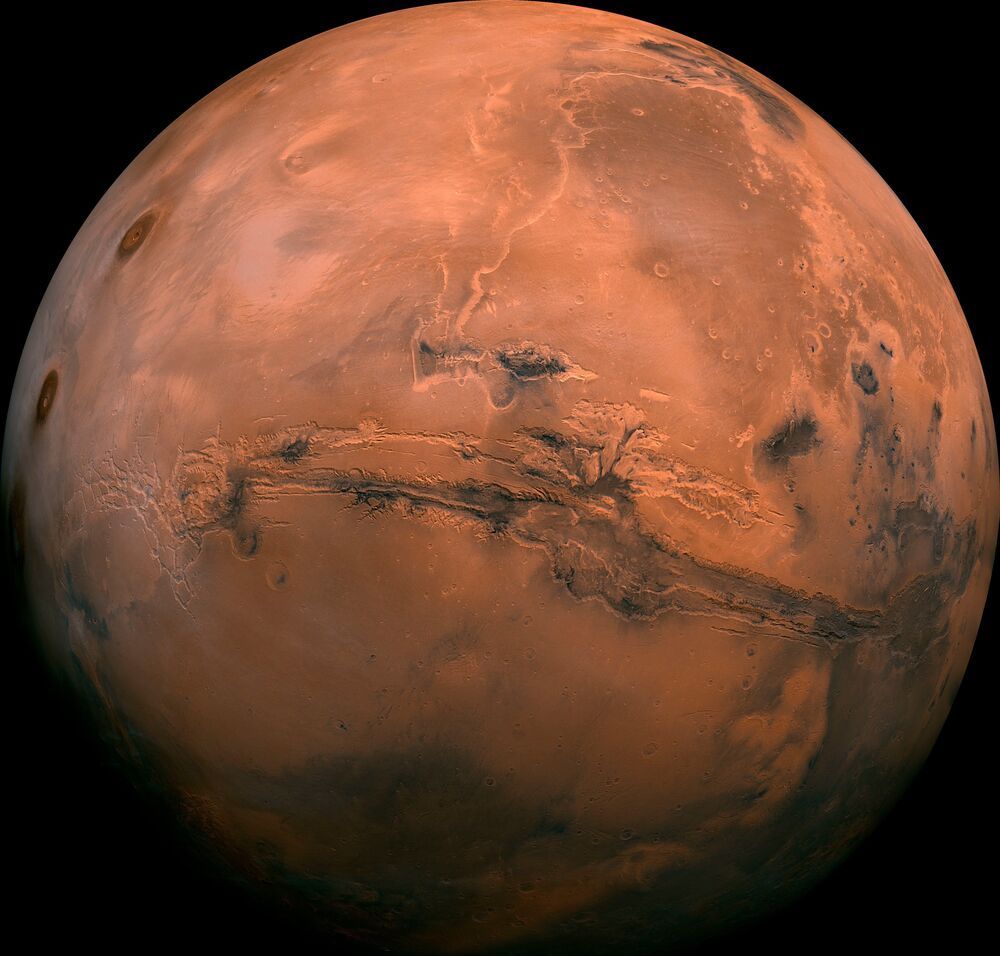
United States’ space agency NASA’s Perseverance rover which was launched in July 2020 is scheduled to land at Jezero Crater on Mars on 18 February 2021. It will look at signs of ancient life and collect rock and soil samples for a possible return to Earth.
It is carrying instruments that will use high-temperature electrolysis but the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) will be producing oxygen only, from the carbon dioxide in the air.