Most computer systems are designed to store and manipulate information, such as documents, images, audio files and other data. While conventional computers are programmed to perform specific operations on structured data, emerging neuro-inspired systems can learn to solve tasks more adaptively, without having to be engineered to carry out a set type of operations.
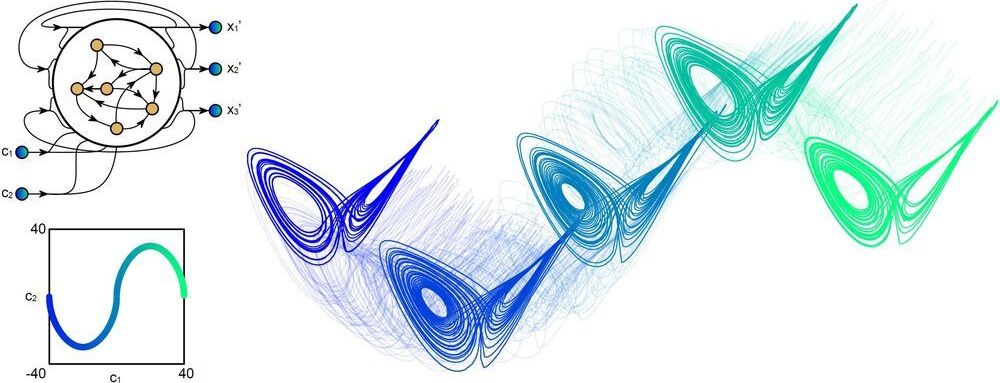
Researchers at University of Pennsylvania and University of California recently trained a recurrent neural network (RNN) to adapt its representation of complex information based only on local data examples. In a paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, they introduced this RNN and outlined the key learning mechanism underpinning its functioning.
“Every day, we manipulate information about the world to make predictions,” Jason Kim, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “How much longer can I cook this pasta before it becomes soggy? How much later can I leave for work before rush hour? Such information representation and computation broadly fall into the category of working memory. While we can program a computer to build models of pasta texture or commute times, our primary objective was to understand how a neural network learns to build models and make predictions only by observing examples.”