The world’s first A.I. fashion designer to create infinitely unique clothes inspired by science and technology. All garments’ source code is embedded in the blockchain as a certificate of authenticity. Exclusively sold in bitcoin on the darkweb.

The world’s first A.I. fashion designer to create infinitely unique clothes inspired by science and technology. All garments’ source code is embedded in the blockchain as a certificate of authenticity. Exclusively sold in bitcoin on the darkweb.

$4.2 billion per ounce. That’s how much the most expensive material on Earth costs. Priced at £100m per gram, the most expensive material on Earth is made up of “endohedral fullerenes,” a cage of carbon atoms containing nitrogen atoms. It could help us make atomic clocks and accurate autonomous cars.
Current atomic clocks are the size of rooms. This material could allow us to make atomic clocks that fit in your smartphone.

A founding father of artificial intelligence talks about the great breakthroughs of his early years.

Machine learning is a bit of a buzz term that describes the way artificial intelligence (AI) can begin to make sense of the world around it by being exposed to massive amount amounts of data.
But a new algorithm developed by researchers in the US has dramatically cut down the amount of learning time required for AI to teach itself new things, with a machine capable of recognising and drawing visual symbols that are largely indistinguishable from those drawn by people.
The research highlights how, for all our imperfections, people are actually pretty good at learning things. Whether we’re learning a written character, how to operate a tool, or how to perform a dance move, humans only need a few examples before we can replicate what we’ve been shown.

Launched in 1958, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency is behind some of the biggest innovations in the military — many of which have crossed over to the civilian technology market. These include things like advanced robotics, global positioning systems, and the Internet.
So what’s going to happen in 2045?
It’s pretty likely that robots and artificial technology are going to transform a bunch of industries, drone aircraft will continue their leap from the military to the civilian market, and self-driving cars will make your commute a lot more bearable.
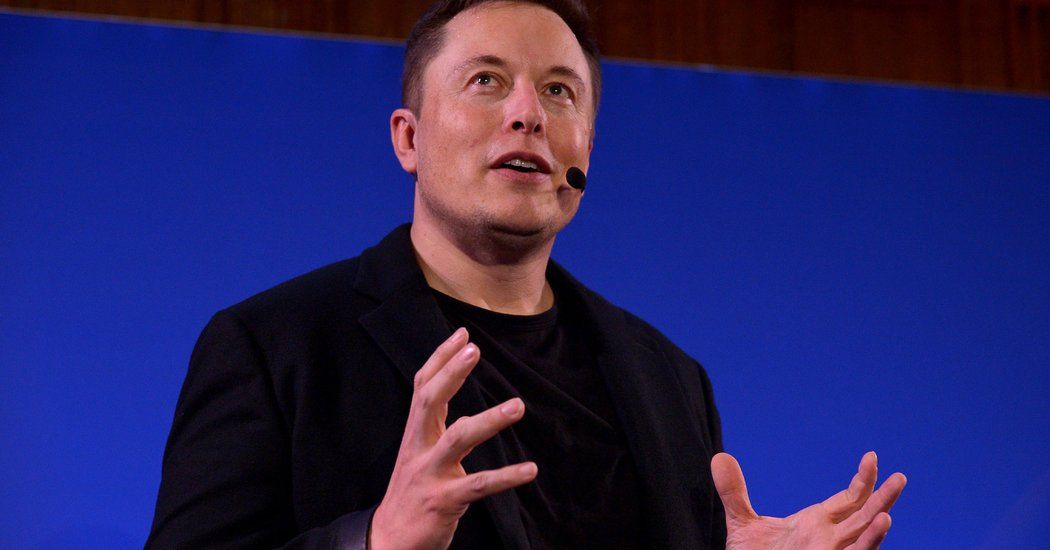

Its long-range goal will be to create an “artificial general intelligence,” a machine capable of performing any intellectual task that a human being can, according to Mr. Musk. He also stressed that the focus was on building technologies that augment rather than replace humans.
The investors — including Elon Musk, Peter Thiel and Reid Hoffman — said they planned to commit $1 billion to the project long term, but would initially spend only a small fraction of that amount in the first few years of the project. But, Mr. Musk said, “Everyone who is listed as a contributor has made a substantial commitment and this should be viewed as at least a billion-dollar project.”
The organization, to be named OpenAI, will be established as a nonprofit, and will be based in San Francisco.
Recently, the study of potential risks from advanced artificial intelligence has attracted substantial new funding, prompting new job openings at e.g. Oxford University and (in the near future) at Cambridge University, Imperial College London, and UC Berkeley.
This is the dawn of a new field. It’s important to fill these roles with strong candidates. The trouble is, it’s hard to find strong candidates at the dawn of a new field, because universities haven’t yet begun to train a steady flow of new experts on the topic. There is no “long-term AI safety” program for graduate students anywhere in the world.
Right now the field is pretty small, and the people I’ve spoken to (including e.g. at Oxford) seem to agree that it will be a challenge to fill these roles with candidates they already know about. Oxford has already re-posted one position, because no suitable candidates were found via the original posting.


Machine learning now allows us to project a particular voice onto someone else’s face, which makes for some pretty hilarious pairings. http://voc.tv/1P6L9zh