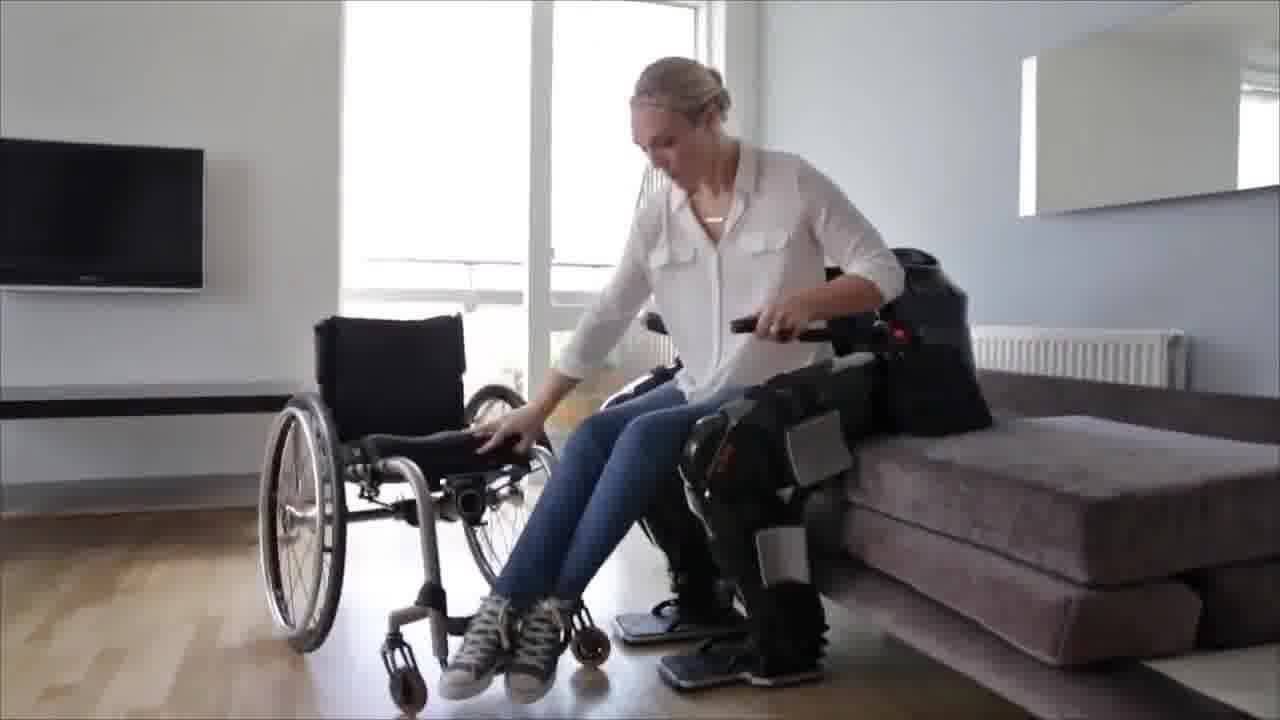
Kudos to Manpower’s CEO Jonas Prising — with the possibility on the horizon of a world wide loss of 5 million jobs; we need to make sure we a structure in place to absorb that hit with needs to include education & retraining and a financial support structure to help those laid off and their immediate family members (namely children). And, the earlier we can train folks; the less costly it will be for governments and countries in the long run.
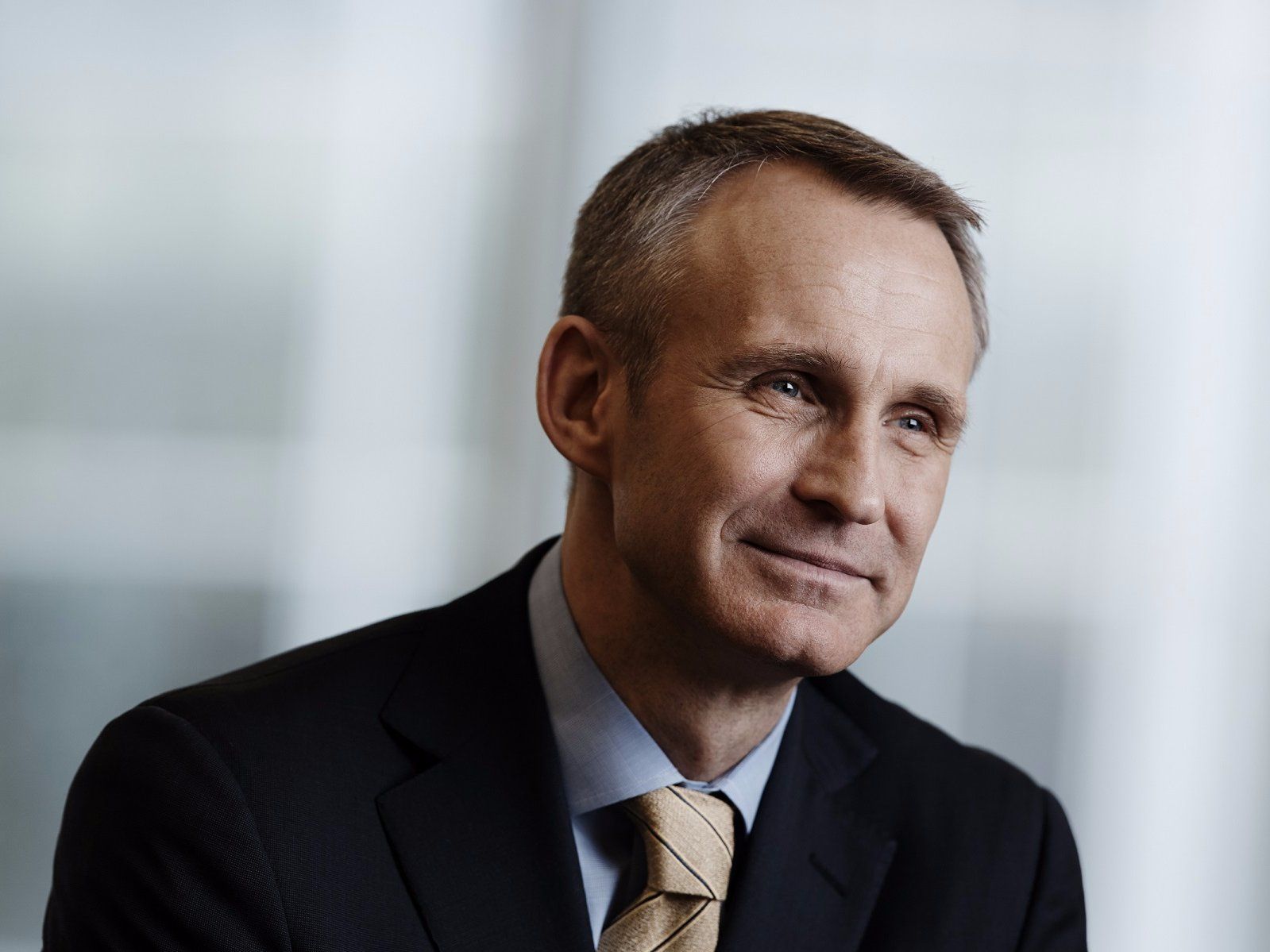 ManpowerJonas Prising, CEO and Executive Chairman of Manpower, spoke to Business Insider in Davos for the WEF meeting.
ManpowerJonas Prising, CEO and Executive Chairman of Manpower, spoke to Business Insider in Davos for the WEF meeting.
Over 2,500 of the world’s most powerful people have talked about the risks and opportunities surrounding “The Fourth Industrial Revolution” this week at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland.
The biggest risk that has been pointed out time and time again when Business Insider spoke to the bosses of the largest corporations in the world is two pronged.