Glad to see others finding value in using Q-Dots with Graphene.
The development of photodetectors has been a matter of considerable interest in the past decades since their applications are essential to many different fields including cameras, medical devices, safety equipment, optical communication devices or even surveying instruments, among others.
Many efforts have been focused towards optoelectronic research in trying to create low cost photodetectors with high sensitivity, high quantum efficiency, high gain and fast photoresponse. This is of paramount importance especially in the short wave infrared which currently is addressed by very expensive III-V InGaAs photodetectors. The development of two main classes of photodetectors, photodiodes and phototransistors, have partially been able to accomplish these goals because even though they both have many outstanding properties, none seem to fulfill all of these requirements. While photodiodes are much faster than phototransistors, phototransistors have a higher gain and do not require low noise preamplifiers for their use.
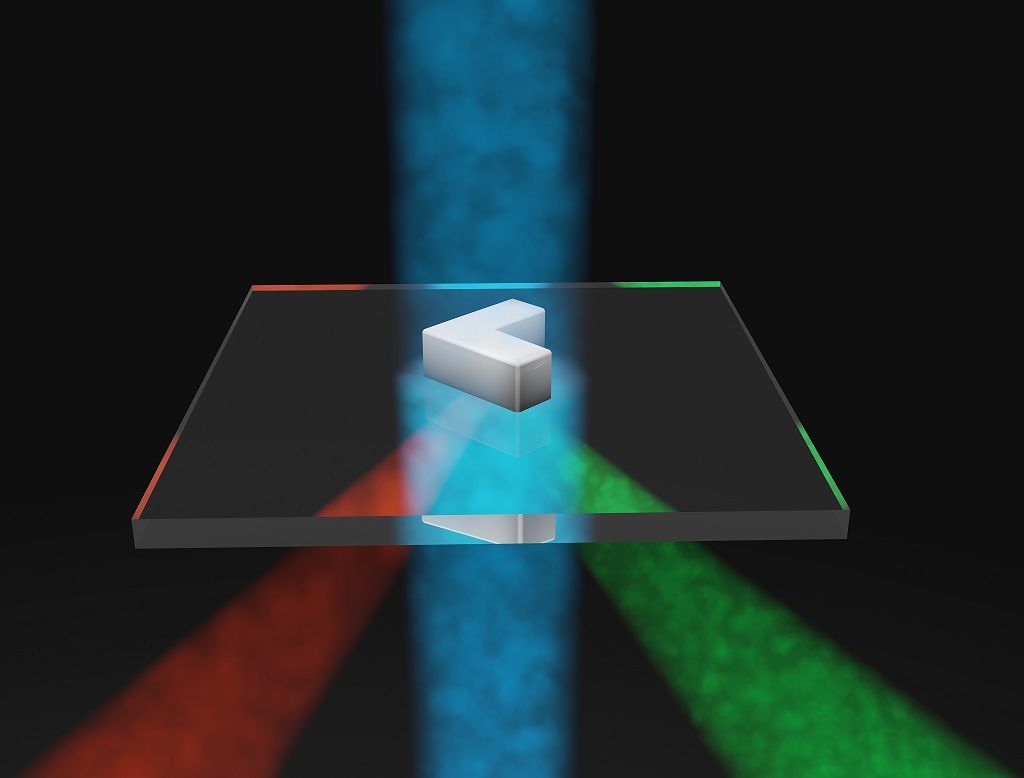
To overcome these limitations, ICFO researchers Ivan Nikitskiy, Stijn Goossens, Dominik Kufer, Tania Lasanta, Gabriele Navickaite, led by ICREA professors at ICFO Frank Koppens and Gerasimos Konstantatos, have been able to develop a hybrid photodetector capable of attaining concomitantly better performance features in terms of speed, quantum efficiency and linear dynamic range, operating not only in the visible but also in the near infrared (NIR: 700-1400nm) and SWIR range (1400-3000nm). At the same time this technology is based upon materials that can be monolithically integrated with Si CMOS electronics as well as flexible electronic platforms. The results of this work have been recently published in Nature Communications.