Scientists at the Energy Department’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) discovered a use for perovskites that runs counter to the intended usage of the hybrid organic-inorganic material.
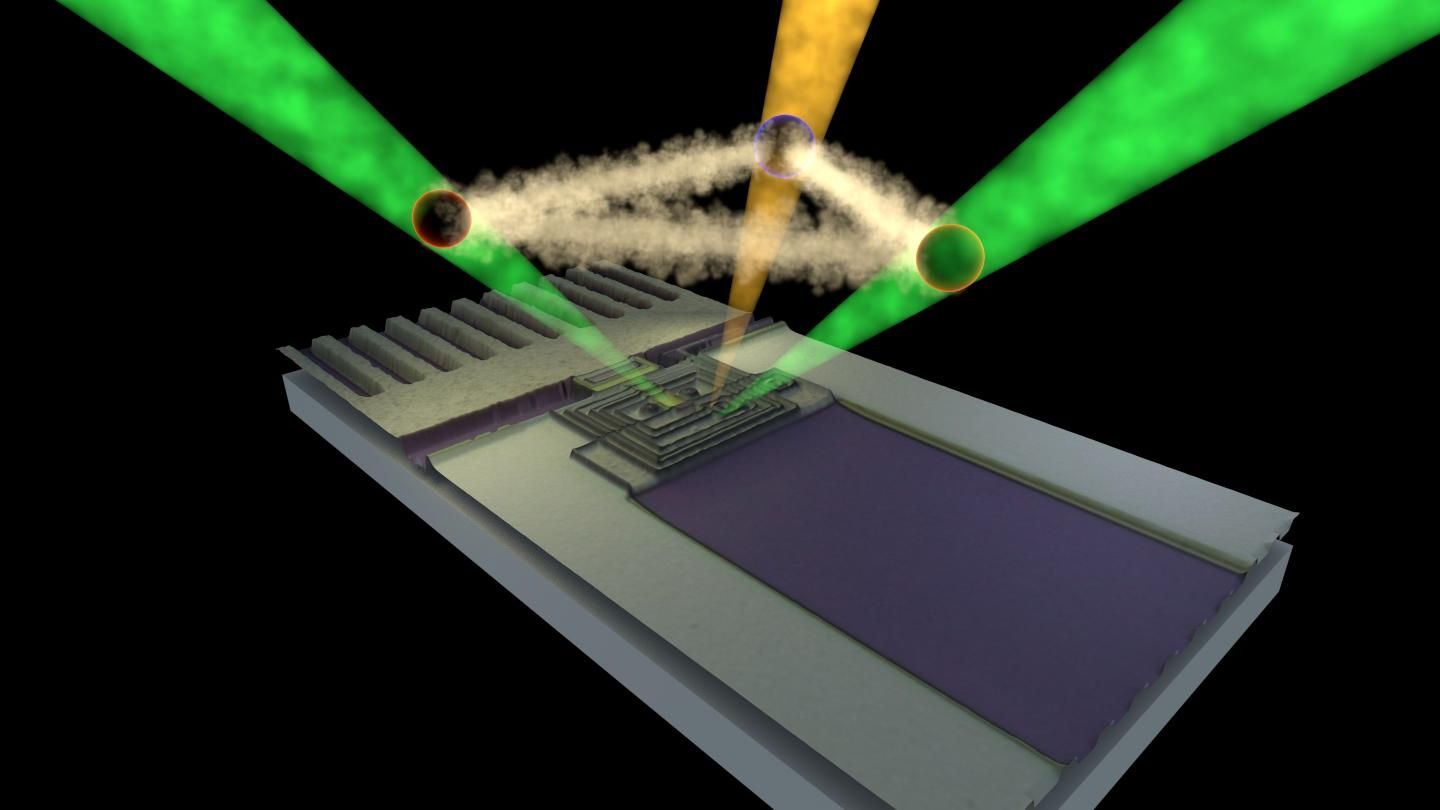
Considerable research at NREL and elsewhere has been conducted into the use of organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites as a solar cell. Perovskite systems have been shown to be highly efficient at converting sunlight to electricity. Experimenting on a lead-halide perovskite, NREL researchers found evidence the material could have great potential for optoelectronic applications beyond photovoltaics, including in the field of quantum computers.
Today, Nature Communications published the research, Large Polarization-Dependent Exciton Optical Stark Effect in Lead Iodide Perovskites. Authors of the paper are Ye Yang, Mengjin Yang, Kai Zhu, Justin Johnson, Joseph Berry, Jao van de Lagemaat, and Matthew Beard.