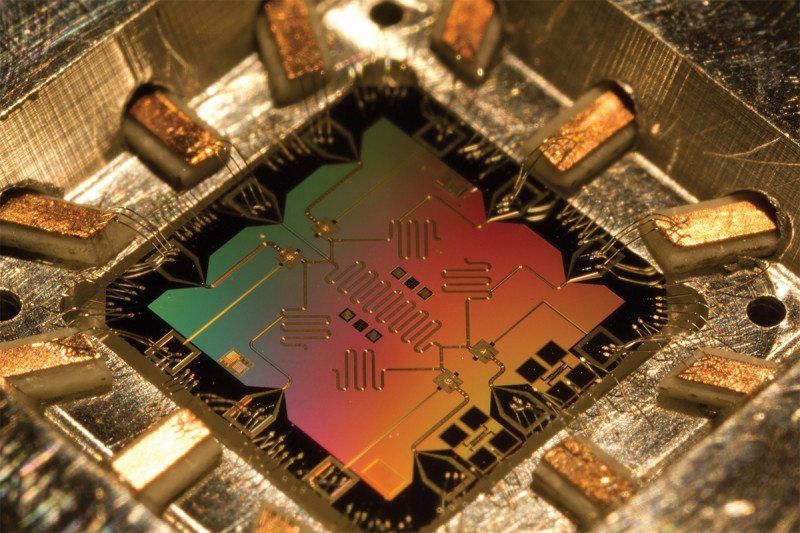
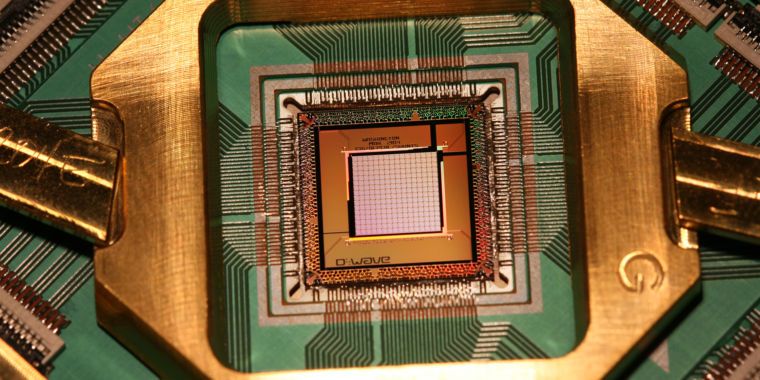
Researchers at the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, in collaboration with researchers at the Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation and the Qatar Environment and Energy Research Institute have discovered qualitatively new states of a superconducting artificial atom dressed with virtual photons.
The discovery was made using spectroscopic measurements on an artificial atom that is very strongly coupled to the light field inside a superconducting cavity. This result provides a new platform to investigate the interaction between light and matter at a fundamental level, helps understand quantum phase transitions and provides a route to applications of non-classical light such as Schrödinger cat states.
It may contribute to the development of quantum technologies in areas such as quantum communication, quantum simulation and computation, or quantum metrology.