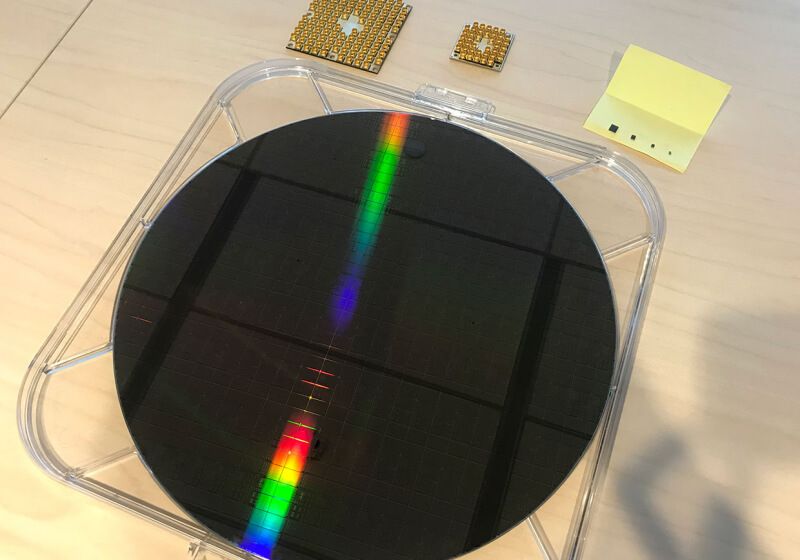
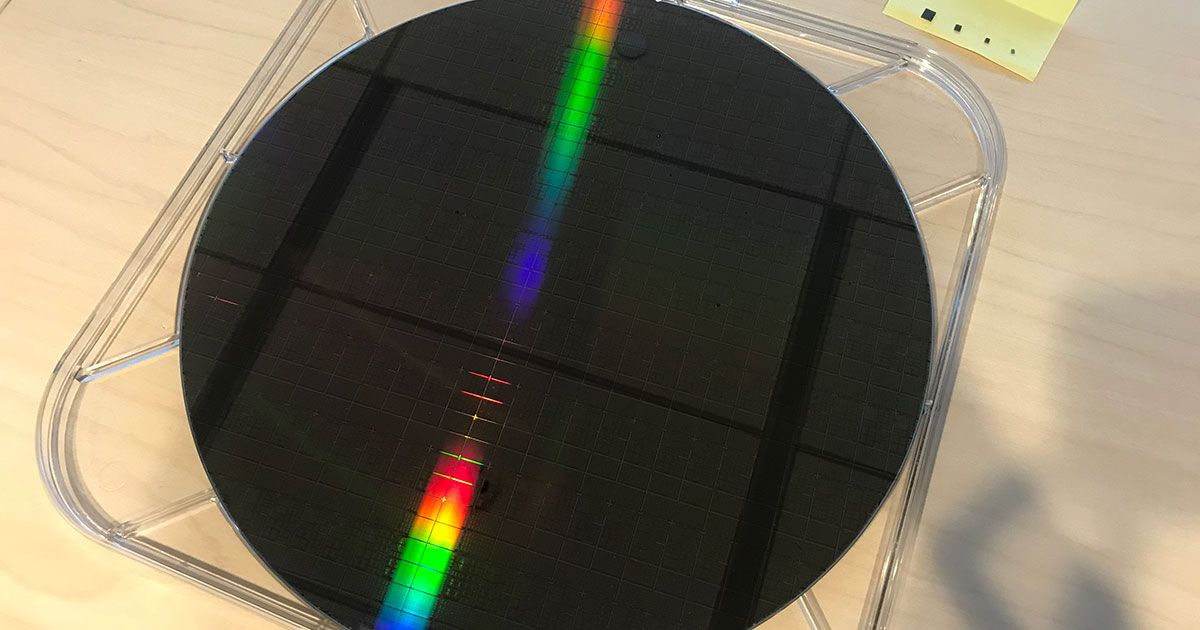
Intel researchers are taking new steps toward quantum computers by testing a tiny new “spin qubit” chip. The new chip was created in Intel’s D1D Fab in Oregon using the same silicon manufacturing techniques that the company has perfected for creating billions of traditional computer chips. Smaller than a pencil’s eraser, it is the tiniest quantum computing chip Intel has made.
The new spin qubit chip runs at the extremely low temperatures required for quantum computing: roughly 460 degrees below zero Fahrenheit – 250 times colder than space.
The spin qubit chip does not contain transistors – the on/off switches that form the basis of today’s computing devices – but qubits (short for “quantum bits”) that can hold a single electron. The behavior of that single electron, which can be in multiple spin states simultaneously, offers vastly greater computing power than today’s transistors, and is the basis of quantum computing.