From Reese Witherspoon to Jeff Bezos, those who are super successful in their chosen domain accept this truth.



The energy use of data centers is a major drag on resources, but they also use a lot of water. Any technology that increases their efficiency while reducing resource waste is a good thing.
“Now, Forced Physics, a company based in Scottsdale, Ariz., has developed a low-power system that it says could slash a data center’s energy requirements for cooling by 90 percent. The company’s JouleForce conductor is a passive system that uses ambient, filtered, nonrefrigerated air to whisk heat away from computer chips.”
The company that created it, Forced Physics, plans to install the technology in a pilot plant in February.

For the first time ever, an international team of researchers imaged the microscopic state of negative capacitance. This novel result provides researchers with fundamental, atomistic insight into the physics of negative capacitance, which could have far-reaching consequences for energy-efficient electronics.


CERN has revealed plans for a gigantic successor of the giant atom smasher LHC, the biggest machine ever built. Particle physicists will never stop to ask for ever larger big bang machines. But where are the limits for the ordinary society concerning costs and existential risks?
CERN boffins are already conducting a mega experiment at the LHC, a 27km circular particle collider, at the cost of several billion Euros to study conditions of matter as it existed fractions of a second after the big bang and to find the smallest particle possible – but the question is how could they ever know? Now, they pretend to be a little bit upset because they could not find any particles beyond the standard model, which means something they would not expect. To achieve that, particle physicists would like to build an even larger “Future Circular Collider” (FCC) near Geneva, where CERN enjoys extraterritorial status, with a ring of 100km – for about 24 billion Euros.
Experts point out that this research could be as limitless as the universe itself. The UK’s former Chief Scientific Advisor, Prof Sir David King told BBC: “We have to draw a line somewhere otherwise we end up with a collider that is so large that it goes around the equator. And if it doesn’t end there perhaps there will be a request for one that goes to the Moon and back.”
“There is always going to be more deep physics to be conducted with larger and larger colliders. My question is to what extent will the knowledge that we already have be extended to benefit humanity?”
There have been broad discussions about whether high energy nuclear experiments could pose an existential risk sooner or later, for example by producing micro black holes (mBH) or strange matter (strangelets) that could convert ordinary matter into strange matter and that eventually could start an infinite chain reaction from the moment it was stable – theoretically at a mass of around 1000 protons.
CERN has argued that micro black holes eventually could be produced, but they would not be stable and evaporate immediately due to „Hawking radiation“, a theoretical process that has never been observed.
Furthermore, CERN argues that similar high energy particle collisions occur naturally in the universe and in the Earth’s atmosphere, so they could not be dangerous. However, such natural high energy collisions are seldom and they have only been measured rather indirectly. Basically, nature does not set up LHC experiments: For example, the density of such artificial particle collisions never occurs in Earth’s atmosphere. Even if the cosmic ray argument was legitimate: CERN produces as many high energy collisions in an artificial narrow space as occur naturally in more than hundred thousand years in the atmosphere. Physicists look quite puzzled when they recalculate it.
Others argue that a particle collider ring would have to be bigger than the Earth to be dangerous.
A study on “Methodological Challenges for Risks with Low Probabilities and High Stakes” was provided by Lifeboat member Prof Raffaela Hillerbrand et al. Prof Eric Johnson submitted a paper discussing juridical difficulties (lawsuits were not successful or were not accepted respectively) but also the problem of groupthink within scientific communities. More of important contributions to the existential risk debate came from risk assessment experts Wolfgang Kromp and Mark Leggett, from R. Plaga, Eric Penrose, Walter Wagner, Otto Roessler, James Blodgett, Tom Kerwick and many more.
Since these discussions can become very sophisticated, there is also a more general approach (see video): According to present research, there are around 10 billion Earth-like planets alone in our galaxy, the Milky Way. Intelligent life might send radio waves, because they are extremely long lasting, though we have not received any (“Fermi paradox”). Theory postulates that there could be a ”great filter“, something that wipes out intelligent civilizations at a rather early state of their technical development. Let that sink in.
All technical civilizations would start to build particle smashers to find out how the universe works, to get as close as possible to the big bang and to hunt for the smallest particle at bigger and bigger machines. But maybe there is a very unexpected effect lurking at a certain threshold that nobody would ever think of and that theory does not provide. Indeed, this could be a logical candidate for the “great filter”, an explanation for the Fermi paradox. If it was, a disastrous big bang machine eventually is not that big at all. Because if civilizations were to construct a collider of epic dimensions, a lack of resources would have stopped them in most cases.
Finally, the CERN member states will have to decide on the budget and the future course.
The political question behind is: How far are the ordinary citizens paying for that willing to go?
LHC-Critique / LHC-Kritik
Network to discuss the risks at experimental subnuclear particle accelerators
LHC-Critique[at]gmx.com
Particle collider safety newsgroup at Facebook:

Researchers at the George Washington University have taken a major step toward reaching one of the most sought-after goals in physics: room temperature superconductivity.
Superconductivity is the lack of electrical resistance and is observed in many materials when they are cooled below a critical temperature. Until now, superconducting materials were thought to have to cool to very low temperatures (minus 180 degrees Celsius or minus 292 degrees Fahrenheit), which limited their application. Since electrical resistance makes a system inefficient, eliminating some of this resistance by utilizing room temperature superconductors would allow for more efficient generation and use of electricity, enhanced energy transmission around the world and more powerful computing systems.
“Superconductivity is perhaps one of the last great frontiers of scientific discovery that can transcend to everyday technological applications,” Maddury Somayazulu, an associate research professor at the GW School of Engineering and Applied Science, said. “Room temperature superconductivity has been the proverbial ‘holy grail’ waiting to be found, and achieving it—albeit at 2 million atmospheres—is a paradigm-changing moment in the history of science.”
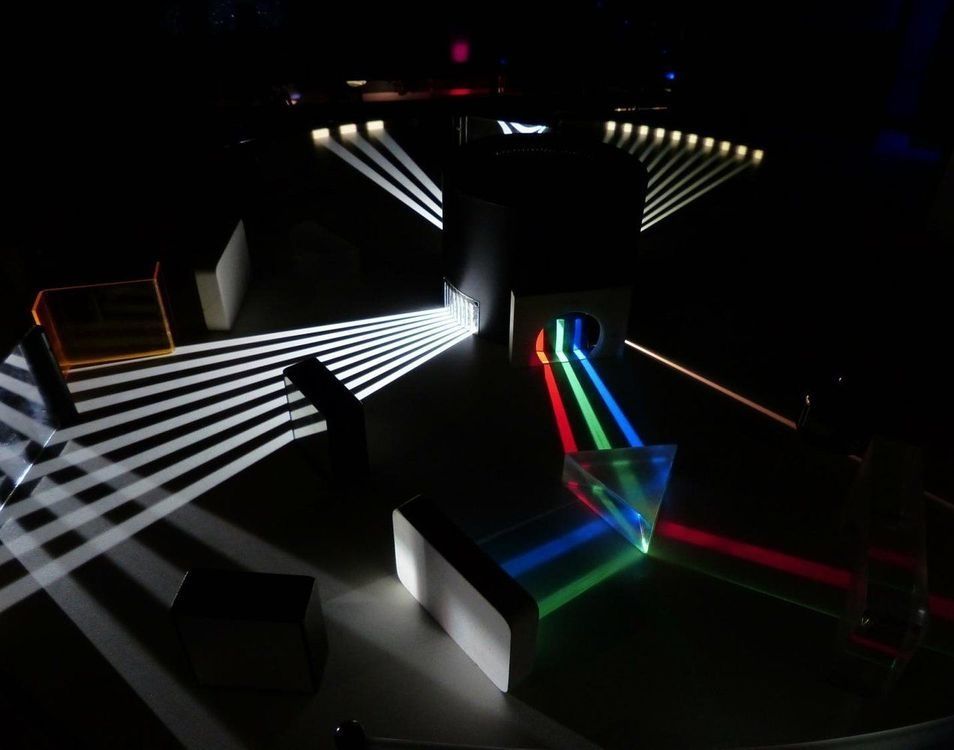


Physicists have built a ring in which pulses of light whip circles around each other and the normal rules that govern light’s behavior no longer apply.
Under normal circumstances, light displays certain kids of physical symmetry. First, if you were to play a tape of light’s behavior forward and then backward, you would see it behave in the same way moving in both directions in time. This is called time-reversal symmetry. And second, light, which can move through the world as a wave, has what is called polarization: how it oscillates relative to the motion of the wave. That polarization usually stays the same, providing another type of symmetry.
But inside this ring-shaped device, light both loses its time-reversal symmetry and changes its polarization. Inside the ring, light waves turn circles and resonate with one another, producing effects that don’t normally exist in the outside world. [The 10 Most Outrageous Military Experiments].
