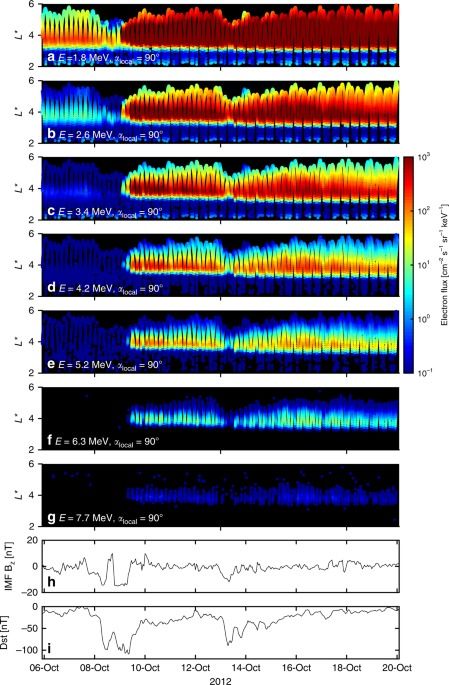
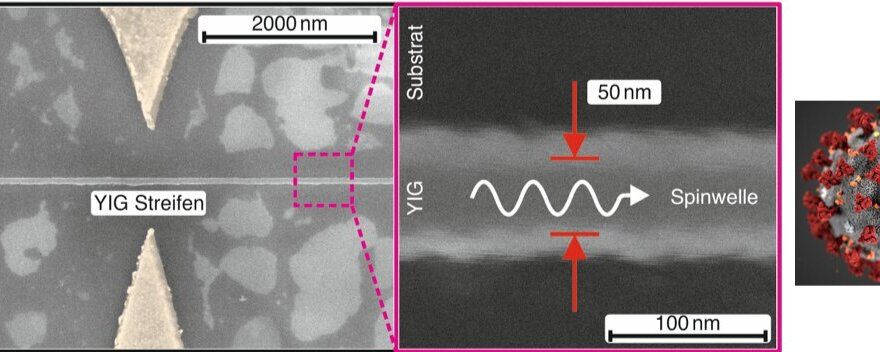
Figures 4 and 5 effectively demonstrate that local acceleration is capable of heating electrons to ~7 MeV as the phase space density profiles show signatures of local acceleration during both of the geomagnetic storms considered. The phase space density enhancements for higher energies followed the enhancements at lower energies. In Supplementary Note 8, additional analysis establishes that locally growing peaks are also observed for lower values of K, corresponding to radiation belt electrons confined closer to the equator. Furthermore, as the values of K and L* are dependent on the magnetic field model chosen, results using an additional two field models are also presented (see Supplementary Note 9) and, once again, growing peaks are observed in the radial phase space density profile. Our results demonstrate that local acceleration had a significant effect on radiation belt particles during both of the storms in October 2012, acting on electrons up to 7 MeV. In the radiation belt region, local acceleration introduces radial gradients in phase space density and so is always accompanied by both outwards and inwards radial diffusion. Locally heating electrons to ~7 MeV provides a very high energy “source population” for inwards radial diffusion and could therefore help explain the occurrence of ~10 MeV electrons in April–May 201716.
A recent study by Zhao et al.15, considered the acceleration of ultra-relativistic electrons via a statistical analysis of events during the Van Allen Probe era. The results were consistent with a two-step acceleration process, where locally heated electrons at large L*, beyond the Van Allen Probes apogee, are radially diffused inwards to reach energies of 7 MeV in the outer radiation belt. While the combination of local acceleration and radial diffusion produces 7 MeV enhancements15, the Van Allen Probe observations for the two storms shown in this study demonstrate that local acceleration can also act directly up to 7 MeV energies. The local energization mechanism responsible for generating 7 MeV electrons in the heart of the outer radiation belt, be that acceleration by chorus waves or some other process, presents an interesting focus for future research. Longer term analysis and statistical studies can be used to better understand the conditions leading to acceleration. Datasets formed via data-assimilation techniques may be useful for this purpose. Long term observations of the ultra-relativistic component of Earth’s radiation belts demonstrate that ≥7 MeV electrons are a relatively rare phenomenon, occurring far less frequently than enhancements at 1 or 2 MeV1. It therefore follows that the circumstances leading to multi-MeV enhancements could be unusual, requiring specific conditions. Our results highlight that wave-particle interactions can provide the primary acceleration mechanism for electrons up to ultra-relativistic energies, a finding applicable to magnetized plasmas throughout the solar system.