(Phys.org)—Many quantum technologies rely on quantum states that violate local realism, which means that they either violate locality (such as when entangled particles influence each other from far away) or realism (the assumption that quantum states have well-defined properties, independent of measurement), or possibly both. Violation of local realism is one of the many counterintuitive, yet experimentally supported, characteristics of the quantum world.
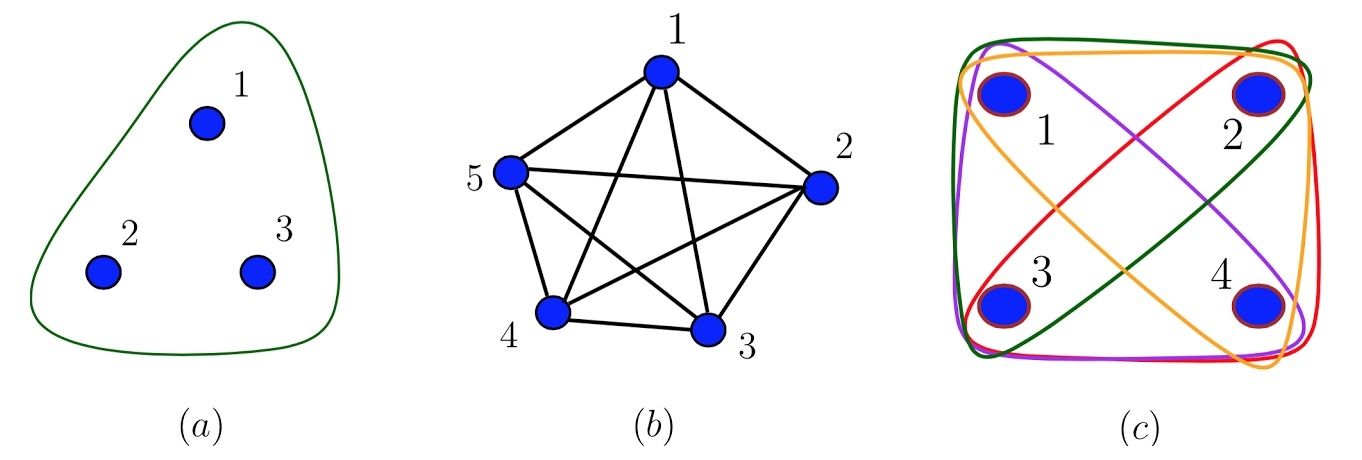
Determining whether or not multiparticle quantum states violate local realism can be challenging. Now in a new paper, physicists have shown that a large family of multiparticle quantum states called hypergraph states violates local realism in many ways. The results suggest that these states may serve as useful resources for quantum technologies, such as quantum computers and detecting gravitational waves.
The physicists, Mariami Gachechiladze, Costantino Budroni, and Otfried Gühne at the University of Siegen in Germany, have published their paper on the quantum hypergraph states in a recent issue of Physical Review Letters.