Quantum mechanics generally refers to the wave-like properties of things that are commonly considered to be particles, such as electrons. This article discusses evidence of a quantum mechanical switching function that is performed by strictly biological structures—ferritin protein layers that are found in cells including neural tissue.
Many scientists are investigating quantum biology, which is the application of quantum mechanics to investigate biological functions. It has recently been used to answer a number of previously unanswered questions, such as the mechanisms behind photosynthesis and the way birds can perceive magnetic fields. These quantum biological effects generally involve electrons hopping or tunneling over distances of several nanometers, behavior that is incompatible with particles but which makes sense with waves.
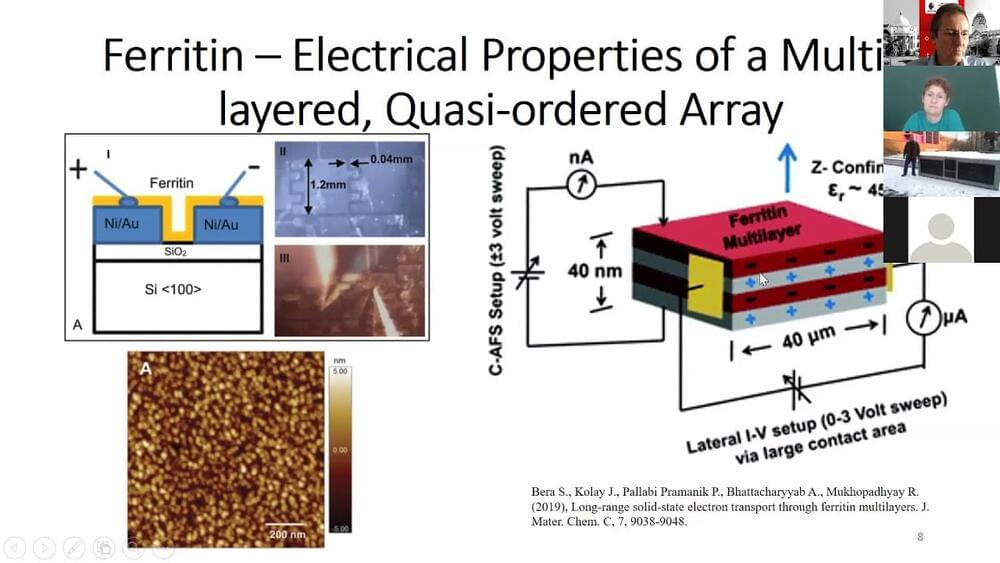
Ferritin is a spherical iron storage protein that is found in plants and animals. Early studies of ferritin to look for quantum mechanical effects were conducted at cryogenic temperatures, because it was thought that biological structures were too “warm and wet” to exhibit such effects. Those studies were somewhat inconclusive. But when ferritin was subsequently electrically tested at room temperature, it was discovered that electron tunneling was occurring.