Now scientists at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at Cern think they may have seen another particle, detected as a peak at a certain energy in the data, although the finding is yet to be confirmed. Again there’s a lot of excitement among particle physicists, but this time it is mixed with a sense of anxiety. Unlike the Higgs particle, which confirmed our understanding of physical reality, this new particle seems to threaten it.
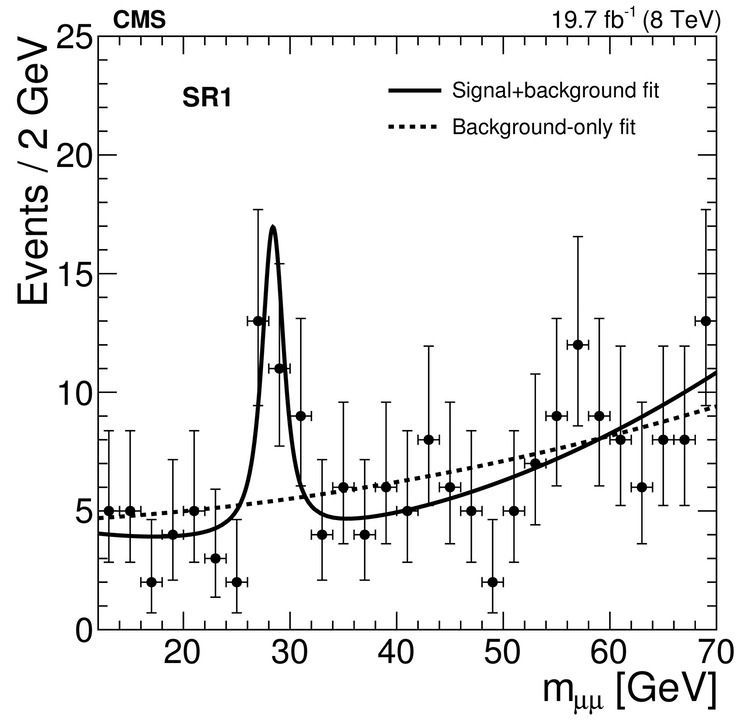
The new result – consisting of a mysterious bump in the data at 28 GeV (a unit of energy) – has been published as a preprint on ArXiv. It is not yet in a peer-reviewed journal – but that’s not a big issue. The LHC collaborations have very tight internal review procedures, and we can be confident that the authors have done the sums correctly when they report a “4.2 standard deviation significance”. That means that the probability of getting a peak this big by chance – created by random noise in the data rather than a real particle – is only 0.0013%. That’s tiny – 13 in a million. So it seems like it must a real event rather than random noise – but nobody’s opening the champagne yet.