Canadian reactor designer StarCore Nuclear has applied to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) to begin the vendor design review process for its Generation IV high temperature gas reactor (HTGR).
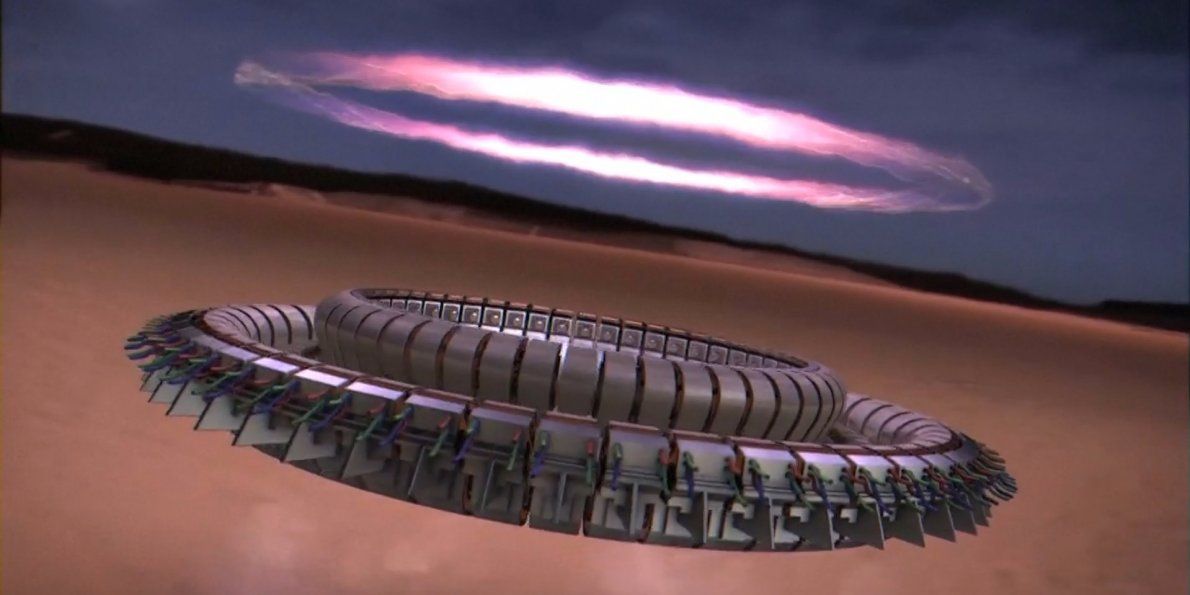
Montréal-based StarCore, founded in 2008, is focused on developing small modular reactors (SMRs) to provide power and potable water to remote communities in Canada. Its standard HTGR unit would produce 20 MWe (36 MWth), expandable to 100 MWe, from a unit small enough to be delivered by truck. The helium-cooled reactor uses Triso fuel — spherical particles of uranium fuel coated by carbon which effectively gives each tiny particle its own primary containment system — manufactured by BWXT Technologies. Each reactor would require refuelling at five-yearly intervals.
StarCore describes its reactor as “inherently safe”, with a steep negative thermal coefficient which eliminates the possibility of a core meltdown. The use of helium — which does not become radioactive — as a coolant means that any loss of coolant would be “inconsequential”, the company says. The reactors would be embedded 50 metres underground in concrete silos sealed with ten-tonne caps.
Read more