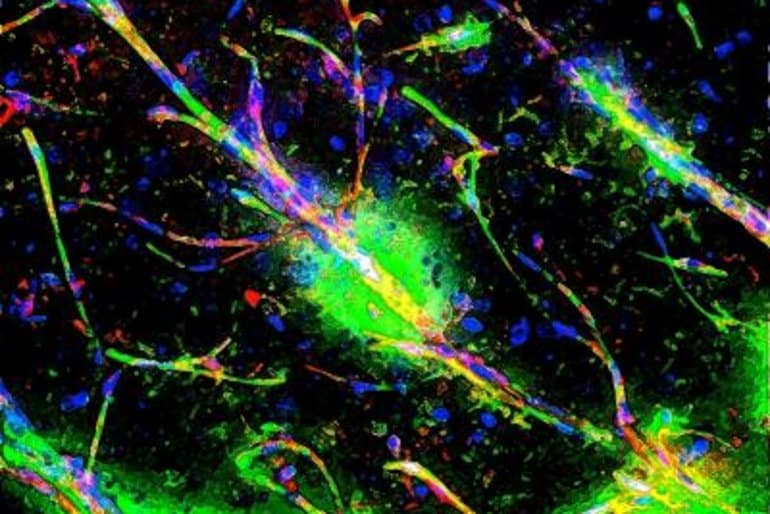
The work adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that schizophrenia and certain other neuropsychiatric conditions may be in part neuroinflammatory disorders.
Summary: People with schizophrenia and other neuropsychiatric disorders may have a more permissive blood-brain barrier which allows the immune system to become more actively involved in the central nervous system. The resulting inflammation may contribute to the clinical manifestation of psychosis-like symptoms.
Source: University of Pennsylvania
Like a stern bodyguard for the central nervous sytem, the blood-brain barrier keeps out anything that could lead to disease and dangerous inflammation–at least when all is functioning normally.
That may not be the case in people with schizophrenia and other mental disorders, suggest new findings from a team led by researchers from the School of Veterinary Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP).