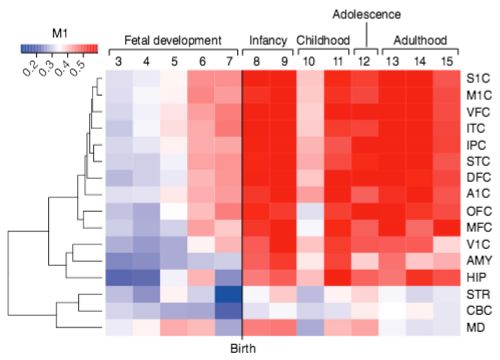
Color-coded heatmap of gradient of expression of the M1 gene network, spanning fetal development to late adulthood and expressed in distinct cortical regions (listed on right, such as primary somatosensory cortex, S1C). Most of the genes in this network express in cortical regions (indicated by red), except for the V1C (primary visual cortex), STR (striatum), CBC (cerebellar cortex), and MD (mediodorsal nucleus of thalamus) brain areas. (credit: Michael R. Johnson et al./Nature Neuroscience)
Scientists from Imperial College London have identified two clusters (“gene networks”) of genes that are linked to human intelligence. Called M1 and M3, these gene networks appear to influence cognitive function, which includes memory, attention, processing speed and reasoning.
Importantly, the scientists have discovered that these two networks are likely to be under the control of master regulator switches. The researcher want to identify those switches and see if they can manipulate them, and ultimately find out if this knowledge of gene networks could allow for boosting cognitive function.
Read more