Just Amazing
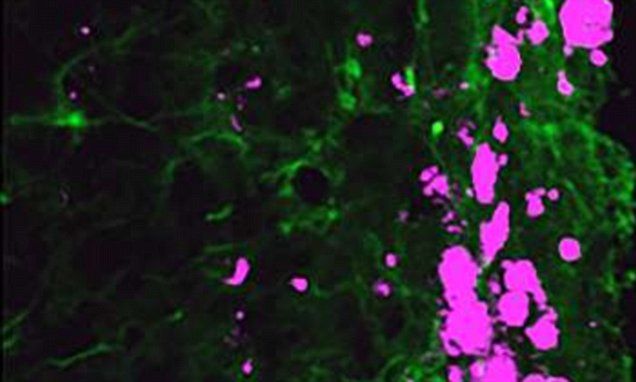
Ralph Mobbs, a neurosurgeon at the Prince of Wales Hospital in Sydney, made medical history in late 2015 when he successfully replaced two vertebrae with custom made prosthesis. The patient, in his 60s, suffered from Chordoma, a particularly nasty form of cancer that had formed on his top two vertebrae and threatened to cinch off his spinal cord as it grew. That would have left him a quadriplegic. Complicating matters, those top two vertebrae are what allow you to turn and tilt your head, so it’s not like doctors can easily fashion a replacement out of bone grafted from another part of the patient’s body. They have to fit perfectly and that’s where the 3D printers come in.
Mobbs worked with Anatomics, an Australian medical device manufacturer, to craft perfect replicas of the patient’s top two vertebrae out of titanium. This is the first time that these two particular neck bones have been printed and installed. “To be able to get the printed implant that you know will fit perfectly because you’ve already done the operation on a model … It was just a pure delight,” Mobbs told Mashable Australia. “It was as if someone had switched on a light and said ‘crikey, if this isn’t the future, well then I don’t know what is’.”
The surgery itself was no small feat. The 15-hour procedure is fraught with peril as the medical team operates within inches of the top of the spinal cord as well as the brainstem and numerous major arteries. “The surgery that we’re doing today is a particularly complicated and long and difficult surgery. It involves exposure at the top of the neck where the neck and the head meets,” Mobbs told ABC 7.30. “It’s essentially disattaching the patient’s head from his neck and taking the tumour out and reattaching his head back onto his neck.” Thankfully, the surgery was a success. Mobbs was able to remove the tumor and implant the prosthetic.