New technique may allow more precise and less invasive study of the brain.
Originally published:
Mar 7 2016 — 11:00am.

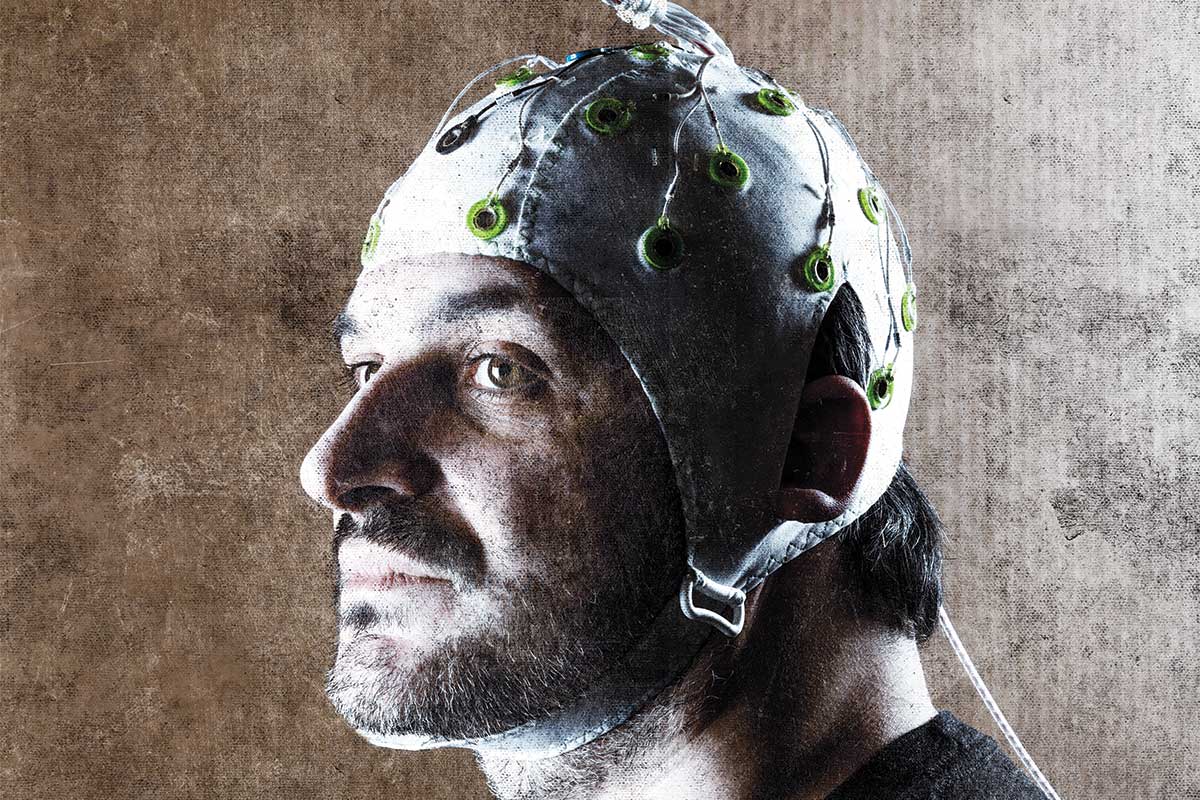
Brain-to-brain communication is becoming a reality, says Andrea Stocco, who sees a future where minds meet to share ideas.
You are working on brain-to-brain communication. Can one person’s thoughts ever truly be experienced by another person?
Each brain is different. And while differences in anatomy are relatively easy to account for, differences in function are difficult to characterise. And then we have differences in experience – my idea of flying could be completely unlike your idea of flying, for example. When you think about flying, a bunch of associated experiences come into your mind, competing for your attention. We somehow need to strip away the individual differences to grasp the basic, shared factors.
But it seems possible. Other researchers have been able to use information collected from a group of people to make surprisingly successful, if basic, predictions about what another individual is thinking.
What do you need to transmit information between brains?
The idea is to record one person’s brain activity using a non-invasive device such as an EEG, which involves wearing a cap of electrodes. A computer program filters out what is thought to be the relevant brain activity, and this is recreated in another person using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) – a non-invasive technique that induces an electrical current in their brain.
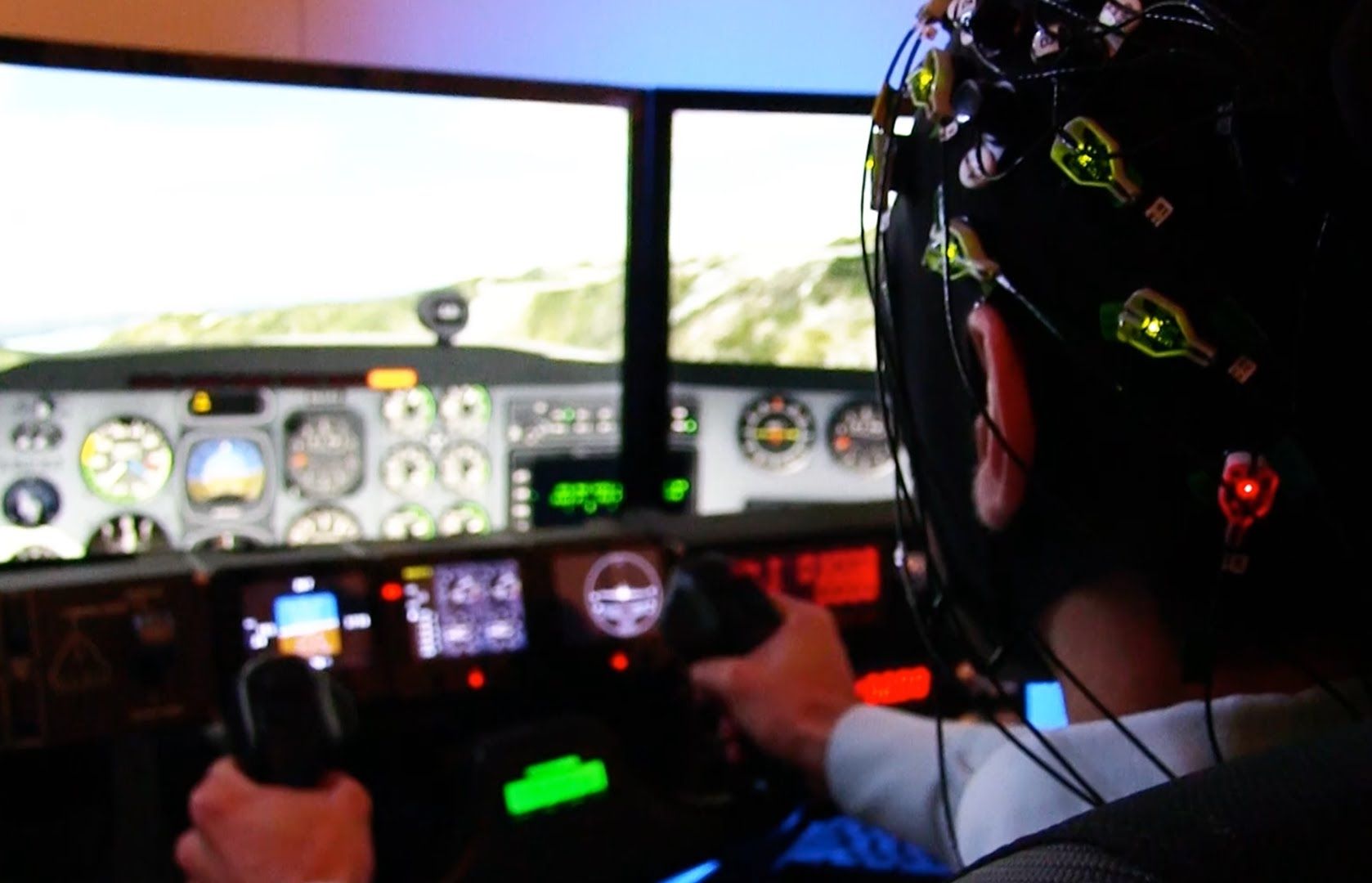

A cognitive neuroscientist and his team at HRL Laboratories in Malibu, California, seem to have achieved the impossible.
According to a press release, the team “measured the brain activity patterns of six commercial and military pilots, and then transmitted these patterns into novice subjects as they learned to pilot an airplane in a realistic flight simulator.”


He pointed out that Horizon Robotics will finish designing its first AI chip for smart home appliances by June and make it commercially available by early 2017.
Mainland Chinese start-up Horizon Robotics, founded by the former head of online search giant Baidu’s Institute of Deep Learning, claims it is on pace to bring chips with built-in artificial intelligence (AI) technology to market.
“General processors are too slow for AI functions. A dedicated chip will dramatically increase the speed of these functions,” Yu Kai, the founder and chief executive of Horizon Robotics told the South China Morning Post.
Founded in Beijing in July, Horizon Robotics is developing chips and software that attempt to mimic how the human brain solves abstract tasks, such as voice and image recognition, that are difficult for regular computer programmes. It also makes sensors for smart devices.




https://youtube.com/watch?v=L2O58QfObus
At this rate, we may see Ray Kurzweil’s vision of connected humans to the cloud and full singularity before 30 years.
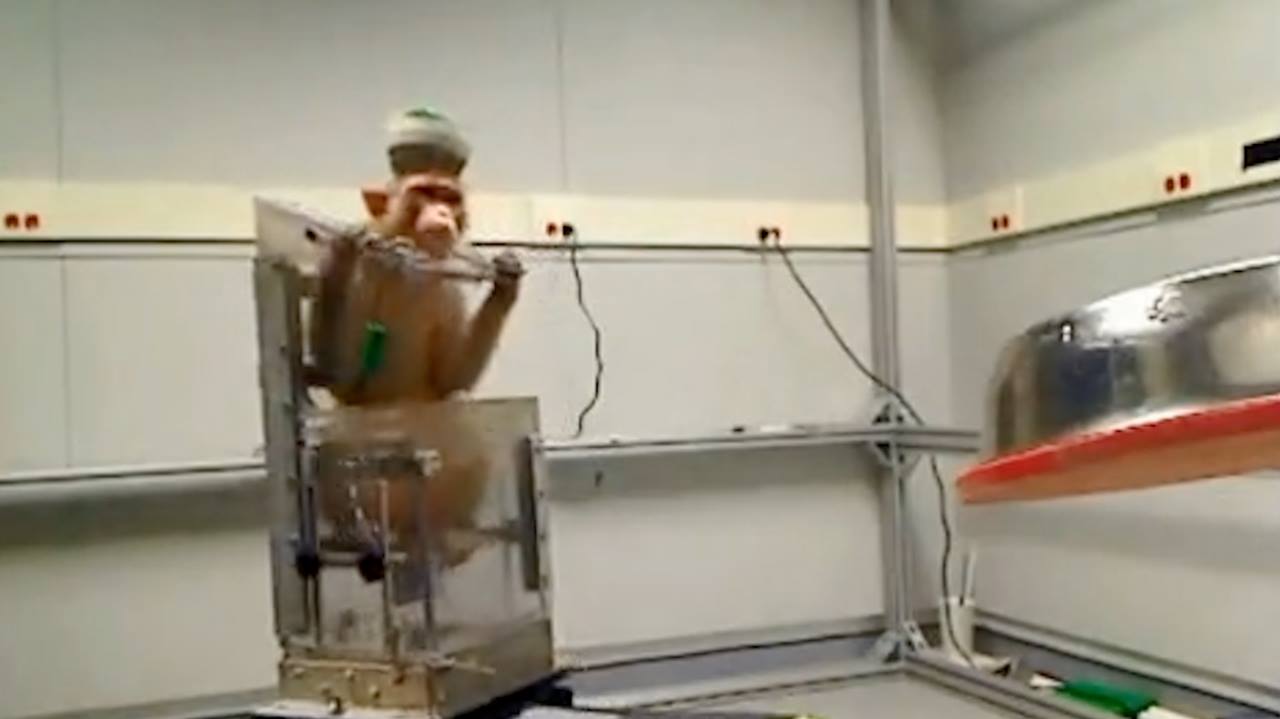
Duke University scientists have given a pair of monkeys the ability to drive a wheelchair with their thoughts alone. The work is described in a paper recently published in the journal Scientific Reports and adds to a growing body of work in brain-machine interfaces aiming to return some freedom to the severely disabled.
Duke neuroscientist Miguel Nicolelis and his team first began experimenting back in 2012, when they implanted hundreds of microfibers as thin as a human hair in the brains of two rhesus macaque monkeys. The fibers recorded cortical activity associated with “whole-body movement” and sent the signals to a computer.
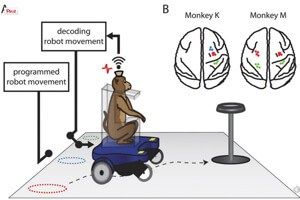 To start, the monkeys sat in wheelchairs that were moved along various paths toward a bowl of grapes across the room. Their brain activity was read and decoded by a computer program and then associated with wheelchair commands.
To start, the monkeys sat in wheelchairs that were moved along various paths toward a bowl of grapes across the room. Their brain activity was read and decoded by a computer program and then associated with wheelchair commands.