Scientists create 3-dimensional brain spheroids—small, spherical, laboratory-grown human brain tissue.
- By Sam Rose on September 25, 2018

Scientists create 3-dimensional brain spheroids—small, spherical, laboratory-grown human brain tissue.
DeepMind is providing more research to show how neuroscience can inspire more sophisticated AI.
There’s a cognitive quirk humans have that seems deceptively elementary. For example: every morning, you see a man in his 30s walking a boisterous collie. Then one day, a white-haired lady with striking resemblance comes down the street with the same dog.
Subconsciously we immediately make a series of deductions: the man and woman might be from the same household. The lady may be the man’s mother, or some other close relative. Perhaps she’s taking over his role because he’s sick, or busy. We weave an intricate story of those strangers, pulling material from our memories to make it coherent.
This ability—to link one past memory with another—is nothing but pure genius, and scientists don’t yet understand how we do it. It’s not just an academic curiosity: our ability to integrate multiple memories is the first cognitive step that lets us gain new insight into experiences, and generalize patterns across those encounters. Without this step, we’d forever live in a disjointed world.

Physicists face the same hard problem as neuroscientists do: the problem of bridging objective description and subjective experience. Physics has encountered consciousness. Quantum theory says an object remains in a superposition of possibilities until observed. We can consider a quantum state as being about our knowledge rather than a direct description of physical reality. The physics of information just may be that bridging of quantum-to-digital reality of subjective experience. We are now at the historic juncture when quantum computing could reveal quantum information processing underpinnings of subjectivity. Quantum mechanics is a spectacularly successful theory of fundamental physics that allows us to make probabilistic predictions derived from its mathematical formalism, but the theory doesn’t tell us precisely how these probabilities should be interpreted in regards to phenomenology, i.e. our experiential reality. There are basically three main interpretive camps within quantum mechanics from which stem at least a dozen further interpretations.
By Alex Vikoulov.
“A quantum possibility is more real than a classical possibility, but less real than a classical reality.” –Boris Tsirelson.
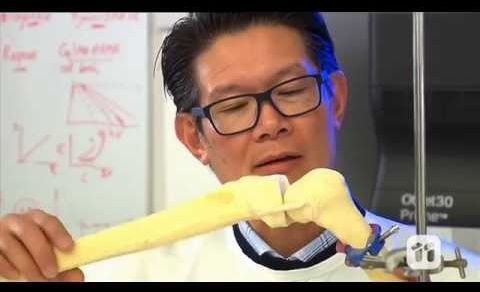
Highly specialized cartilage is characteristically avascular and non-neural in composition with low cell numbers in an aliphatic environment. Despite its apparent simplicity, bioengineering regenerative hyaline cartilage in a form effective for implantation remains challenging in musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Existing surgical techniques including autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) and matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI) are considered superior to self-repair induction techniques. However, both MACI and ACI are complex, multistage procedures that require a double operation; first for surgical excision of native cartilage, followed by expansion of adult chondrocytes in vitro prior to implantation by a second operation.
Regenerating robust articular hyaline-like cartilage is a key priority in musculoskeletal tissue engineering to prevent cost-intensive degenerative osteoarthritis that limits the quality of life in global healthcare. Integrating mesenchymal stem cells and 3D printing technologies has shown significant promise in bone tissue engineering– although the key challenge remains in transferring the bench-based technology to the operating room for real-time applications. To tackle this, a team of Australian orthopedic surgeons and bioengineers collaboratively proposed an in situ additive manufacturing technique for effective cartilage regeneration. The handheld engineered extrusion device known as the BioPen offers an advanced, co-axial extrusion strategy to deposit cells embedded in a hydrogel material within a surgical setting.
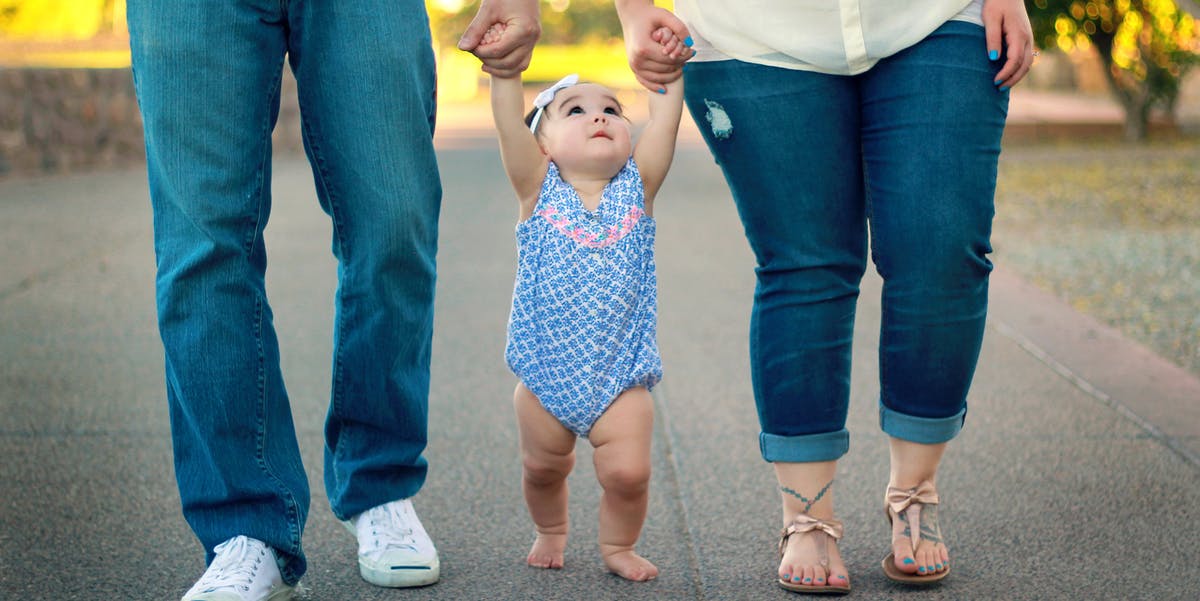

Babies notice more than we think they do, and the things they notice can tell us a lot about the kind of people they’ll grow up to be. Previously, scientists determined that toddlers younger than two years old exhibit signs of altruism — selfless concern for the well-being of others — that in turn predicted what they’d be like in the future. Now, new research in the journal PLOS Biology suggests that these signs emerge even earlier than we thought. The way a baby acts before it even turns one year old can reliably predict whether it will display altruistic behavior by the time it’s 14 months old.
Research in this field is an attempt to understand whether it’s really in our nature to be altruistic, and why. Acting selflessly, after all, is not immediately beneficial, at least from a purely evolutionary standpoint. And yet even our non-human primate relatives will sacrifice themselves for their neighbors, leading to the understanding that the behavior is somehow conserved.
In the new paper, published Tuesday, a team of psychologists and cognitive scientists show that a 7-month-old baby that pays close attention to the face of someone who is afraid is more likely to display prosocial behavior by the time they’re 14 months old.
Some patterns of electrical activity generated by the brain during sleep are inherited, according to a study of teenage twins published in JNeurosci. Pinpointing the relative contributions of biology and experience to sleep neurophysiology could inform therapies for numerous psychiatric disorders in which alterations in brain activity during sleep can be detected.
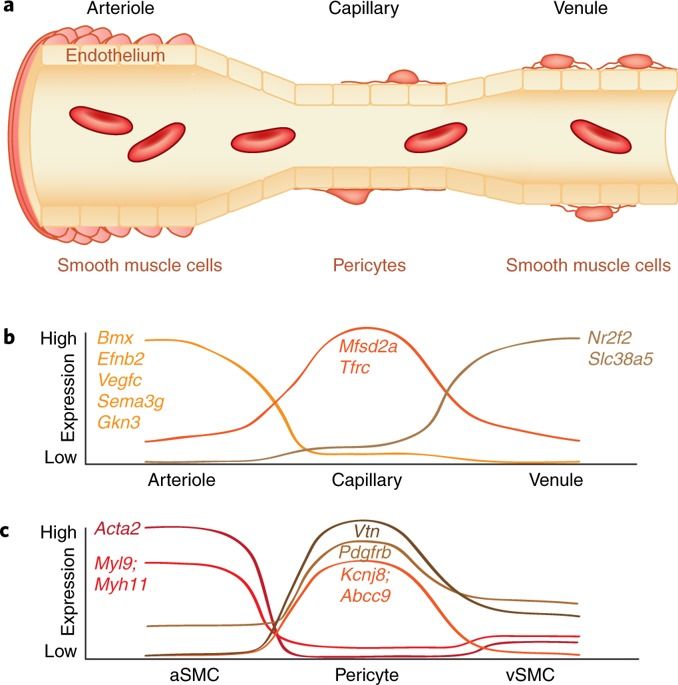
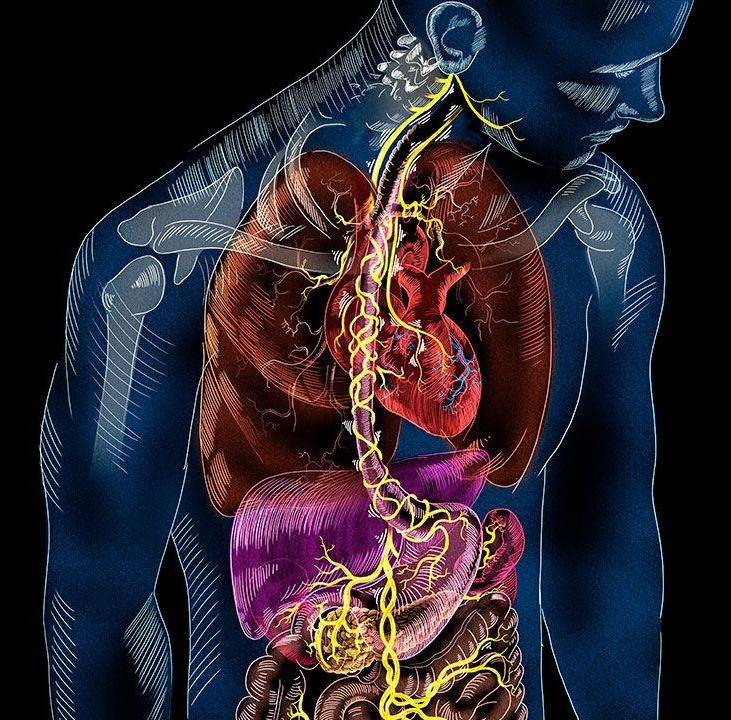
Adequate supply of blood and structural and functional integrity of blood vessels are key to normal brain functioning. On the other hand, cerebral blood flow shortfalls and blood–brain barrier dysfunction are early findings in neurodegenerative disorders in humans and animal models. Here we first examine molecular definition of cerebral blood vessels, as well as pathways regulating cerebral blood flow and blood–brain barrier integrity. Then we examine the role of cerebral blood flow and blood–brain barrier in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple sclerosis. We focus on Alzheimer’s disease as a platform of our analysis because more is known about neurovascular dysfunction in this disease than in other neurodegenerative disorders. Finally, we propose a hypothetical model of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers to include brain vasculature as a factor contributing to the disease onset and progression, and we suggest a common pathway linking brain vascular contributions to neurodegeneration in multiple neurodegenerative disorders.

Five years after he was paralysed in a snowmobile accident, a man in the US has learned to walk again aided by an electrical implant, in a potential breakthrough for spinal injury sufferers.
A team of doctors at the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota say the man, using a front-wheeled walker, was able to cover the equivalent of the length of a football pitch, issuing commands from his brain to transfer weight and maintain balance—all previously thought impossible for paralysed patients.
The man, now 29, severed his spinal cord in the middle of his back when he crashed his snowmobile in 2013. He is completely paralysed from the waist down, and cannot move or feel anything below the middle of his torso.
Apparently, amyloid beta drives its own production in a vicious circle.
In a study at King’s College London, scientists have shown that a vicious circle in which the ill-famed amyloid-beta protein stimulates its own production might be a key factor in the etiology of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease; furthermore, a drug known as fasudil seems to be effective against amyloid-beta in a mice model of the disease [1].
Study abstract
In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the canonical Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) is induced by β-amyloid (Aβ) and shifts the balance from canonical towards non-canonical Wnt signalling. Canonical (Wnt-β-catenin) signalling promotes synapse stability, while non-canonical (Wnt-PCP) signalling favours synapse retraction; thus Aβ-driven synapse loss is mediated by Dkk1. Here we show that the Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) co-activates both arms of Wnt signalling through physical interactions with Wnt co-receptors LRP6 and Vangl2, to bi-directionally modulate synapse stability. Furthermore, activation of non-canonical Wnt signalling enhances Aβ production, while activation of canonical signalling suppresses Aβ production. Together, these findings identify a pathogenic-positive feedback loop in which Aβ induces Dkk1 expression, thereby activating non-canonical Wnt signalling to promote synapse loss and drive further Aβ production.