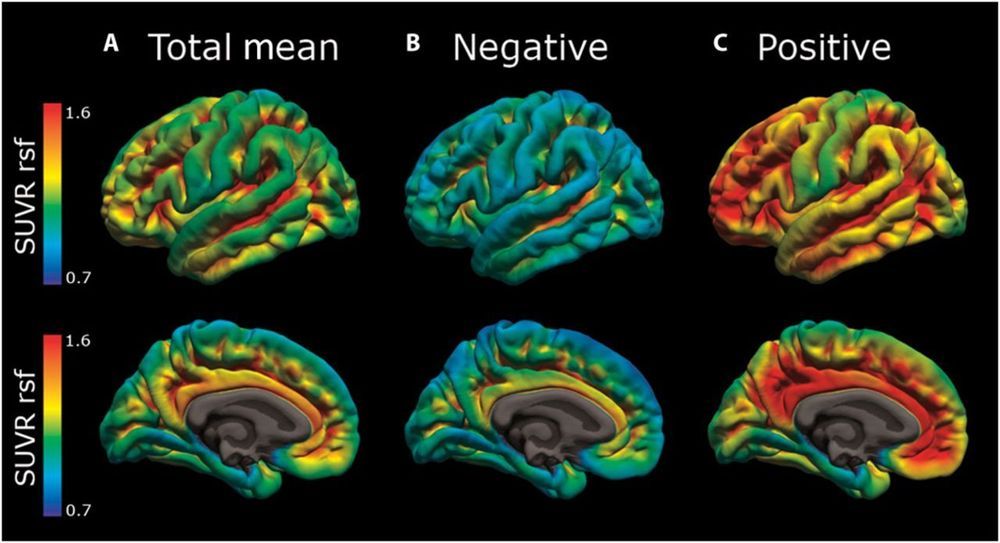
In patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and tau protein tangles accumulate in the brain long before the appearance of clinical symptoms. Early intervention is critical for slowing neurodegeneration and disease progression. Therefore, reliable markers of early AD are needed. Lucey et al. analyzed sleep patterns in aging cognitively normal subjects and showed that non–rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep negatively correlated with tau pathology and Aβ deposition in several brain areas. The results show that alterations in NREM sleep may be an early indicator of AD pathology and suggest that noninvasive sleep analysis might be useful for monitoring patients at risk for developing AD.
In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), deposition of insoluble amyloid-β (Aβ) is followed by intracellular aggregation of tau in the neocortex and subsequent neuronal cell loss, synaptic loss, brain atrophy, and cognitive impairment. By the time even the earliest clinical symptoms are detectable, Aβ accumulation is close to reaching its peak and neocortical tau pathology is frequently already present. The period in which AD pathology is accumulating in the absence of cognitive symptoms represents a clinically relevant time window for therapeutic intervention. Sleep is increasingly recognized as a potential marker for AD pathology and future risk of cognitive impairment. Previous studies in animal models and humans have associated decreased non–rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep slow wave activity (SWA) with Aβ deposition. In this study, we analyzed cognitive performance, brain imaging, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) AD biomarkers in participants enrolled in longitudinal studies of aging.