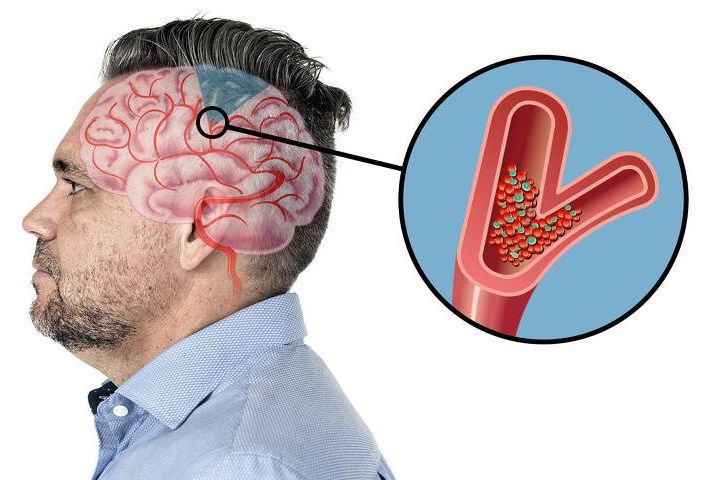
Klotho, named after one of the Fates of Greek mythology, is the queen of anti-aging proteins. There are no close contenders at this time. Klotho gene therapy, like the one offered by Integrated Health Systems, has tremendous benefits. While it is produced primarily in the kidneys and brain, its soluble form circulates throughout the body. Many of the investigations so far have been done nephrologists interested in its prominent role in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), yet over the last decade its multifaceted role in the aging process has become a topic of intense research.
Klotho deficient mice show premature aging in multiple organs.
Inducing KL overexpression with a viral vector, like AAV, not only reverses this premature aging, but also enhances resistance to oxidative and ischemic damage. More impressive, KL outright extends the lifespans of mice, likely be inhibiting IGF and insulin signalling. Dubbed an “aging suppressor gene,” it can yield results similar to caloric restriction – what is, at this time, the most tried and true method of extending the lifespans of a variety of model organisms.