#13 in our top science stories of 2019.



https://youtube.com/watch?v=Tnr4EyTegcs
In his new book, The Deep History of Ourselves: The Four-Billion-Year Story of How We Got Our Conscious Brains, neuroscientist Joseph Ledoux assigns himself the simple tasks of explaining how consciousness developed and redefining how we create and experience emotions.
Obviously, I’m being facetious. There’s nothing simple about these tasks, yet in Ledoux’s capable hands the reader is led, step by step, through the past four billion years of life on this planet. Consciousness, a phenomenon responsible for your ability to read and understand these words (as well as much, much more), often feels like a given, yet that’s only because human life is short and evolution is so very long.
Ledoux writes about history splendidly. In his last book, Anxious (which I write about here and here), he investigates the development of nervous systems, entertaining the prospect that anxiety and fear are not innate physiological states but rather assembled experiences that can be sorted through and overcome. Throughout the book he overturns common assumptions about behavior and cognition.



Happy New year everyone! We wanted to give you an inside look as to what happens on our Dr. Joe live calls that take place once a month. Here’s a moment from our last Dr. Joe live call.
Some of the subjects Dr. Joe may address: latest scientific discoveries; health and wealth; love and relationships; neuroscience and epigenetics; happiness and vitality; the quantum model of reality; how you can make great and lasting changes in yourself and your life!
With his vast experience and deepening knowledge of how each one of us can unlock unlimited abilities and transform our lives for the better, these classes offer you a unique opportunity to continually learn and interact with Dr. Joe! If you want to take it a step further in the work, Dr. Joe live is a great way to deepen your understanding, keep you plugged into the community and interact with Dr. Joe personally..

A group of scientists from the Russian Academy of Sciences (ICG SB RAS) and the TSU Biological Institute has established a path through which nanoparticles of viruses and organic and inorganic substances from the environment enter the brain. Additionally, the researchers report a simple and inexpensive way to block their entry. The data obtained by the project could play a large role in medicine and pharmaceuticals, where nanoparticles are increasingly used for the diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases.
“There are a large number of nanoparticles of a wide variety of chemical elements and their compounds in the environment, ranging from harmless to toxic, for example, heavy metal oxides,” says Mikhail Moshkin, director of the Center for Laboratory Animal Genetic Resources of the ICG SB RAS. “Scientists have accumulated data that indicate the adverse effect of nanoparticles, for example, people who live closer than 50 meters to large highways may develop neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and others) due to the accumulation of nanosized particles in the brain.”
The researchers sought to determine how nanoparticles enter the brain. They cannot penetrate through the lungs and blood vessels because the blood-brain barrier blocks them from the brain. Experiments conducted on rodents helped calculate the trajectory of the movement of nanoparticles.
Do you ever wish you could just turn on the happy chemicals in your brain? Imagine how much easier it would make getting out of bed each morning, getting even the most tedious parts of your job done, and finding the energy to consistently show up as your best self for the people you care about the most. But is it really possible – never mind advisable – to try and train our brains for more happiness?
“The quest for good feelings is nature’s survival engine,” explained Professor Loretta Breuning, founder of the Inner Mammal Institute, when I interviewed her recently. “For example, animals seek food to relieve the bad feeling of hunger. They seek warmth to relieve the bad feeling of cold. And happy chemicals start flowing before a mammal even eats or warms up because the brain turns them on as soon as it sees a way to meet a need.”
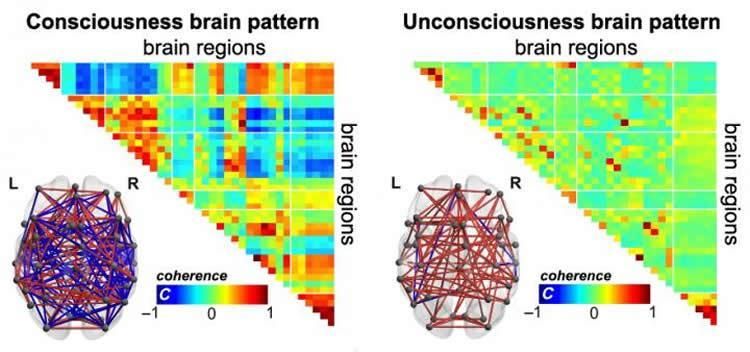
Summary: Researchers say human consciousness is supported by dynamic, complex patterns of brain signal coordination.
Source: AAAS.
Amid longstanding difficulties distinguishing consciousness in humans in unconscious states, scientists report fMRI-based evidence of distinct patterns of brain activity they say can differentiate between consciousness or unconsciousness. Detecting these patterns in real-time could allow for externally induced manipulations that noninvasively restore consciousness.

UConn engineers have designed a non-toxic, biodegradable device that can help medication move from blood vessels into brain tissues —a route traditionally blocked by the body’s defense mechanisms. They describe their invention in the 23 December issue of PNAS.
Blood vessels in the brain are lined by cells fitted together tightly, forming a so-called blood-brain barrier, which walls off bacteria and toxins from the brain itself. But that blood-brain barrier also blocks medication for brain diseases such as cancer.
“A safe and effective way to open that barrier is ultrasound,” says Thanh Nguyen, a biomedical engineer at UConn. Ultrasonic waves, focused in the right place, can vibrate the cells lining blood vessels enough to open transient cracks in the blood-brain barrier large enough for medication to slip through. But the current ultrasound technology to do this requires multiple ultrasound sources arrayed around a person’s skull, and then using an MRI machine to guide the person operating the ultrasounds to focus the waves in just the right place. It’s bulky, difficult, and expensive to do every time a person needs a dose of medication.
