Share your videos with friends, family, and the world.

Share your videos with friends, family, and the world.

Summary: A ten-minute run increases activation of the bilateral prefrontal cortex, improving mood and cognitive function.
Source: University of Tsukuba
Running may be a useful activity to undertake for better mental health. University of Tsukuba researchers have found that only ten minutes of moderate-intensity running increases local blood flow to the various loci in the bilateral prefrontal cortex —the part of the brain that plays an important role in controlling mood and executive functions.
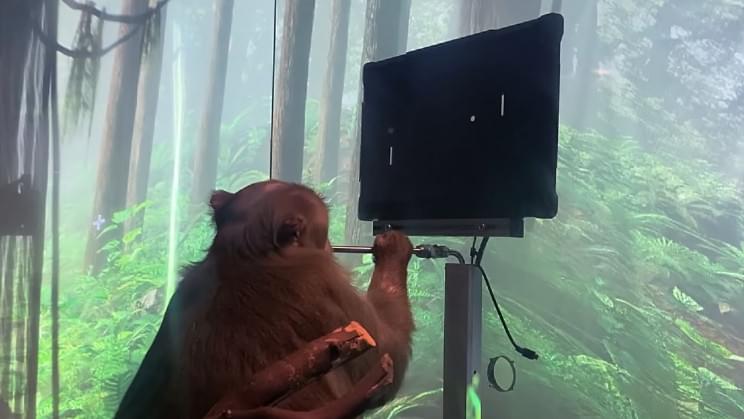

Are we there already?
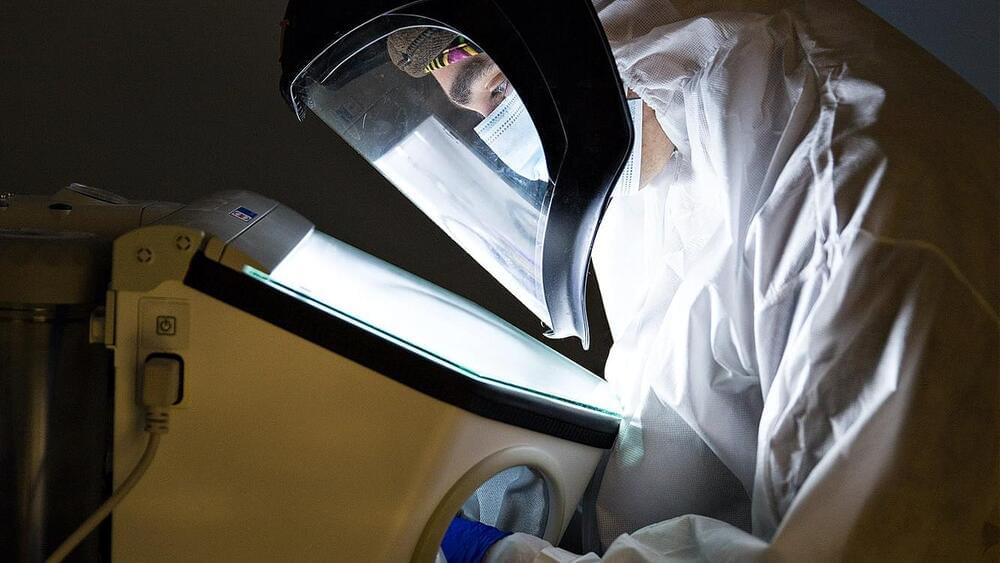
Less than a year has passed since we saw Pager play Ping-Pong using Neuralink. The company’s owner, Elon Musk has now said that he is confident of testing the chip in humans next year.
Founded in July 2016, the company is busy building an implantable chip that will allow the human brain to interact with computers directly. The company made headlines when its experimental macaque played Ping-Pong telepathically, without the help of a joystick. The company seems to have made rapid progress in its technology since its founder is quite optimistic about human testing.
Although there is no official communiqué from Neuralink, a stock investor on Twitter quoted Musk to say that the company was planning to test the chip soon. The tweet that tagged both Musk and Neuralink said that Musk was “cautiously optimistic” about restoring full-body functionality for tetraplegics & quadriplegics.

What if the next global health crisis is a mental health pandemic? It is here now.
According to Gallup, anger, stress, worry and sadness have been on the rise globally for the past decade — long before the COVID-19 pandemic — and all reached record highs in 2020.
People die from COVID-19 — they also die from depression and anxiety disorders. The U.S. has seen spikes in deaths from suicide and “deaths of despair.”
Deaths of despair — a new designation made prominent by Princeton economists Anne Case and Nobel laureate Sir Angus Deaton in their book of the same name — are suicides and deaths caused by fatal behaviors such as drug overdoses and liver failure from chronic alcohol consumption. They have particularly harmed working-class males in the American heartland and increased dramatically since the mid-1990s, from about 65,000 in 1995 to 158,000 in 2018.
Think of deaths of despair as suicide in slow motion.

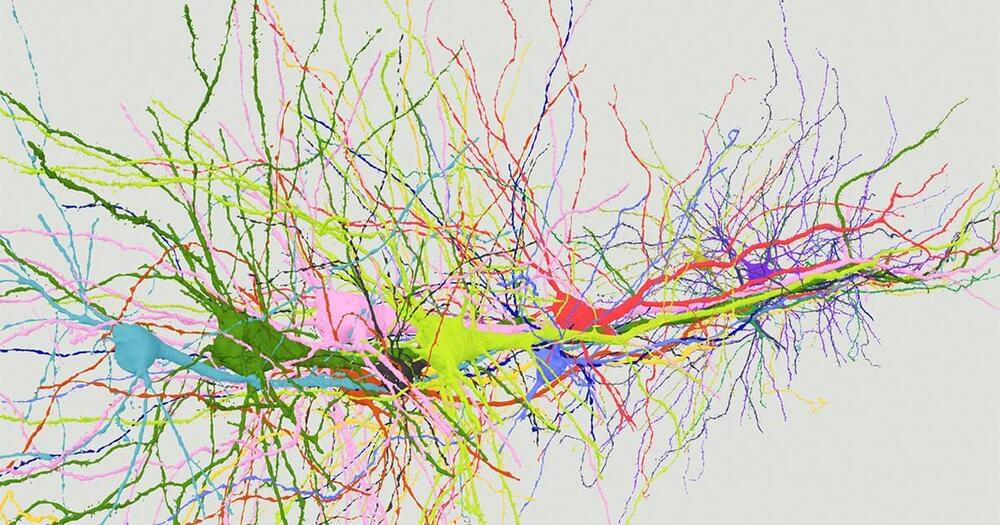

Theoretical physicist Sean Carroll joins us to discuss whether it make sense to think of consciousness as an emergent phenomenon, and whether contemporary physics points in this direction.
We discussed Sean’s essay responding to Philip’s book ‘Galileo’s Error,’ and Philip’s counter-response essay. Both are available here: https://conscienceandconsciousness.com/2021/08/01/19-essays-on-galileos-error/
We also discussed Philip’s Scientific American article making the case that the move from the fine-tuning to the multiverse commits the ‘inverse gambler’s fallacy’: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/our-improbable-existence-is-no-evidence-for-a-multiverse/#:~:text=We%20exist%2C%20and%20we%20are, with%20the%20existence%20of%20life.
Finally, Keith and Philip discussed the PhilPapers 2020 survey of philosophers’ opinions on philosophical questions, which is linked to from this blog post of Philip’s: https://conscienceandconsciousness.com/2021/11/01/materialism-remains-the-majority-view-but-only-just/
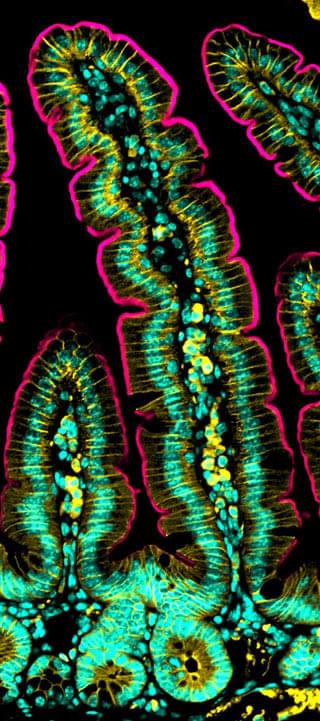
Science isn’t all lab coats and test tubes. Beautiful visuals can engage people—especially students—and inspire them to learn about science more broadly.
Scientists have often invited the public to see what they see, using everything from engraved woodblocks to electron microscopes to explore the complexity of the scientific enterprise and the beauty of life. Sharing these visions through illustrations, photography, and videos has allowed laypeople to explore a range of discoveries, from new bird species to the inner workings of the human cell.
As a neuroscience and bioscience researcher, I know that scientists are sometimes pigeonholed as white lab coats obsessed with charts and graphs. What that stereotype misses is their passion for science as a mode of discovery. That’s why scientists frequently turn to awe-inducing visualizations as a way to explain the unexplainable.
The BioArt Scientific Image and Video Competition, administered by the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology images with the public that are rarely seen outside the laboratory in order to introduce and educate laypeople about the wonder often associated with biological research. BioArt and similar contests reflect the lengthy history of using imagery to elucidate science.
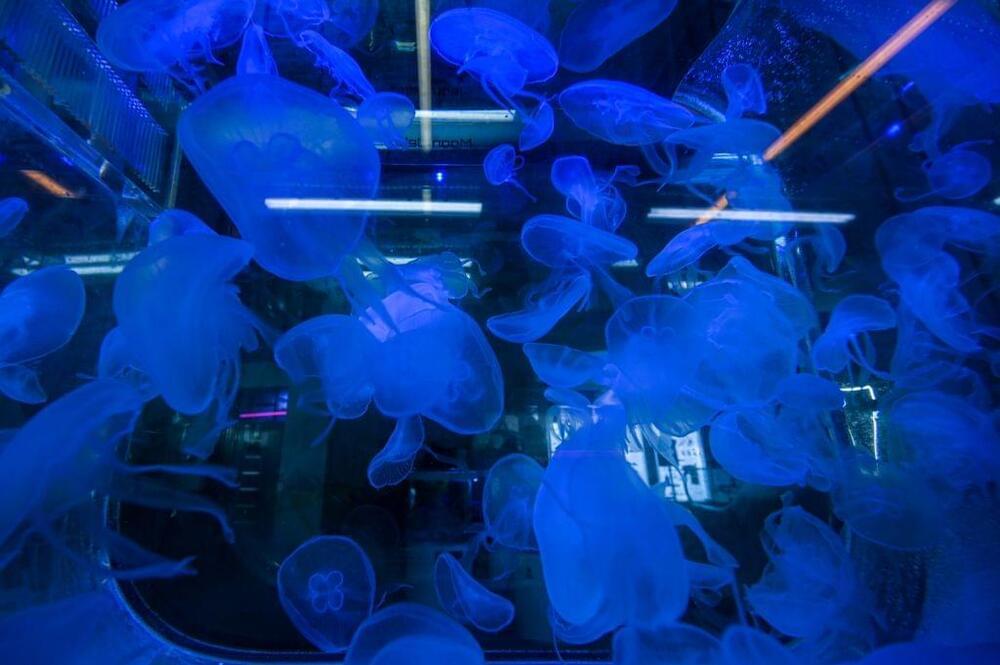

Scientists have found a way to interpret jellyfish’s thoughts regardless of not having any neurons, study finds.
They were able to observe how well the cells in a tiny type of see-through jellyfish operate collectively, to produce complicated independent motions, such as capturing and consuming food source. This is all thanks to ingenious molecular manipulation.