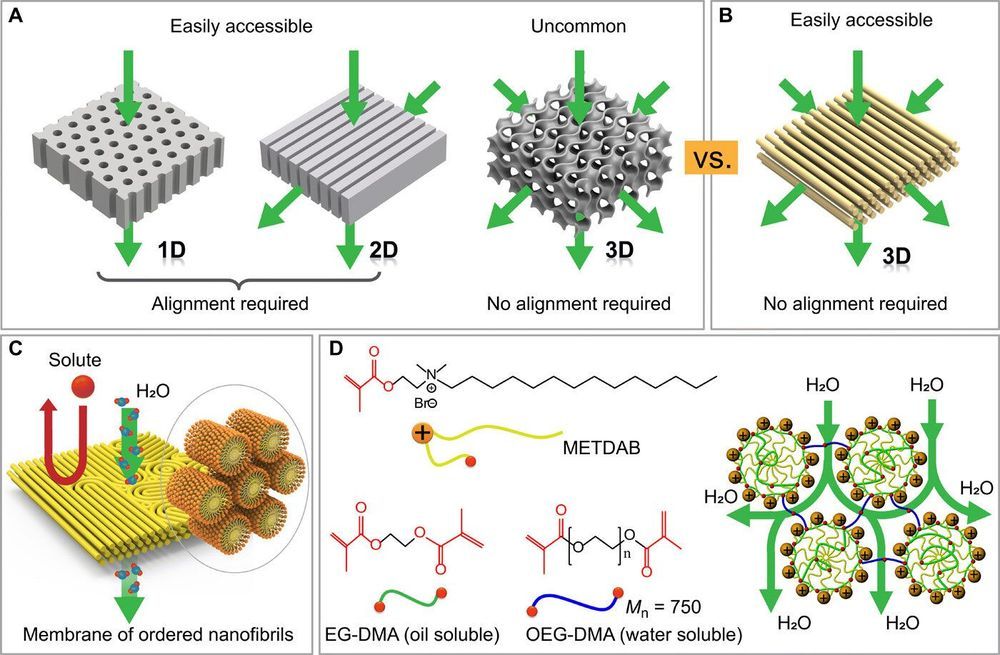
Self-assembled materials are attractive for next-generation materials, but their potential to assemble at the nanoscale and form nanostructures (cylinders, lamellae etc.) remains challenging. In a recent report, Xundu Feng and colleagues at the interdisciplinary departments of chemical and environmental engineering, biomolecular engineering, chemistry and the center for advanced low-dimension materials in the U.S., France, Japan and China, proposed and demonstrated a new approach to prevent the existing challenges. In the study, they explored size-selective transport in the water-continuous medium of a nanostructured polymer template formed using a self-assembled lyotropic H1 (hexagonal cylindrical shaped) mesophase (a state of matter between liquid and solid). They optimized the mesophase composition to facilitate high-fidelity retention of the H1 structure on photoinduced crosslinking.
The resulting nanostructured polymer material was mechanically robust with internally and externally crosslinked nanofibrils surrounded by a continuous aqueous medium. The research team fabricated a membrane with size selectivity at the 1 to 2 nm length scale and water permeabilities of ~10 liters m−2 hour−1 bar−1 μm. The membranes displayed excellent anti-microbial properties for practical use. The results are now published on Science Advances and represent a breakthrough for the potential use of self-assembled membrane-based nanofiltration in practical applications of water purification.
Membrane separation for filtration is widely used in diverse technical applications, including seawater desalination, gas separation, food processing, fuel cells and the emerging fields of sustainable power generation and distillation. During nanofiltration, dissolved or suspended solutes ranging from 1 to 10 nm in size can be removed. New nanofiltration membranes are of particular interest for low-cost treatment of wastewaters to remove organic contaminants including pesticides and metabolites of pharmaceutical drugs. State-of-the-art membranes presently suffer from a trade-off between permeability and selectivity where increased permeability can result in decreased selectivity and vice-versa. Since the trade-off originated from the intrinsic structural limits of conventional membranes, materials scientists have incorporated self-assembled materials as an attractive solution to realize highly selective separation without compromising permeability.