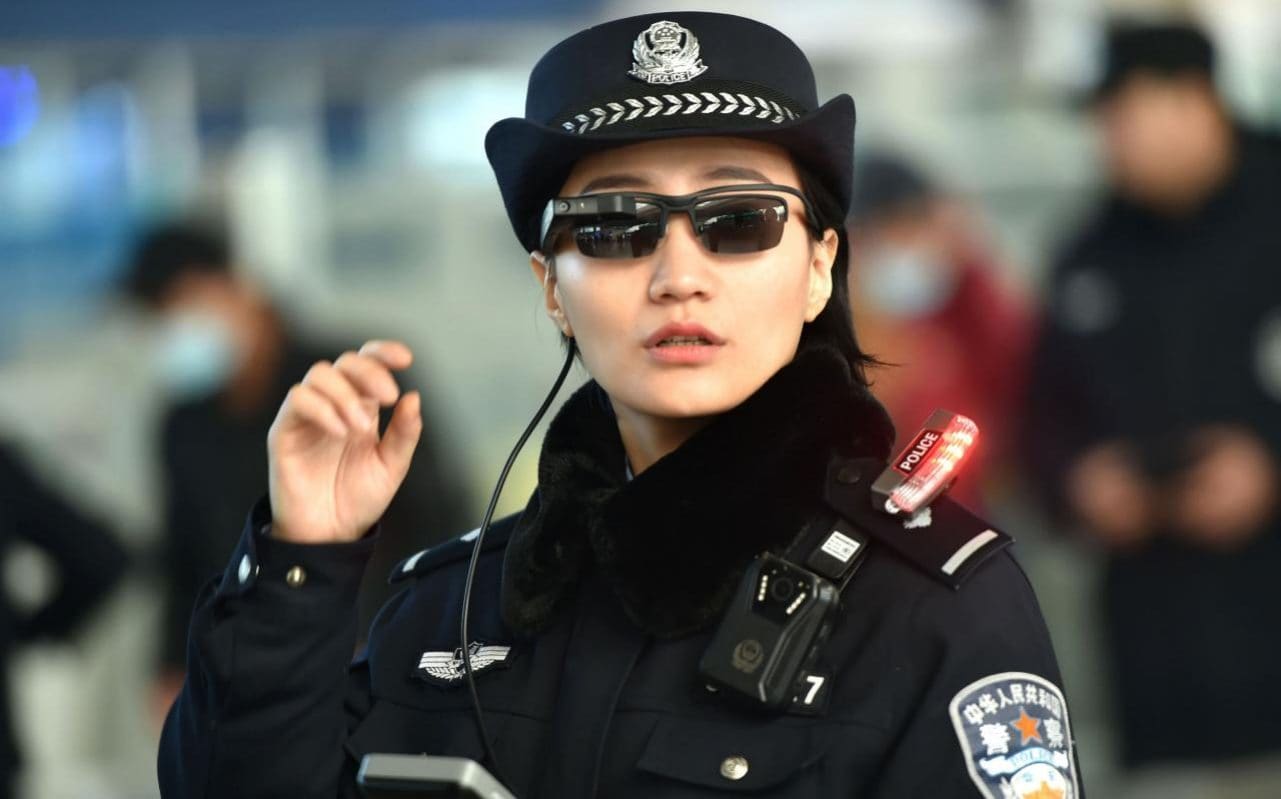
Artificial intelligence is permeating everybody’s lives through the face recognition, voice recognition, image analysis and natural language processing capabilities built into their smartphones and consumer appliances. Over the next several years, most new consumer devices will run AI natively, locally and, to an increasing extent, autonomously.
But there’s a problem: Traditional processors in most mobile devices aren’t optimized for AI, which tends to consume a lot of processing, memory, data and battery on these resource-constrained devices. As a result, AI has tended to execute slowly on mobile and “internet of things” endpoints, while draining their batteries rapidly, consuming inordinate wireless bandwidth and exposing sensitive local information as data makes roundtrips in the cloud.
That’s why mass-market mobile and IoT edge devices are increasingly coming equipped with systems-on-a-chip that are optimized for local AI processing. What distinguishes AI systems on a chip from traditional mobile processors is that they come with specialized neural-network processors, such as graphics processing units or GPUs, tensor processing units or TPUs, and field programming gate arrays or FPGAs. These AI-optimized chips offload neural-network processing from the device’s central processing unit chip, enabling more local autonomous AI processing and reducing the need to communicate with the cloud for AI processing.