Google and Amazon are on the forefront of AI innovation. But have they already gone too far?
 By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com
By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com

Google and Amazon are on the forefront of AI innovation. But have they already gone too far?
 By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com
By John Brandon Contributing editor, Inc.com
Take a listen to the recordings. That’s an AI doing that.
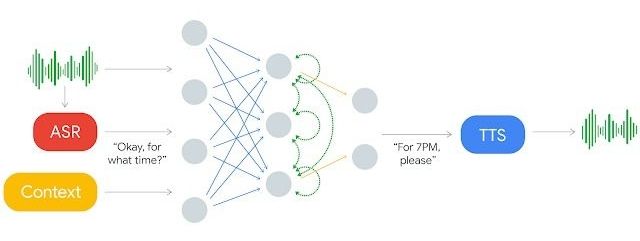
A long-standing goal of human-computer interaction has been to enable people to have a natural conversation with computers, as they would with each other. In recent years, we have witnessed a revolution in the ability of computers to understand and to generate natural speech, especially with the application of deep neural networks (e.g., Google voice search, WaveNet). Still, even with today’s state of the art systems, it is often frustrating having to talk to stilted computerized voices that don’t understand natural language. In particular, automated phone systems are still struggling to recognize simple words and commands. They don’t engage in a conversation flow and force the caller to adjust to the system instead of the system adjusting to the caller.
Today we announce Google Duplex, a new technology for conducting natural conversations to carry out “real world” tasks over the phone. The technology is directed towards completing specific tasks, such as scheduling certain types of appointments. For such tasks, the system makes the conversational experience as natural as possible, allowing people to speak normally, like they would to another person, without having to adapt to a machine.
One of the key research insights was to constrain Duplex to closed domains, which are narrow enough to explore extensively. Duplex can only carry out natural conversations after being deeply trained in such domains. It cannot carry out general conversations.

How did your smartphone end up in your hands? The microchips that help power our smartphones and computers start out as sand. Explore how microchips come to live in our phones, with the help of IoT technologies.

My #transhumanism work in this fun new article on future of sports:
Can bionic limbs and implanted technology make you faster and stronger? Meet biohackers working on the frontier.
Zoltan Istvan has achieved every runner’s fantasy: the ability to run without the hassle of carrying his keys. Thanks to a tiny chip implanted in his hand, Istvan doesn’t have to tie a key onto his laces, tuck it under a rock in the front yard, or find shorts with little zipper pockets built in. Just a wave of the microchip implanted in his hand will unlock the door of his home. The chip doesn’t yet negate the need for a Fitbit, a phone, or a pair of earbuds on long runs, but Istvan says it’s only a matter of time.
A long-time athlete and technology geek, Istvan identifies as a transhumanist: he believes that the transformation of the human body through ever-developing and evolving technologies will improve human life and ultimately lead to immortality.
“Athletes should be able to use drugs and technologies to enable them to be more competitive. To restrict that is to go against the very best of what we can become. If somebody wants to take these risks, they should have the rights to do so in full.”

Are we witnessing, as Truthstream Media calls it, “A Zombie Apocalypse” Where reality is becoming a little less real by the day or is this trend something else?
Are people merging with their Smart Phones and becoming programmed by them using Cyborgification or is this something different? Find out…
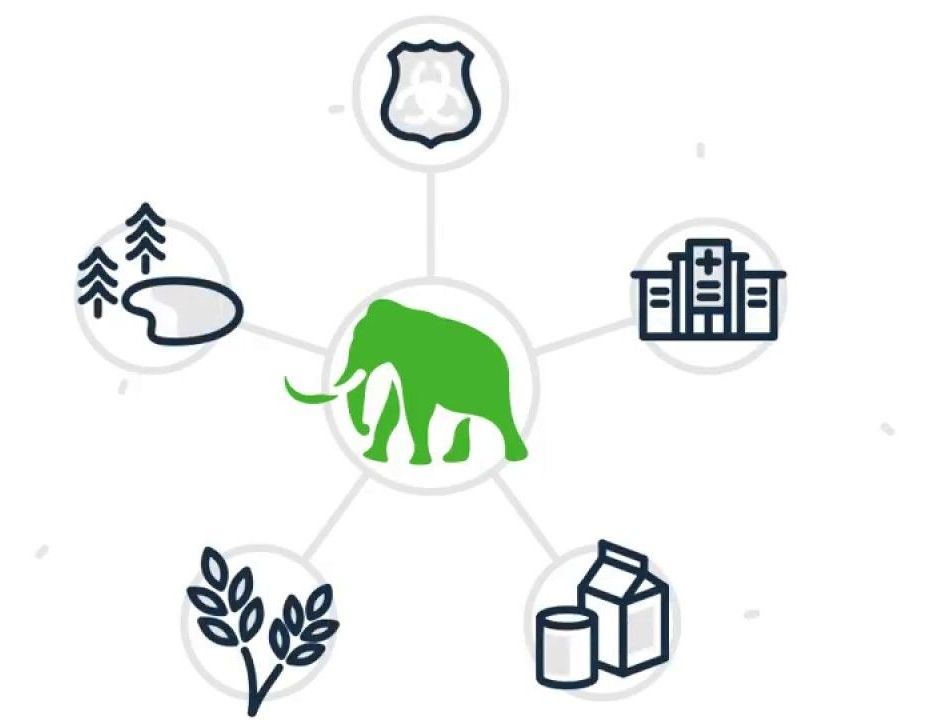

A new biotech company co-founded by CRISPR pioneer Jennifer Doudna is developing a device that uses CRISPR to detect all kinds of diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and Zika. The tech is still just in prototype phase, but research in the field is showing promising results. These CRISPR-based diagnostic tools have the potential to revolutionize how we test for diseases in the hospital, or even at home.
Called Mammoth Biosciences, the company is working on a credit card-sized paper test and smartphone app combo for disease detection. But the applications extend beyond that: The same technology could be used in agriculture, to determine what’s making animals sick or what sorts of microbes are found in soil, or even in the oil and gas industry, to detect corrosive microbes in pipelines, says Trevor Martin, the CEO of Mammoth Biosciences, who holds a PhD in biology from Stanford University. The company is focusing on human health applications first, however.
About a year ago, Apple made the bold proclamation that it was zeroing in on a future where iPhones and MacBooks were created wholly of recycled materials. It was, and still is, an ambitious thought. In a technologically-charged world, many forget that nearly 100 percent of e-waste is recyclable. Apple didn’t.
Named “Daisy,” Apple’s new robot builds on its previous iteration, Liam, which Apple used to disassemble unneeded iPhones in an attempt to scrap or reuse the materials. Like her predecessor, Daisy can successfully salvage a bulk of the material needed to create brand new iPhones. All told, the robot is capable of extracting parts from nine types of iPhone, and for every 100,000 devices it manages to recover 1,900 kg (4,188 pounds) of aluminum, 770 kg of cobalt, 710 kg of copper, and 11 kg of rare earth elements — which also happen to be some of the hardest and environmentally un-friendly materials required to build the devices.
In its latest environmental progress report, Apple noted:

You might only know JPEG as the default image compression standard, but the group behind it has now branched out into something new: JPEG XS. JPEG XS is described as a new low-energy format designed to stream live video and VR, even over WiFi and 5G networks. It’s not a replacement for JPEG and the file sizes themselves won’t be smaller; it’s just that this new format is optimized specifically for lower latency and energy efficiency. In other words, JPEG is for downloading, but JPEG XS is more for streaming.
The new standard was introduced this week by the Joint Photographic Experts Group, which says that the aim of JPEG XS is to “stream the files instead of storing them in smartphones or other devices with limited memory.” So in addition to getting faster HD content on your large displays, the group also sees JPEG XS as a valuable format for faster stereoscopic VR streaming plus videos streamed by drones and self-driving cars.
“We are compressing less in order to better preserve quality, and we are making the process faster while using less energy,” says JPEG leader Touradj Ebrahimi in a statement. According to Ebrahimi, the JPEG XS video compression will be less severe than with JPEG photos — while JPEG photos are compressed by a factor of 10, JPEG XS is compressed by a factor of 6. The group promises a “visual lossless” quality to the images of JPEG XS.
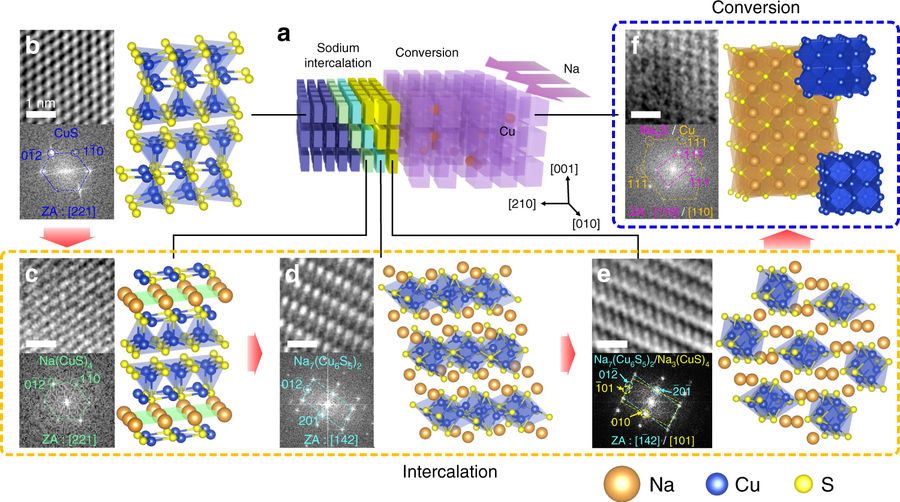
A KAIST research team recently developed sodium ion batteries using copper sulfide anode. This finding will contribute to advancing the commercialization of sodium ion batteries (SIBs) and reducing the production cost of any electronic products with batteries.
Professor Jong Min Yuk and Emeritus Professor Jeong Yong Lee from Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a new anode material suitable for use in an SIB. Compared to the existing anode materials, the copper sulfide anode was measured to exhibit 1.5 times better cyclability with projected 40 percent reduction in cost.
Lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion batteries or LIBs) are widely used in mobile phones and other personal electronics. However, large-scale energy storage systems require less expensive, more abundant materials. Hence, a SIBs have attracted enormous attention for their advantage over lithium-based batteries.

Processors with artificial intelligence will spread from today’s top-end phones to cars, PCs, security cameras, smart speakers and mainstream phones.