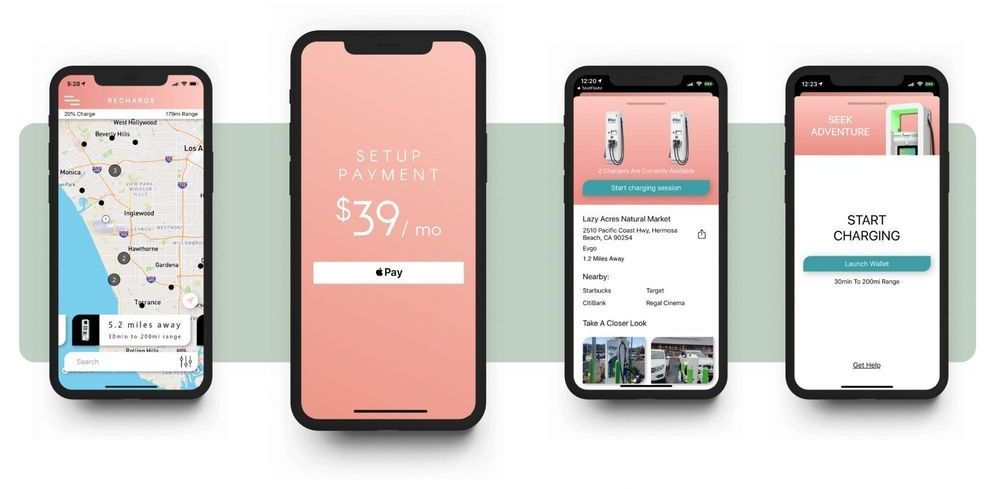
EVPassport is an upcoming app that promises $39/mo unlimited charging on major EV charge networks. The included networks are Electrify America, EVgo, Chargepoint, Hubject and Greenlots, along with some smaller regional networks on the US West Coast. The app plans to launch in “a few weeks” but is taking wait list signups now.
The app will start with support for iPhone and DC fast charging in the US at first, with initial support for 2,500 DC chargers. It will expand to Android later this year, along with European support (including IONITY). If all goes well, it plans to add Level 2 AC charging support next year.