As well as Kronshtadt, many other Russian enterprises in the military-industrial complex are developing drones for deployment on the front lines. For example, aircraft manufacturer Sukhoi has teamed up with defense company Mikoyan to build the Okhotnik-B, which will have a top speed of 1000 km/h. Another aerospace company, called OKB Sokol, has developed a UAV named Altius, due to be delivered to the Russian Army this year.
A Russian company is building the country’s first-ever specialized factory solely for manufacturing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). It plans to mass-produce military drones, like those deployed by the Russian Army in Syria.
The 45000-square-meter plant, under construction in the town of Dubna near Moscow, will cost at least four billion rubles ($52 million) and will create jobs for more than 1500 people. If all goes to plan, it will be built in record time, with the launch of production scheduled for November 2021.
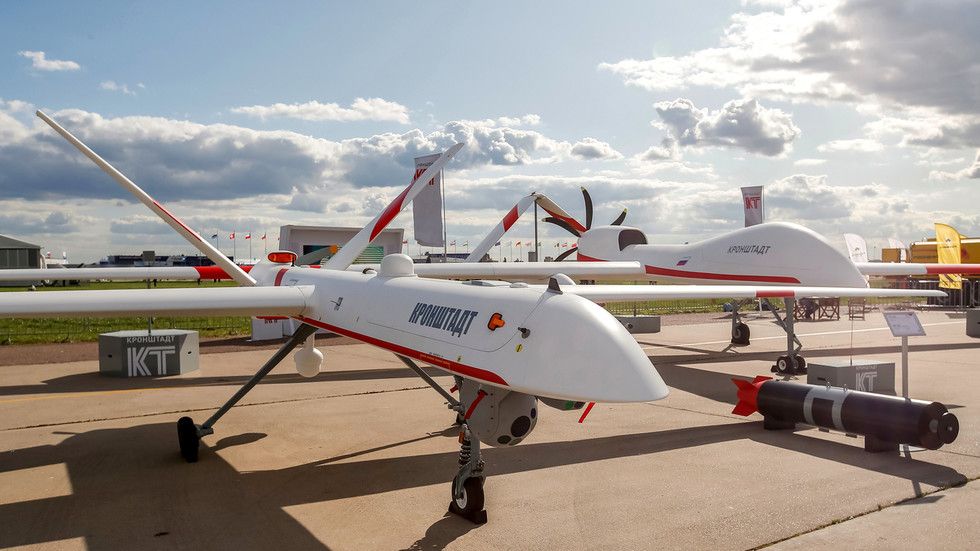
The company, called ‘Kronshtadt Group,’ is the developer and manufacturer of the Inokhodets UAV, also known as the Orion. This medium-altitude drone, which is capable of flying for a whole day, can carry a payload of up to 200kg, and has already seen action in the Middle East.