Harvard University’s David Sinclair, world renowned for his anti-aging research, sees no limit on human life span and is collaborating on a clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of a new drug aimed at slowing the aging process…
“There is no maximum human life span,” says Sinclair, Ph.D., who is a professor in the Department of Genetics and co-director of the Paul F. Glenn Center for the Biology of Aging at Harvard Medical School. “Anyone who says that doesn’t know what they are talking about.”
Sinclair hopes to demonstrate what he has been researching, – and talking about, for the past 20 years – that aging is a disease, which can be treated.
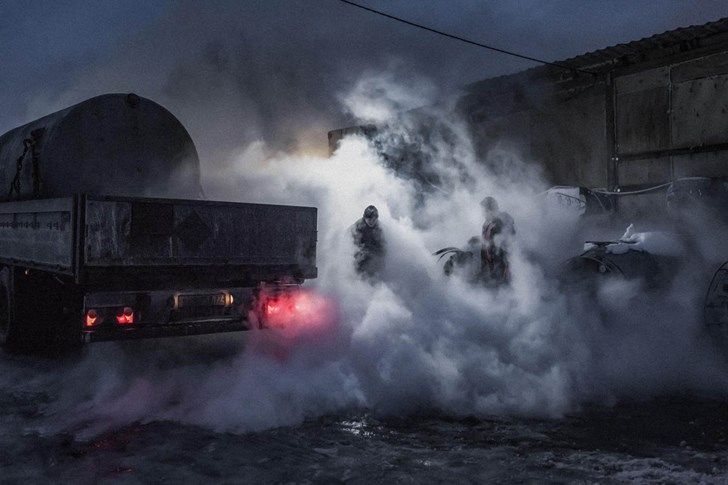



 Employees of a liquid nitrogen and dry ice factory on the outskirts of Moscow are shrouded in fog while refilling their liquid nitrogen tanks. Founded by former KrioRus employees, the company now supplies them. PHOTOGRAPH BY GIUSEPPE NUCCI
Employees of a liquid nitrogen and dry ice factory on the outskirts of Moscow are shrouded in fog while refilling their liquid nitrogen tanks. Founded by former KrioRus employees, the company now supplies them. PHOTOGRAPH BY GIUSEPPE NUCCI