The Facebook CEO talks to Casey Newton about why he is putting his company’s resources toward the “metaverse,” a future that imagines an internet that combines physical, augmented, and virtual realities.
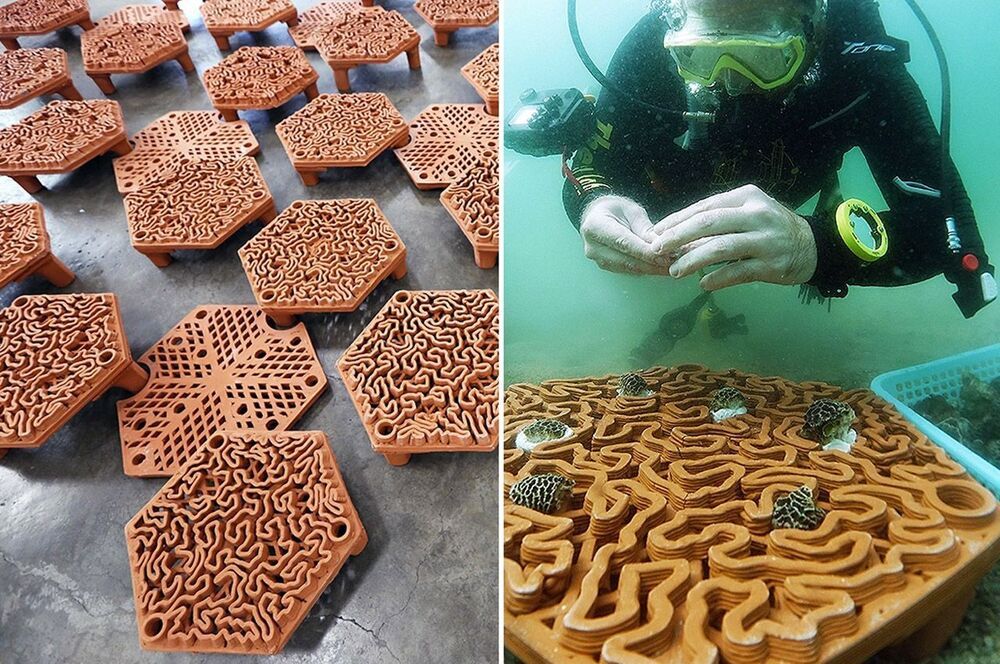



3D Printing is gaining more momentum and popularity than ever! Designers and architects all over the world are now adopting 3D Printing for the creation of almost all types of products and structures. It’s a technique that is being widely utilized in product design, owing to its simple and innovative nature. But designers aren’t employing 3D printing only to create basic models, they’re utilizing this technique in mind-blowing ways as well! From 3D printed artificial coral reefs to a menacing two-wheeler design with 3D printed bodywork, the scope of this dependable technique is unlimited! Dive into this collection of humble yet groundbreaking 3D printed designs!

Manipulating RNA can allow plants to yield dramatically more crops, as well as increasing drought tolerance, announced a group of scientists from the University of Chicago, Peking University and Guizhou University.
In initial tests, adding a gene encoding for a protein called FTO to both rice and potato plants increased their yield by 50% in field tests. The plants grew significantly larger, produced longer root systems and were better able to tolerate drought stress. Analysis also showed that the plants had increased their rate of photosynthesis.
“The change really is dramatic,” said University of Chicago Prof. Chuan He, who together with Prof. Guifang Jia at Peking University, led the research. “What’s more, it worked with almost every type of plant we tried it with so far, and it’s a very simple modification to make.”
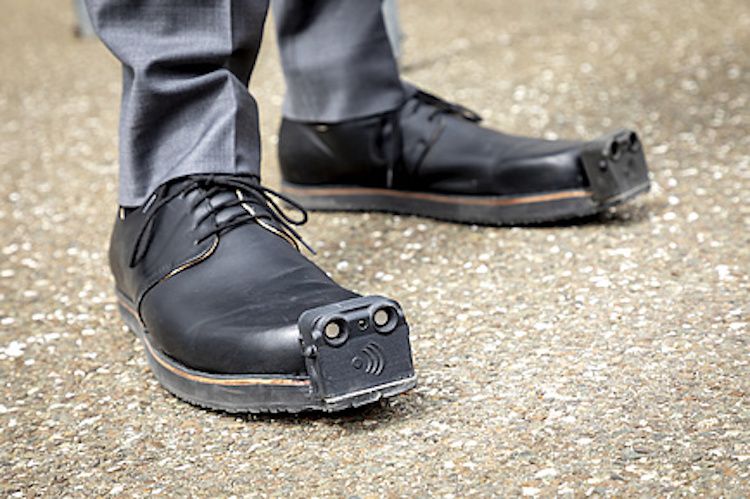

Austrian shoe company Tec-Innovation has partnered with students at the Graz University of Technology in Austria to implement camera-based AI image recognition into their line of shoes that are specifically made to help those who are visually impaired.
The original version of these “seeing eye” shoes features ultrasonic sensors, which warn the person wearing them of obstacles in their way through haptic or auditory signals. AI image recognition that constantly learns, allows the shoes to provide more specific information to the wearer.

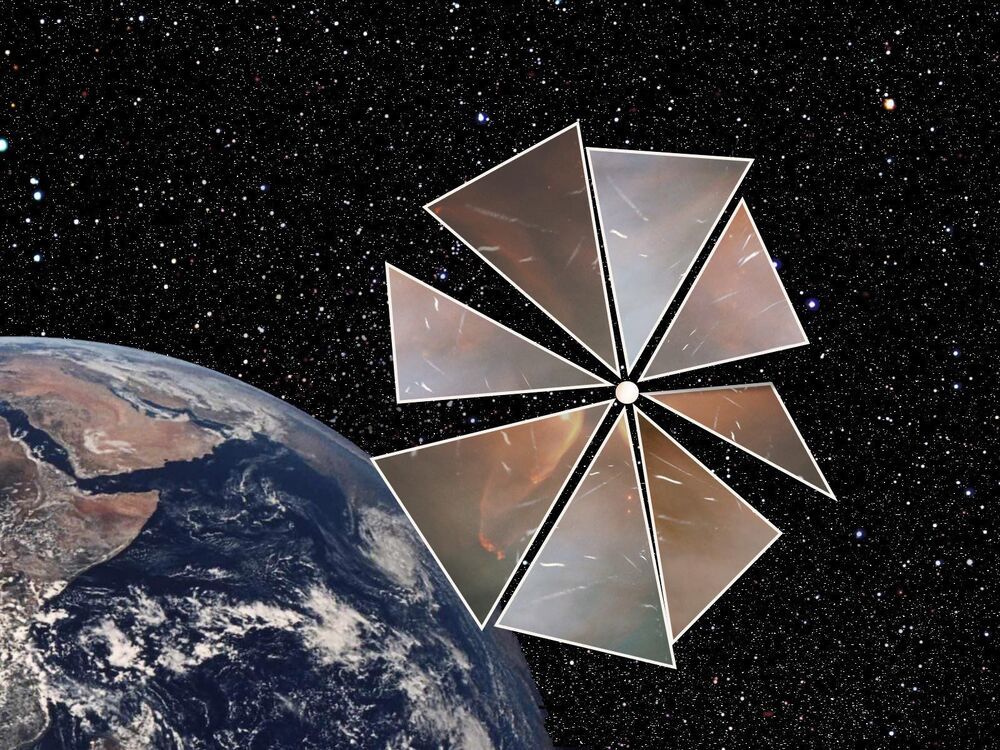
When Oumuamua, the first interstellar object ever observed passing through the Solar System, was discovered in 2017, it exhibited some unexpected properties that left astronomers scratching their heads. Its elongated shape, lack of a coma, and the fact that it changed its trajectory were all surprising, leading to several competing theories about its origin: was it a hydrogen iceberg exhibiting outgassing, or maybe an extraterrestrial solar sail (sorry folks, not likely) on a deep-space journey? We may never know the answer, because Oumuamua was moving too fast, and was observed too late, to get a good look.
It may be too late for Oumuamua, but we could be ready for the next strange interstellar visitor if we wanted to. A spacecraft could be designed and built to catch such an object at a moment’s notice. The idea of an interstellar interceptor like this has been floated by various experts, and funding to study such a concept has even been granted through NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program. But how exactly would such an interceptor work?
A new paper released on ArXiv on June 27th explores one possible mission design. Derived from the NIAC study, the proposal suggests combining solar sail technology with the ability to miniaturize space probes to small, lightweight sizes.

Elon Musk is boring his way to the beach in Fort Lauderdale.
Local lawmakers accepted a proposal from Musk’s Boring Co. Tuesday to build an underground transit system that would whisk people from the Florida city’s downtown area to the beach in Teslas.
“Other firms have 45 days to submit competing proposals. This could be a truly innovative way to reduce traffic congestion,” Mayor Dean Trantalis wrote on Twitter.
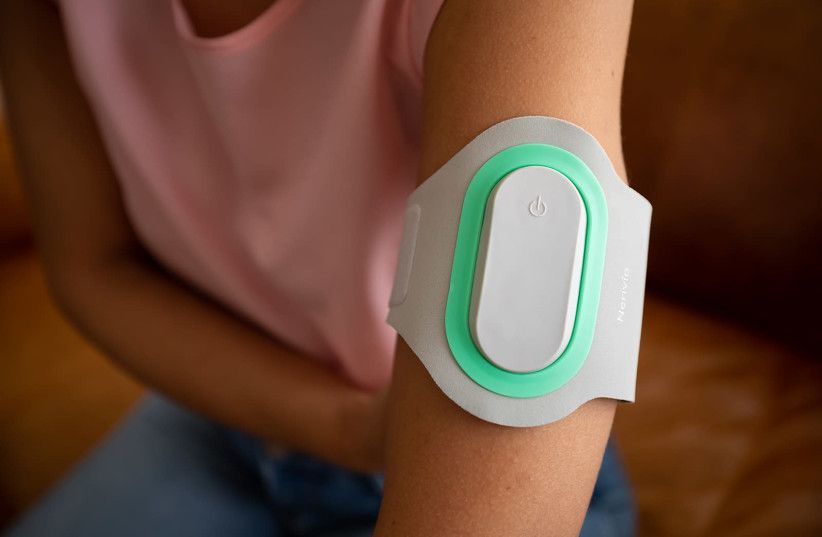
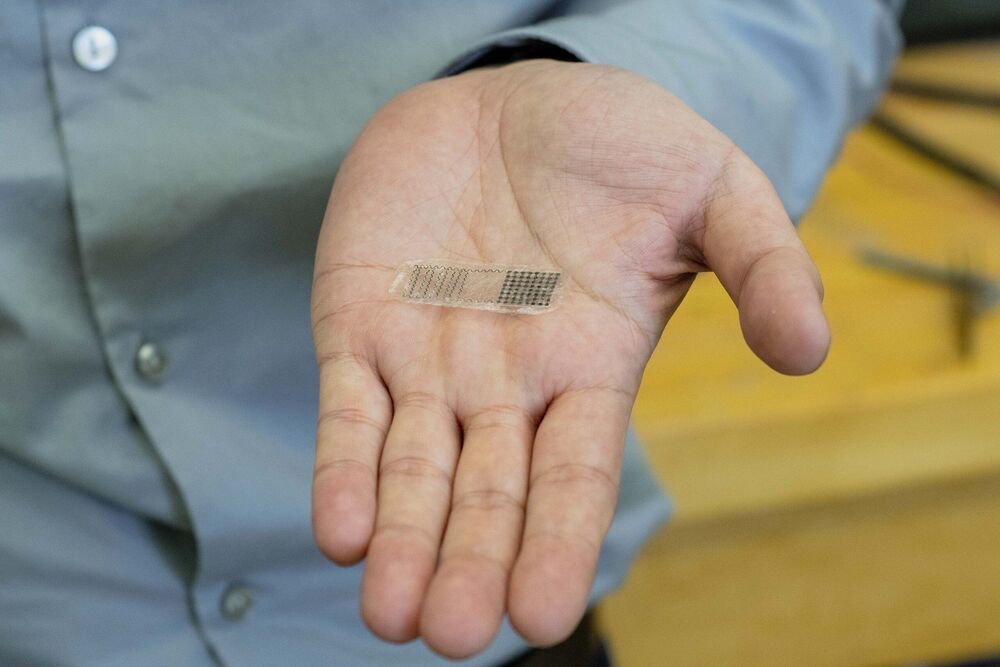


In 2017, Green Bay Packers quarterback Aaron Rodgers broke his right collarbone in a game against the Minnesota Vikings. Typically, it takes about 12 weeks for a collarbone to fully heal, but by mid-December fans and commentators were hoping the three-time MVP might recover early and save a losing season.
So did Xudong Wang, a professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and an expert in creating thin, movement-powered medical devices. “I started wondering if we could provide a new solution to bring athletes back to the field quicker than ever,” Wang says.
Researchers know that electricity can help speed up bone healing, but “zapping” fractures has never really caught on, since it requires surgically implanting and removing electrodes powered by an external source.
A major update of that same electrostimulation concept, Wang’s latest invention didn’t come in time to help the 2017 Packers–however, it may help many others by making electrostimulation a much more convenient option to speed up bone healing.
His thin, flexible device is self-powered, implantable and bioresorbable, so once the bone is knitted back together, the device’s components dissolve within the body.
Wang and his collaborators, including Weibo Cai, a UW-Madison professor of radiology and medical physics, described the new device today (July 5, 2021) in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
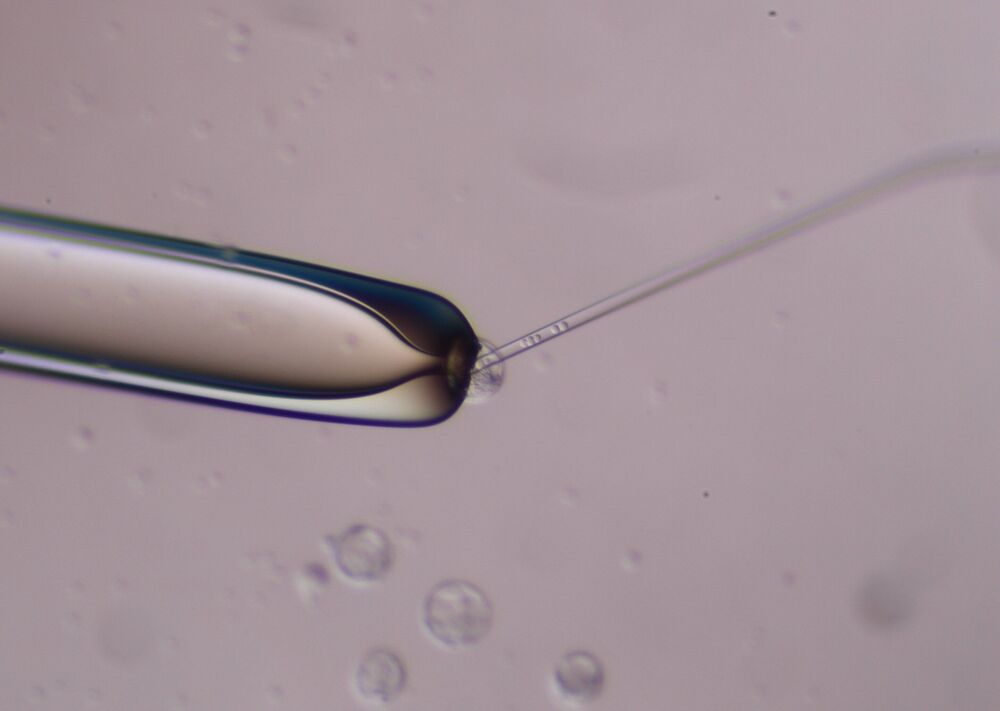
A year after University at Buffalo scientists demonstrated that it was possible to produce millions of mature human cells in a mouse embryo, they have published a detailed description of the method so that other laboratories can do it, too.
The ability to produce millions of mature human cells in a living organism, called a chimera, which contains the cells of two species, is critical if the ultimate promise of stem cells to treat or cure human disease is to be realized. But to produce those mature cells, human primed stem cells must be converted back into an earlier, less developed naive state so that the human stem cells can co-develop with the inner cell mass in a mouse blastocyst.
The protocol outlining how to do that has now been published in Nature Protocols by the UB scientists. They were invited to publish it because of the significant interest generated by the team’s initial publication describing their breakthrough last May.