Google and Facebook are releasing troves of deepfakes to teach algorithms how to detect them. But the human eye will be needed for a long time.


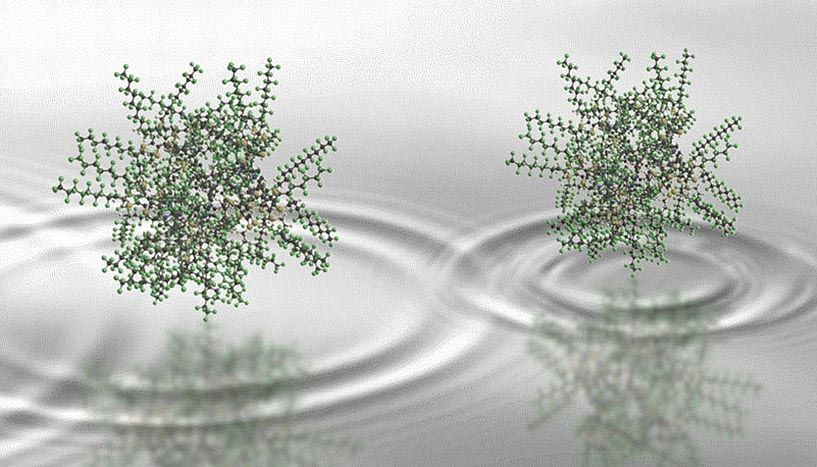
The quantum superposition principle has been tested on a scale as never before in a new study by scientists at the University of Vienna in collaboration with the University of Basel. Hot, complex molecules composed of nearly two thousand atoms were brought into a quantum superposition and made to interfere. By confirming this phenomenon – “the heart of quantum mechanics”, in Richard Feynman’s words – on a new mass scale, improved constraints on alternative theories to quantum mechanics have been placed. The work was published in Nature Physics on September 23, 2019.
Quantum to classical?
The superposition principle is a hallmark of quantum theory which emerges from one of the most fundamental equations of quantum mechanics, the Schrödinger equation. It describes particles in the framework of wave functions, which, much like water waves on the surface of a pond, can exhibit interference effects. But in contrast to water waves, which are a collective behavior of many interacting water molecules, quantum waves can also be associated with isolated single particles.
For the first time, physicists in the US have confirmed a decades-old theory regarding the breaking of time-reversal symmetry in gauge fields. Marin Soljacic at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and an international team of researchers have made this first demonstration of the “non-Abelian Aharonov-Bohm effect” in two optics experiments. With improvements, their techniques could find use in optoelectronics and fault-tolerant quantum computers.
First emerging in Maxwell’s famous equations for classical electrodynamics, a gauge theory is a description of the physics of fields. Gauge theories have since become an important part of physicists’ descriptions of the dynamics of elementary particles – notably the theory of quantum electrodynamics.
A salient feature of a gauge theory is that the physics it describes does not change when certain transformations are made to the underlying equations describing the system. An example is the addition of a constant scalar potential or a “curl-free” vector potential to Maxwell’s equations. Mathematically, this does not change the electric and magnetic fields that act on a charged particle such as an electron – and therefore the behaviour of the electron – so Maxwell’s theory is gauge invariant.
Circa 2012
Hundreds of the world’s brightest minds — engineers from Google and IBM, hedge funds quants, and Defense Department contractors building artificial intelligence — were gathered in rapt attention inside the auditorium of the San Francisco Masonic Temple atop Nob Hill. It was the first day of the seventh annual Singularity Summit, and Julia Galef, the President of the Center for Applied Rationality, was speaking onstage. On the screen behind her, Galef projected a giant image from the film Blade Runner: the replicant Roy, naked, his face stained with blood, cradling a white dove in his arms.
At this point in the movie, Roy is reaching the end of his short, pre-programmed life, “The poignancy of his death scene comes from the contrast between that bitter truth and the fact that he still feels his life has meaning, and for lack of a better word, he has a soul,” said Galef. “To me this is the situation we as humans have found ourselves in over the last century. Turns out we are survival machines created by ancient replicators, DNA, to produce as many copies of them as possible. This is the bitter pill that science has offered us in response to our questions about where we came from and what it all means.”
The Singularity Summit bills itself as the world’s premier event on robotics, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technologies. The attendees, who shelled out $795 for a two-day pass, are people whose careers depend on data, on empirical proof. Peter Norvig, Google’s Director of Research, discussed advances in probabilistic first-order logic. The Nobel prize-winning economist Daniel Kahneman lectured on the finer points of heuristics and biases in human psychology. The Power Point presentations were full of math equations and complex charts. Yet time and again the conversation drifted towards the existential: the larger, unanswerable questions of life.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=gHBhMGbJHe8
In music, “portamento” is a term that’s been used for hundreds of years, referring to the effect of gliding a note at one pitch into a note of a lower or higher pitch. But only instruments that can continuously vary in pitch—such as the human voice, string instruments, and trombones—can pull off the effect.
Now an MIT student has invented a novel algorithm that produces a portamento effect between any two audio signals in real-time. In experiments, the algorithm seamlessly merged various audio clips, such as a piano note gliding into a human voice, and one song blending into another. His paper describing the algorithm won the “best student paper” award at the recent International Conference on Digital Audio Effects.
The algorithm relies on “optimal transport,” a geometry-based framework that determines the most efficient ways to move objects—or data points—between multiple origin and destination configurations. Formulated in the 1700s, the framework has been applied to supply chains, fluid dynamics, image alignment, 3D modeling, computer graphics, and more.

Last year, Princeton researchers identified a disturbing security flaw in which hackers could someday exploit internet-connected appliances to wreak havoc on the electrical grid. Now, the same research team has released algorithms to make the grid more resilient to such attacks.
In a paper published online in the journal IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, a team from Princeton’s Department of Electrical Engineering presented algorithms to protect against potential attacks that would spike demand from high-wattage devices such as air conditioners—all part of the “internet of things”—in an effort to overload the power grid.
“The cyberphysical nature of the grid makes this threat very important to counter, because a large-scale blackout can have very critical consequences,” said study author Prateek Mittal, an associate professor of electrical engineering.
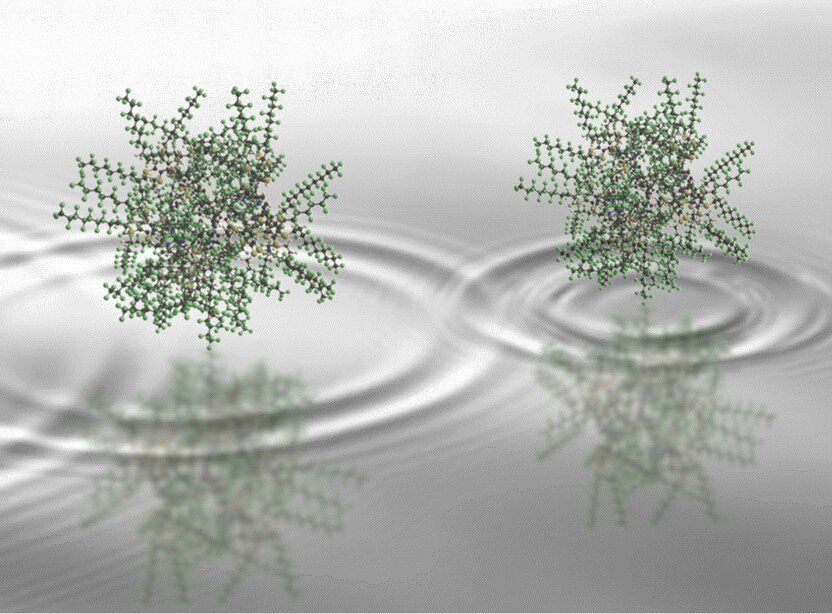
The quantum superposition principle has been tested on a scale as never before in a new study by scientists at the University of Vienna in collaboration with the University of Basel. Hot, complex molecules composed of nearly two thousand atoms were brought into a quantum superposition and made to interfere. By confirming this phenomenon—” the heart of quantum mechanics,” in Richard Feynman’s words—on a new mass scale, improved constraints on alternative theories to quantum mechanics have been placed. The work will be published in Nature Physics.
Quantum to classical?
The superposition principle is a hallmark of quantum theory which emerges from one of the most fundamental equations of quantum mechanics, the Schrödinger equation. It describes particles in the framework of wave functions, which, much like water waves on the surface of a pond, can exhibit interference effects. But in contrast to water waves, which are a collective behavior of many interacting water molecules, quantum waves can also be associated with isolated single particles.
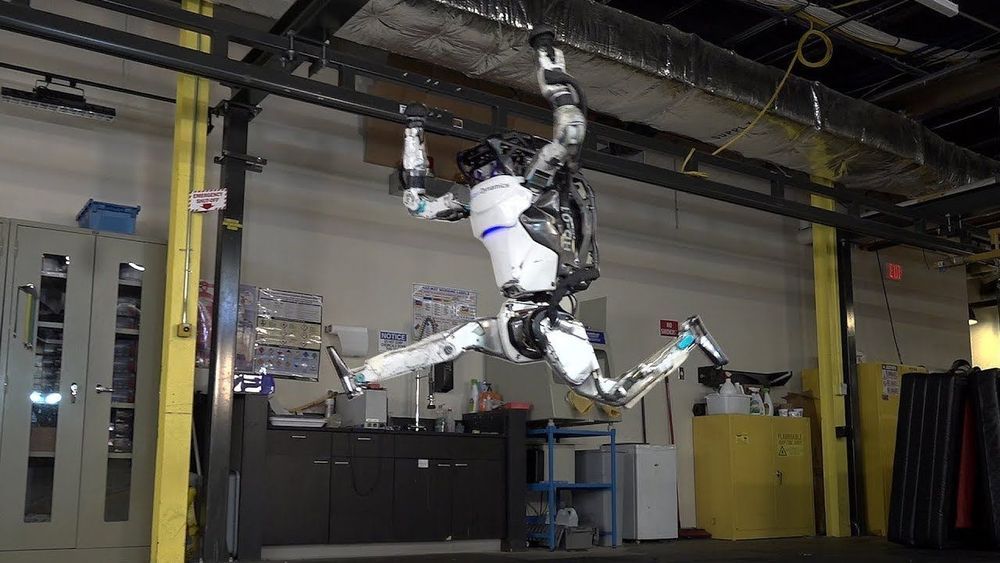

Atlas uses its whole body — legs, arms, torso — to perform a sequence of dynamic maneuvers that form a gymnastic routine. We created the maneuvers using new techniques that streamline the development process. First, an optimization algorithm transforms high-level descriptions of each maneuver into dynamically-feasible reference motions. Then Atlas tracks the motions using a model predictive controller that smoothly blends from one maneuver to the next. Using this approach, we developed the routine significantly faster than previous Atlas routines, with a performance success rate of about 80%. For more information visit us at www.BostonDynamics.com.
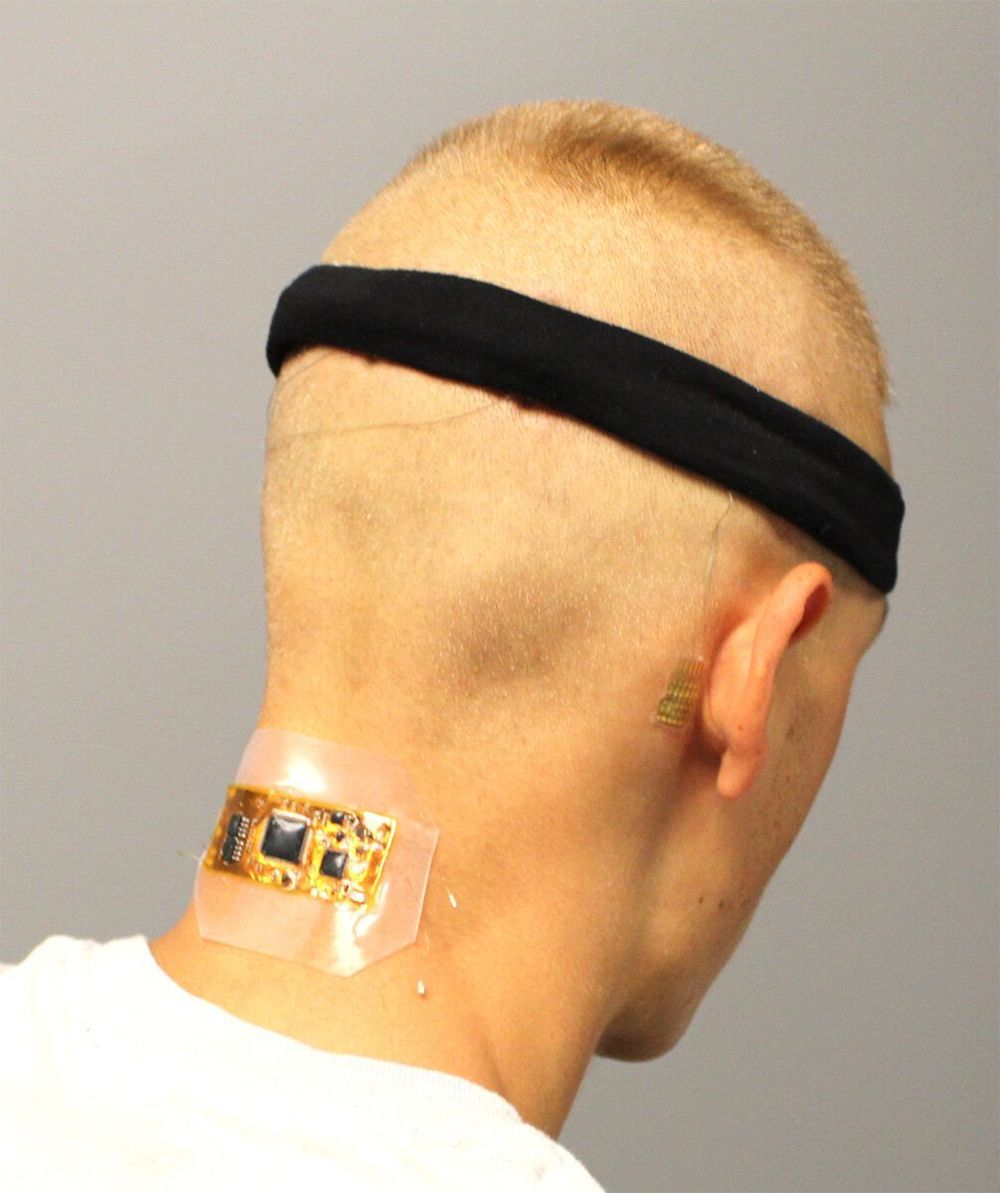
Combining new classes of nanomembrane electrodes with flexible electronics and a deep learning algorithm could help disabled people wirelessly control an electric wheelchair, interact with a computer or operate a small robotic vehicle without donning a bulky hair-electrode cap or contending with wires.
By providing a fully portable, wireless brain-machine interface (BMI), the wearable system could offer an improvement over conventional electroencephalography (EEG) for measuring signals from visually evoked potentials in the human brain. The system’s ability to measure EEG signals for BMI has been evaluated with six human subjects, but has not been studied with disabled individuals.
The project, conducted by researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology, University of Kent and Wichita State University, was reported on September 11 in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence.

Rural communities are often built on agriculture and livestock. That means they’re also dependent upon a strong irrigation system – a potential weakness as the global water crisis grows. To more efficiently manage and coordinate the use of a scarce water supply in agricultural communities, a team from the Polytechnic University of Madrid proposed a blockchain-based automatic water control system.
“We investigated how blockchain technologies can be used to solve the problem of user competition for scarce resources in communities,” said Borja Bordel, the project’s lead investigator. “We particularize the problem to the irrigation communities, where independent users must trust a system that automates a fair and trustworthy distribution of the available water resources, according to an individual quota set by the community and the consumption forecasts of its users.”
Rules are paramount for the proposed system and must be established upfront by the community of users. In a prosumer environment, users establish regulations for their individual and community water quotas. Those regulations are then taken by a transformation engine and are built, compiled, and deployed. A simple infrastructure of common valves and pumps are complemented by interactive electronic devices and allow a SmartContract to oversee decision-making and control algorithms, as well as the state of the water sources.