Researchers have developed a computer algorithm that mimics the brain’s electrical signalling and helps memory. The FT reports.

Researchers have developed a computer algorithm that mimics the brain’s electrical signalling and helps memory. The FT reports.

The word on every tech executive’s mouth today is data. Curse or blessing, there’s so much data lying around – with about 2.5 quintillion bytes of data added each day – that it’s become increasingly difficult to make sense of it in a meaningful way. There’s a solution to the big data problem, though: machine learning algorithms that get fed countless variables and spot patterns otherwise oblivious to humans. Researchers have already made use of machine learning to solve challenges in medicine, cosmology and, most recently, crime. Tech giant Hitachi, for instance, developed a machine learning interface reminiscent of Philip K. Dick’s Minority Report that can predict when, where and possibly who might commit a crime before it happens.

Turing Test-style competitions in writing stories, music & poetry.
HT: @Grady_Booch
DigiLit is a competition that encourages the creation of algorithms able to produce a “human-level” short story of the kind that might be intended for a short story collection produced in a well-regarded MfA program or a piece for The New Yorker. The prize seeks to reward algorithms that could, for example, write stories for a creative writing class in which students are asked to submit a new short story each day. (Artwork by Annelise Capo http://www.annelisecapossela.com)

By Steve Gorman LOS ANGELES (Reuters) — A brain-to-computer technology that can translate thoughts into leg movements has enabled a man paralyzed from the waist down by a spinal cord injury to become the first such patient to walk without the use of robotics, doctors in Southern California reported on Wednesday. The slow, halting first steps of the 28-year-old paraplegic were documented in a preliminary study published in the British-based Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, along with a YouTube video. The feat was accomplished using a system allowing the brain to bypass the injured spinal cord and instead send messages through a computer algorithm to electrodes placed around the patient’s knees to trigger controlled leg muscle movements.
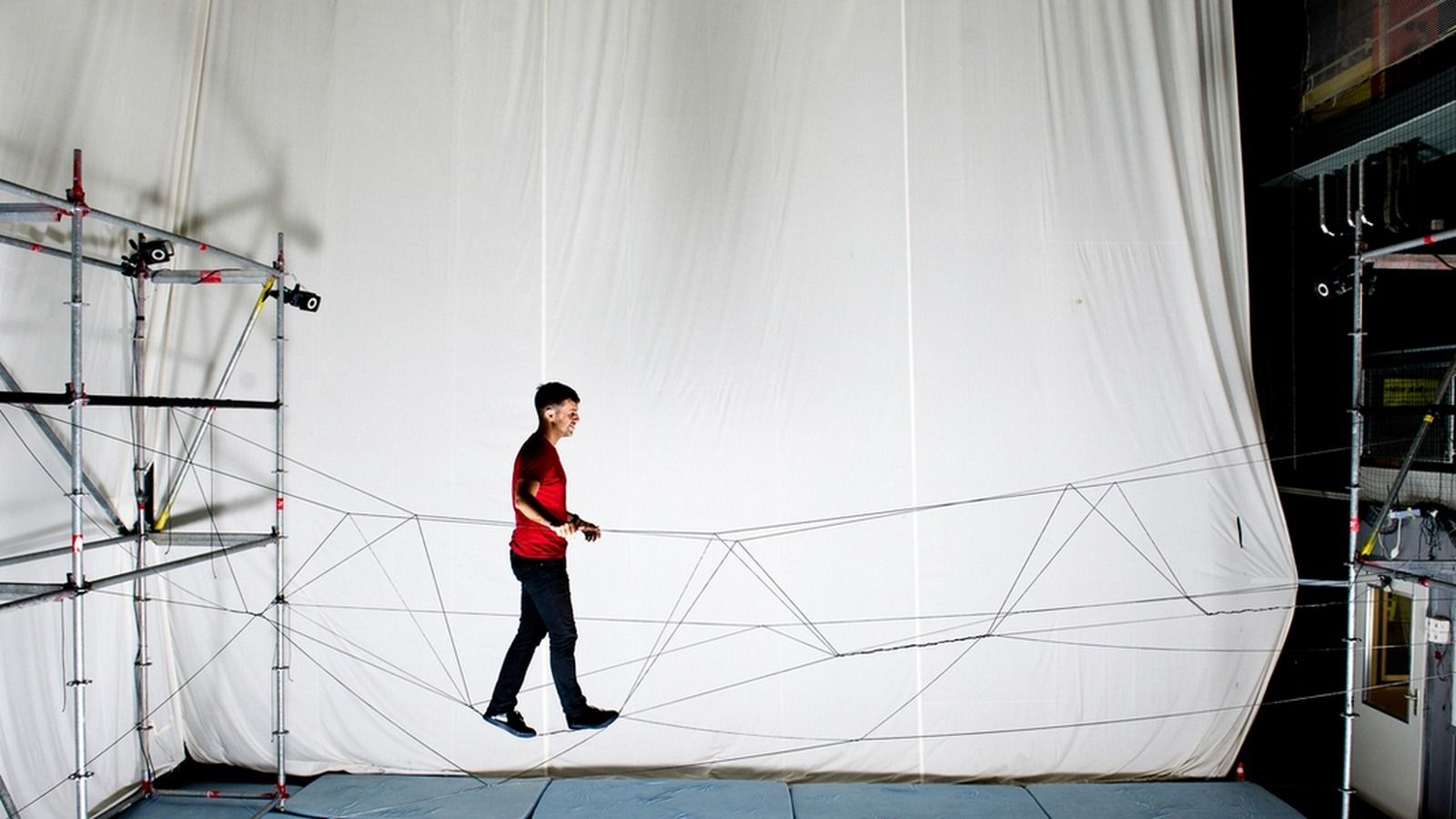

Two quadrocopters construct a rope bridge strong enough to carry the weight of a human in the hypnotic video (above), uploaded to YouTube this week by researcher Federico Augugliaro. The impressive feat wasn’t a one-person operation. It’s the latest accomplishment from many researches and contributors at the Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control and Gramazio Kohler Research, and incorporates lessons learned from other tests at the Flying Machine Arena in Zurich, Switzerland.
The 10-by-10-by-10-meter portable space doubles as the setting of the footage and the lab in which many of the researchers, including Augugliaro, perform drone experiments and exercises. According to the Flying Machine Arena’s website, the room “consists of a high-precision motion capture system, a wireless communication network, and custom software executing sophisticated algorithms for estimation and control.”



Neil deGrasse Tyson and Edward Snowden recently discussed the idea that encryption mechanisms with advanced extraterrestrial species and humans could theoretically render communication as indistinguishable from cosmic background radiation. With only a short period of time in a species growth where open communication is broadcast to the stars (through the sluggish and primitive nature of radio broadcasts), this could prevent us (or other species) from making contact with one another.
With the Drake Equation stating a high probability of communicative extraterrestrial civilizations and the contrasting Fermi Paradox citing lacking evidence of such, it begs the question of whether outlying reasons have an impact. In my opinion, the Drake Equation rings true in the sense that hundreds of billions of stars exist in our galaxy alone (many with their own diverse planetary bodies), setting the stage for extraterrestrial life to disavow itself as insatiable ramblings. Unlike that which is eminent in the Fermi Paradox, I believe, in this case, a conclusion based off of inductive reasoning seems to hold more water than an evidence-only approach.
Keeping in mind the discussion in The Guardian article, a flaw of the Fermi Paradox’s evidence-based perspective should become apparent: secure, encrypted communication (cloaked by design) would render the existence of extraterrestrial intelligence invisible to the prying ear. If intentional, there could be many reasons for withholding this whereabouts of a species location. An abstract theory from science fiction may itself hold a degree of truth. An example of which, is the video game series ‘Mass Effect,’ where an advanced, sentient machine-race cleanse the galaxy of advanced life every 40,000 years. The reasoning for doing so is to “bring order to chaos” and for reasons “unfathomable.” Be it for an abstract reason such as this or simply for secure communication, the encryption of the resultant transmission’s presence wouldn’t register as noticeable to any observers. As nearly all signs of outside life would be mute, it then lays in the other senses that hold the most promise of enlightenment.
The dimensionless aspect, since it has no dimensions, is outside of space and time. This is the key aspect to existence: an aspect outside of space and time perpetually interacting dialectically with an aspect inside space and time. All of the weird and wonderful phenomena of the universe are the products of this ultimate dichotomy.
http://youtu.be/MbRda_sCgkQ
Does this sound crazy? Then consider the evidence provided by black holes.
The R = 0 Universe.
Black holes are objects where gravity is so strong that light itself cannot escape the gravitational pull. They are the most mysterious objects in the universe and hold the key to the nature of reality. They open the door to understanding the fundamental composition of the universe.
Their hypothetical existence was first predicted in Einstein’s famous theory of General Relativity, but Einstein himself believed it was impossible for them to become real objects in the universe. The reason for that is that they exhibit a feature that physics cannot cope with or comprehend.
Einstein’s equations contain a term that involves dividing the mass of the black hole by the distance “r” from the black hole. The question is what happens when r=0? Division by zero gives a result of infinity. To physicists, it is impossible for infinity to appear in the real world, so they consider r = 0 to be the point at which physics breaks down. At r = 0, the centre of a black hole, gravity is infinite and time itself stops: all of the mass of the black hole is contained within an infinitely small point where the concept of space no longer makes any sense. The point takes up precisely no space at all. Since this point is outside space and time, it is dimensionless. The physical universe collapses into an ineffable twilight state at this point. This apparently impossible object of infinite density and infinite gravity is known as the singularity. No predictions can be made about it, or about what might emerge from it. At the singularity, physicists’ understanding of nature fails completely. Therefore, they believe that there is a fatal flaw in the formulation of Einstein’s theory of general relativity, despite its immense success.
The one thing no physicist has ever contemplated is this: there is no flaw whatsoever. The reason why physics seems to disintegrate at r = 0 is for the extremely simple reason that r = 0 is not in the physical universe. It is in the mental universe, the universe of mind, as we have described in the previous section.
Physicists, so blindly and irrationally wedded to materialism, have never taken their own equations to their logical conclusion. What their equations actually point to at the limit of r = 0 is a different aspect of existence — mental rather physical, dimensionless rather than dimensional, outside of space and time. Rather than face up to that, physicists would prefer to futilely search for a new theory. But they have nowhere else to go. They will always run up against exactly the same problem: that the universe of dimensions, of space and time, coexists with another universe of no dimensions, outside space and time. Reality can never be comprehended if either aspect is ignored.
To talk of “two universes” is convenient but technically incorrect. The true nature of existence is that it has two aspects coexisting in a single continuum. The r = 0 (dimensionless, mental) universe and the r 0 (dimensional, physical) universe are both part of a single universe r = 0 (r greater than or equal to zero).
If you want an equation for everything, you could choose r = 0 because that encapsulates the true dual nature of reality; physical and mental.
There is a black hole at the centre of every galaxy. At the centre of ours is one that is four million times more massive than our sun. Such black holes are called supermassive. They are essential for galaxy formation, and hence for life itself.
Black holes shape the evolution of the universe. They are everywhere in the universe, millions upon millions of them, and in every place where they occur Einstein’s equations catastrophically break down (as far as physicists are concerned).
Black holes are real objects in outer space that lie beyond current scientific understanding. A new theory beyond Einstein is required. It already exists — it is that of the Illuminati. It is that of the r = 0 universe, the “within” of things, the inner aspect, the dimensionless reality that science chooses to ignore even though their equations point directly to it.
*****
Einstein’s General Relativity is one of the two most successful scientific theories of all time, the other being Quantum Mechanics. General Relativity provides a stunningly accurate account of how gravity dictates the motions of planets, stars and galaxies (the universe of the very large), but it cannot describe the universe of the very small (atoms and subatomic particles), from which all the planets, stars and galaxies are constructed. Here, the effects of gravity on these hypersmall, hyperlight entities are negligible.
Physicists dream of combining these two astonishingly successful theories into one grand unified theory that describes everything from the smallest scale to the largest, from the slowest speeds to the fastest. At the moment, each theory is incomplete as a full description of reality, but a combination might offer completeness.
The two theories meet head-on at one place: black holes. A black hole is a macroscopic entity associated with enormous amounts of mass and gravity, yet the singularity at the centre of the black hole is exactly of the hyper-microscopic scale of the quantum world.
To fully account for what goes on in inside a black hole at the mysterious singularity, quantum mechanics is essential.
When it comes to the quantum world, these are the types of statement that are typically made:
a) The act of observing changes what you see.
b) It is impossible to exactly specify where something is; you can only state where it is likely to be.
c) Anything that is possible, no matter how improbable, happens all the time and gives rise to measurable phenomena. A good example is the phenomenon of quantum tunnelling whereby if you place a particle in a box and lock the box, there is a tiny but finite chance that you will subsequently find the particle outside the box i.e. it has apparently tunnelled its way through a solid object. In the case of the particles being electrons, you can find electrical phenomena occurring in seemingly impossible places.
d) Particles can literally be in many different places at the same time.
Our whole common sense view of the world vanishes at the quantum level. All of our most treasured notions of how things behave change beyond recognition.
Quantum mechanics is routinely described as the best idea in physics. It has furnished the most successful predictions ever made by any theory. Everything is ultimately composed of quantum particles, and quantum mechanics comes closer than anything else to describing the true nature of reality. But it doesn’t incorporate gravity, the universal force that holds everything together. Without gravity, the sun would explode and the earth would disintegrate. Gravity is the universal binding force. It is caused, according to General Relativity, by the bending of space and time by massive objects. The effect of gravity on quantum-scale particles is usually negligible, but when it comes to black holes we are dealing with quantum-scale particles (singularities) and the most enormous gravitational effects conceivable. The singularity that exists at the centre of a black hole is both infinitesimally small and astronomically massive. Hence black holes are the key to understanding the universe, for combining general relativity and quantum mechanics.
Physicists now want to extend quantum mechanics by introducing gravitational effects. This new theory is referred to as “quantum gravity”. In effect, it is a quantum version of Einstein’s general relativity. The problem is that the two theories have proved incompatible. They simply don’t talk to each other. Whereas black holes generate an infinity caused by division by zero, in quantum gravity an infinity of infinities is generated i.e. the problem becomes infinitely worse.
The only entity comparable to black holes is the singularity that gave birth to the Big Bang itself. Here, too, scientific understanding collapses.
The Big Bang is conceived of as a dimensionless point in nothingness from which the whole of the observable physical, dimensional universe of time and space miraculously emerged some 14 billion years ago. To get an idea of how much matter has emerged from “nothing” consider that the sun is a million times more massive than the earth. Our galaxy has a million million stars like our sun. The observable universe has a million million galaxies like ours. All of this material, together with vast numbers of black holes and “dark matter” all, supposedly, came from absolutely nothing. All of it spewed out of the primordial singularity, a dimensionless point that gave birth to the biggest explosion of all time. It was the event, so we are told, that created space and time themselves, and some physicists contend that it is absurd to speculate about space and time before then because they did not exist.
So we are all the progeny of the mother of all singularities. We all came out of a dimensionless point. We are the children of nothingness, the products of nothing. Or so says science.
If science can solve the mysteries of the black hole by understanding the complete nature of a singularity then it should also be able to answer the question of how the universe began and where we all came from. And perhaps the other “big” question can be answered — what was there before the universe existed?
There are two numbers that have proved an insurmountable problem to science, two numbers that provide the limits of existence: zero and infinity. Infinity is a number without limit, while zero is an anti-number that doesn’t count anything (for example we can point to three apples, but not to zero apples). Zero and infinity are two of the most obscure topics in mathematics and, because of their mysterious nature, both arrived on the scene much later than ordinary numbers such as 1, 2, 3, 4 etc. It wasn’t until Georg Cantor’s work of the late nineteenth century that infinity became a respectable subject of study. Moreover, zero is simply the inverse of infinity, and vice versa: 1 divided by infinity = 0, and 1 divided by zero = infinity. Science will never be complete until it is able to fully incorporate zero and infinity.
Science is the theory that only Descartes’ “extended” substance exists i.e. things must have dimensions before they can be “real”. Illumination is the doctrine that “things” without dimensions are as real as those with dimensions. To express it mathematically, r = 0 is as real as r 0. Science has no legitimate basis for excluding r = 0, and, indeed, r = 0 appears right at the heart of science, right at the centre of the Genesis Singularity, the Big Bang itself. Science says the Big Bang arose out of nothingness (an impossible and non-existent state) while Illumination teaches that the physical universe of dimensions (r 0) emerged not from “nowhere and nothing” but from the mental, dimensionless universe (r = 0). Something did not come from nothing but from a different aspect of something: matter from mind, dimensions from non-dimensions. Equally, dimensional matter can be transformed into dimensionless mind, and this is the process that take place at a black hole singularity where r = 0. Which paradigm is the more logical and consistent? Which does not require something to spontaneously arise from nothing?
Scientists have never asked themselves the most basic question of all: why should dimensional entities (r 0) be privileged over non-dimensional entities (r = 0)? What is the sufficient reason for existence to exclude dimensionless entities and be wholly based on dimensional entities? There is no such reason. It is blind, irrational prejudice that causes scientists to ignore the r = 0 universe. They suffer from “group think”.
Any scientist who dared to suggest that the r = 0 dimensionless aspect of existence was as real as the r 0 dimensional aspect would be ridiculed by his peers. This is the terrible danger of institutionalized thinking. It breeds fear; it prevents the most radical ideas from being contemplated, unless such ideas conform to the ruling paradigm.
Yet no scientist can provide any legitimate scientific or philosophical reason why dimensionless existence is not every bit as real as dimensional existence and, indeed, the Big Bang singularity itself is a dimensionless entity, as is the singularity at the centre of any black hole. Why don’t scientists face the facts provided by their own most cherished theories?
Dimensionless entities can, do and must exist.
*****
http://www.armageddonconspiracy.co.uk/The-Genesis-Singularity(1886319).htm
Becoming God (video):
Illumination — Complete Mathematics (video):
http://youtu.be/qwDhjYqwKOE
An introduction to r = 0:
http://rondetafelbeleid.nl/illumination
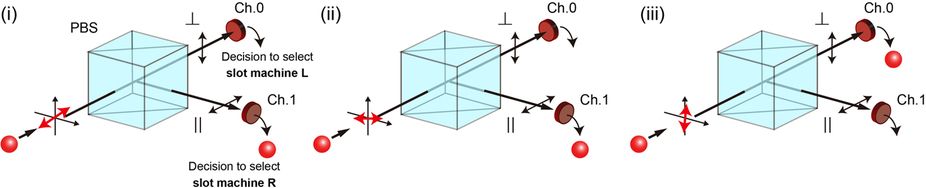
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-armed_bandit
In probability theory, the multi-armed bandit problem (sometimes called the K- or N-armed bandit problem) is a problem in which a gambler at a row of slot machines (sometimes known as “one-armed bandits”) has to decide which machines to play, how many times to play each machine and in which order to play them. When played, each machine provides a random reward from a distribution specific to that machine. The objective of the gambler is to maximize the sum of rewards earned through a sequence of lever pulls.
(Phys.org)—A combined team of researchers from France and Japan has created a decision-making device that is based on basic properties of quantum mechanics. In their paper published in Scientific Reports (and uploaded to the arXiv preprint server), the team describes the idea behind their device and how it works.
There is a classic decision-making problem that is known as the exploration-exploitation dilemma—it is typically described by suggesting a scenario where a gambler faced with a floor full of slot machines must decide which offers the best payout on a regular basis. In real life, the solution involves feeding all of the machines coins until a discernible pattern emerges. Computer algorithms have been developed to run essentially the same process. Now, however, that approach appears to be ready for an update, as the researchers with this new effort have come up with a way to run the same sort of algorithm without using any kind of computer. Instead, they use a laser, a photon detector and feedback device. The idea is based on the fact that quantum mechanics laws are probabilistic in nature.
The device is based on prior research that has shown that if photons are fired from a proton gun at a 45 degree angle, they will each have an equal chance of being vertically or horizontally polarized when they strike a detector—thus a stream will have equal numbers of both. But, if the filter on the gun is changed slightly, to say fire at 44 or 46 degree angles, that increase the odds of the associated polarization. The team used that fact by adding a feedback loop to the system—data sent back representing a “win” on a slot machine caused the filter to move in one direction, while a loss moved it in the other. Over time, the preponderance of wins (indicating a learning process) from one virtual machine would drive the device towards indicating it was the winning choice.

Scientists have designed a novel type of nanoscale solar cell. Initial studies and computer modelling predict these cells will outperform traditional solar panels, reach power conversion levels by over 40 percent.
Solar power cells work through the conversion of sunlight into electricity using photovoltaics. Here solar energy is converted into direct current. A photovoltaic system uses several solar panels; with each panel composed of a number of solar cells. This combines to create a system for the supply usable solar power.
To investigate what is possible in terms of solar power, the researchers have examined the Shockley-Queisser limit for different materials. This equation describes the maximum solar energy conversion efficiency achievable for a particular material, allowing different materials to be compared as candidates for power generation.

The concept of artificial intelligence got it’s start at a conference at Dartmouth in 1956. Optimism ran high and it was believed that machines would be able to do the work of humans within 20 years. Alas, it was not to be. By the 1970’s, funding dried up and technology entered the period now known as the AI winter.
Slowly, however, progress was made. Computers became increasingly able to do human tasks, such as character recognition, making recommendations on Amazon and organizing itineraries on travel sites. We didn’t see the algorithms at work, but they were there, computing on our behalf.
So the answer to our technological dilemma is, in fact, all too human. While the past favored those who could retain and process information efficiently, the future belongs to those who can imagine a better world and work with others to make it happen.