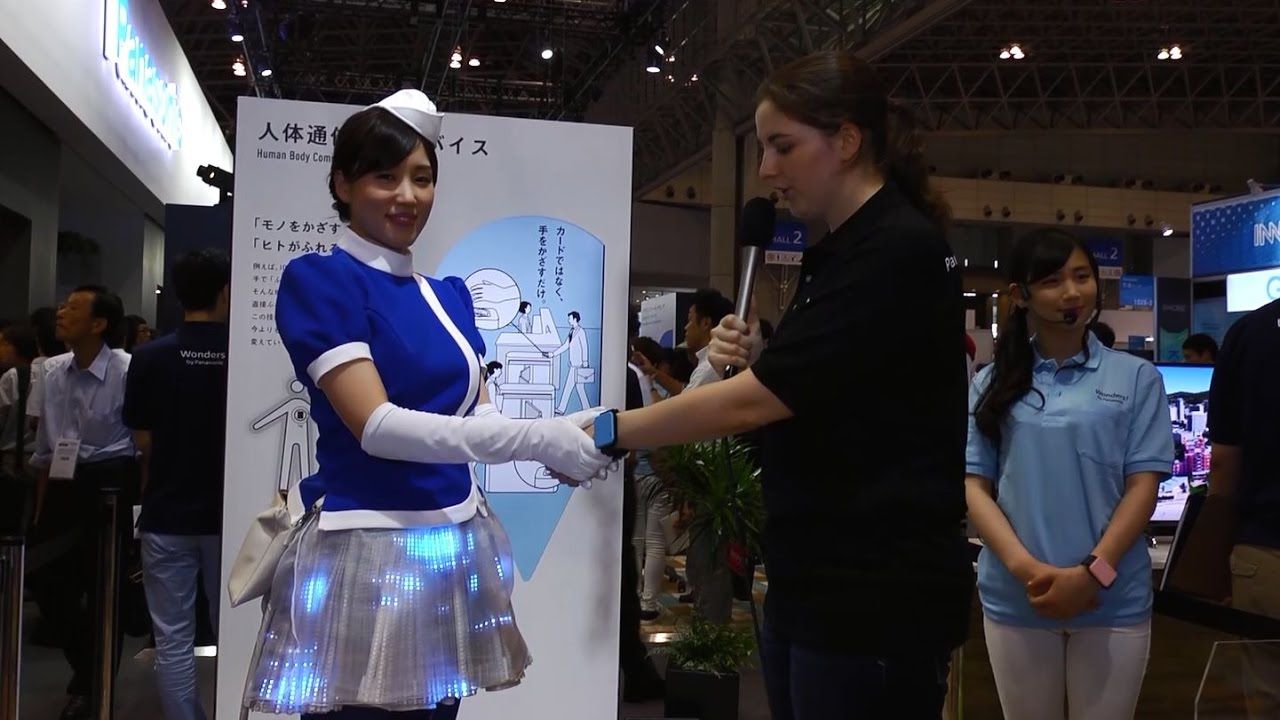
In an age when digital information can fly around the connected networks of the world in the blink of an eye, it may seem a little old timey to consider delivering messages by hand. But that’s precisely what Panasonic is doing at CEATEC this week. The company is demonstrating a prototype communication system where data is transmitted from one person to another through touch.
There’s very little information on the system available, but Panasonic says that the prototype uses electric field communication technology to move data from “thing-to-thing, human-to-human and human-to-thing.” Data transfer and authentication occurs when the objects or people touch, with digital information stored in a source tag instantaneously moving to a receiver module – kind of like NFC tap to connect technology, but with people in the equation as well as devices.
It has the potential to allow business types to exchange contact information with a handshake, mood lighting in a room to be changed to match or contrast with clothing when a lamp is touched or access to a building granted by placing a hand or object on a lock interface or door handle. And Panasonic suggests that because the data is traveling through the body and not over the air, secure transmission is assured.